Chapter 26 - Saving, Investment, and the Financial System
advertisement

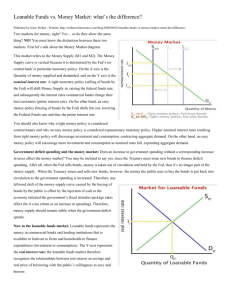
Name: ________________________________________________________________________________ CHAPTER 26 – Saving, Investment, and the Financial System Activator 1. What would be the disadvantage of putting your savings under your mattress? ______________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. List some places that you could invest your money that might cause it to gain interest/grow.___________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Chapter 26 – Saving, Investment, and the Financial System Financial System – a group of institutions that turn ____________________________________________________ Financial Markets – institutions through which savers can _______________________________________________ Saving – the absence of _________________________ Savings – dollars that become available to ____________________________________________________________ The Bond Market Bond – IOU, certificate of _____________________________ that specifies the obligations of the ________________________________ to the _______________________________________________ Corporate, _________________________, U.S. _________________________ Debt finance – sale of bonds __________________________________________________ Principal – initial ___________________________________, $1000 Date of maturity – time at which the __________________________________________________, 10-2030 Term – length of time ______________________________________, 30 years Interest – rate at which the __________________________________________________, 6% Credit risk – the ____________________ or loss by an investor arising from a __________________________________________________ some interest or _________________________ Junk bonds – bonds offered by _________________________, _________________________corporations Default – failure to __________________________________________________ Tax treatment – the way tax laws treat the ___________________________________________________________ The interest on most bonds is considered _____________________________________________ Municipal bonds – bonds offered by ___________________________________________________________; bond holders are ___________________________________________________________ on interest Federal bonds – U.S. Treasury bonds are exempt from ____________________________________ The Stock Market Stock – partial ______________________________ of a firm through the purchase of a ______________________ Disney, ______________________________, Babies ‘r Us, etc. 1 share of a company, company has 1,000,000 shares, you own 1/1,000,000 of the business Equity finance – sale of stocks to raise money; right to __________________________________________________ Difference between Stocks and Bonds Owner of shares in a company is a ______________________________________________________________ Owner of bonds is a _________________________________________________________________________ Stockholders enjoy benefits of _________________________while bondholders receive __________________ ___________________________________________________________ Bondholders ___________________________________________________________before stockholders if the company is in _________________________________ Stocks have a higher ___________________ than bonds, but a potentially higher __________________ Stock Exchanges Stock Exchanges – places where __________________________________________meet to trade stocks Perfectly competitive market – ____________________________________, prices are based solely on ______________________________________________________________________________________ New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) - a stock exchange located at __________________________________________, New York City, USA. It is the world's _____________________________________________ National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotation System (NASDAQ) - the largest ___________________________________________________________ trading market in the United States Bidding system – brokers bid up the price of a share of stock through _________________________________ Price of shares based on the following: _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ Intermediaries Financial Intermediaries – entity that channel ______________________ from people who have ___________________________ (______________________) to those who do __________________________________________________________________ (______________________). Banks – takes deposits from ______________________ and loan to ______________________ Mutual Funds – sell ______________; pool money from investors into a ___________________________________ (stocks, ______________________, __________________________, etc.) Saving & Investment in National Income Accounts Gross domestic product (GDP) Total income = ___________________________ Y = ____ +____ + ____ + ____ Y = gross domestic product GDP C = consumption G = government purchases NX = net exports Closed economy – one that does ___________________________________________________________________ NX = ____ Y = ____ + ____ + ____ Open economy - interact with other ______________________________________________________ National saving (saving), S – total ________________________ in the economy that remains after paying for _____________________________ and ______________________________ purchases ____ – ____ – ____ = I; S = ____ – ____ – ____ ____ = ____ T = taxes minus _________________________________ (amount it pays back to _________________, _________________________ and _____________________) National Saving, S = ____ – ____ – ____ Private saving – amount of ____________________ that households have left after paying for _________________and _________________ Y – ____ – ____ Public saving – tax __________________ that the government has left after paying for its _____________________ T–G Budget surplus – income in ____________________________________ over government spending; occurs when the government _____________________________________________________________ ____ – ____> 0 Budget deficit – shortfall of ____________________________________ from government spending; occurs when the ________________________________________________________________ ____ – ____< 0 The Market for Loanable Funds Market for loanable funds – market for those who want to ____________________________________and those who want to ________________________________________________________________________ Loanable funds – all ____________________ people have chosen to ____________________________________ rather than use for ________________________________ Assumes a closed economy and only one market for loanable funds Market for loanable funds is governed by ____________________________________ Source of the supply of loanable funds is __________________________ Source of the demand for loanable funds is __________________________ Price of a loan = _____________________________ Borrowers ____________________________________ Lenders receive a ____________________________________ Supply and demand of loanable funds Demand curve – ____________________________________ As interest rates rise _________________________________________________ Supply curve - ____________________________________ As interest rate rises _________________________________________________ The Loanable Funds Model The interest rate in the economy adjusts to balance the supply and demand for loanable funds. The supply of loanable funds comes from national saving, including both private saving and public saving. The demand for loanable funds comes from firms and households that want to borrow for purposes of investment. Here the equilibrium interest rate is labeled ir, and quantity of loanable funds are supplied and demanded q. Application – Loanable Funds Graphing Using a properly labeled graph, illustrate each of the following scenarios: 1. Suppose the economy is in a recession and the demand for loanable funds decreases. 2. Suppose the economy is in a recession and the government injects funds into the market. 3. Suppose the government implements a tax credit for consumers in the housing market which stimulates demand. 4. Suppose the government runs a budget deficit and increases their reliance on loanable funds (closed economy). Chapter 26 Homework, pgs. 586 - 593 Answer the following questions based on the reading: 1. How do American families compare to other countries when it comes to saving? ____________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What principles of economics relate to Americans' saving habits? _________________________________________ 3. How does the U.S. federal government discourage saving? ______________________________________________ 4. Describe the example provided in the book regarding a 25 year old investing in a bond. ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What example is provided as a way to improve saving in the U.S.? ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What curve would this policy affect; Which way would the curve shift? ____________________________________ 7. How would this affect both the quantity of loanable funds and the interest rates? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What does an investment tax credit refer to? _________________________________________________________ 9. Which curve would it affect; which way would it shift? __________________________________________________ 10. How would an investment tax credit affect the interest rate and the loanable funds? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. How does a budget deficit affect the supply for loanable funds; which way does the curve shift? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 12. What does crowding out refer to? __________________________________________________________________ 13. Why does increased borrowing by the government shift the supply curve and not the demand curve? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Describe what a declining debt-GDP ratio , and a rising debt-GDP ratio indicates as it relates to indebtedness. ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 15. How does war affect the debt to GDP ratio? __________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 16. Describe the two reasons that debt financing is an appropriate policy. _____________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 17. How was government debt affected as a result of the Ronald Reagan administration? ________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 18. What was a primary goal of the Clinton administration? ________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________