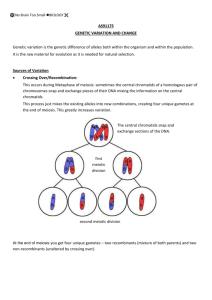
Meiosis, Genetics & Dihybrid Crosses Worksheet
advertisement

SNURFLE Meiosis and Genetics 2 (Diversity and Dihybrid Crosses Name__________________________________________ Crossing Over! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. At the start of Meiosis, what type of cell and how many are there? At the end of Meiosis I, what type of cells and how many are there? At the end of Meiosis II, what type of cells and how many are there? What are produced by Meiosis? Without crossing over, how many possible combinations have been produced? Question, Do you get it? 6. So far, we have examined a cell that DOES NOT do crossing over. What is true about such a cell? Gene Key! 7. The following letters represent alleles for what specific genes? G= g= B= b= 8. Without crossing over, what combinations of alleles would always be passed on together? GB= gb= 9. What do we call genes that are on the same chromosome and are inherited together? Question, Do you get it? 10. So far, we have examined…. Question, Do you get it? 11. Genes that are usually inherited together because they are on the same chromosome are known as… 12. When does CROSSING OVER occur? 13. What type of chromosome trades information? Question, Do you get it? 14. What exchanges DNA during crossing over? Meiosis Summary (Crossing Over) 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. When does crossing over occur? At the end of Meiosis I, what kind of cells and how many exist? At the end of Meiosis II, what kind of cells and how many exist? What is the result of more variety in possible gametes due to crossing over? How many different games are produced? Question, Do you get it? 20. If the cell to the right were to cross over one time during Prophase I of Meiosis, how many genetically distinct gametes would be produced? Question, Do you get it? 21. If the cell to the right does not cross over, how many genetically distinct varieties of gametes are produced? Recombination 22. What is another name for crossing over? 23. What are gametes with recombinant chromosomes called? 24. What does the recombination allow for? Question 25. These cells have __________________ chromosomes as a result of crossing over. More about CROSSING OVER 26. What type of event is crossing over? 27. Where can crossing occur along a chromosome? Question, Do you get it? 28. Which of the following statements are true about crossing over? Independent Assortment! 29. 30. 31. 32. What does Independent Assortment produce? What does Independent Assortment refer to? How do the homologous compare? What happens during Metaphase I of Meiosis I? Question, Do you get it? 33. When does independent assortment occur? 34. Does the way one pair of chromosomes line up affect the way that any other pairs line up? Question, Do you get it? 35. Which of the following statements is true as a result of independent assortment? 36. What happens during the process of meiosis? Question, Do you get it? 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. How does independent assortment during Metaphase I help to produce diverse gametes? When else can Independent Assortment occur? Where can these different combinations or variations found? What independently assorts during Metaphase II? Does the alignment of sister chromatids for one chromosome affect the alignment of sister chromatids of the other chromosome? Question, Do you get it? 42. How does independent assortment during METAPHASE II help to produce diverse gametes? 43. What does independent assortment produce? 44. What does genetic diversity in gametes produce? Random Fertilization! 45. What is fertilization? 46. What is an important thing to remember about fertilization? 47. How many genetic combinations are possible for human beings having a baby together? Question, Do you get it? 48. Which of the following are true? Random Fertilization and Dihybrid Crosses 49. What two genes are being examined in the example? The Gene Key 50. What do the following letter represents for the genes? G= g= F= 51. What is a dihybrid cross? Question, Do you get it? 52. 53. 54. 55. When doing a dihybrid cross, how many genes are examined? How many squares are represented by a Punnett square? Where are the parent gametes written in a Punnett square? Where are the possible genotypes of the offspring written? f= Question, Do you get it? 56. What goes on the top and left side of the Punnett Square? Question, Do you get it? 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. When filling in a Punnett Square, what goes inside the boxes? What are the genotype crosses used in the example? What does each parent produce through the process of meiosis? What does the male snurfle make? What does the female snurfle make? What happens to the fur color gene and fin gene since they are on different chromosomes? How many genetically distinct possibilities of gametes are shown? How does the females eggs compare with the males process of meiosis? What is FOIL? What are the possible Male Gametes? What are the possible Female Gametes? Question, Do you get it? 68. What process is meiosis is represented by FOIL? Question, Do you get it? 69. 70. 71. 72. Which is the following is true? What do the 4 letters in each box represent? What are the fertilized eggs in each box called? What are the traits of the offspring called? Question, Do you get it? 73. Which of the following is the correct genotype for the following Snurfle baby? Question, Do you get it? 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. Which of the following is the correct phenotype for the following Snurfle baby? How are the results of a Punnett square often expressed? What is the number of snurfles with the phenotype: Yellow with no fins? What is the number of snurfles with the phenotype: Yellow with fins? What is the number of snurfles with the phenotype: Green with NO fins? What is the number of snurfles with the phenotype: Green with fins? What is the phenotype ratio is expressed as?