Perfect Competition
advertisement
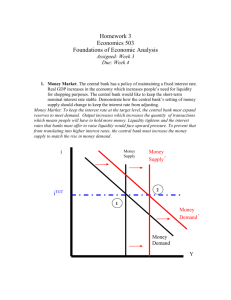
Models in AP Economics Sally Meek Sally.meek@pisd.edu Models in AP Macroeconomics Let’s focus on models Directions for FRQ’s include: ……. … it is not enough to list the results of your analysis. Include correctly labeled diagrams, if useful or required, in explaining your answers. A correctly labeled diagram must have all axes and curves clearly labeled and must show directional changes. Use a pen with black or dark blue ink. Production Possibilities Frontier (opportunity cost, economic growth, trade) Circular Flow Model (National Income Accounting) Market Supply and Demand (foreign exchange markets) Macroeconomics Key Graphs •Aggregate Supply and Demand, Including LRAS (monetary policy, fiscal policy, market self regulation) •Investment demand •Money Market (monetary policy) Macroeconomics Key Graphs Loanable funds market (fiscal policy) Phillips Curve – short run and long run Macroeconomics Key Graphs Increasing opportunity costs Good X Constant opportunity costs Good X Good Y Good Y Production Possibility Frontier Radios Radios 3 2 12 Wheat 4 Wheat Using PPFs and comparative advantage Assume they trade 1 r for 3 w Radios 4 Radios 3 2 12 Wheat 4 6 Wheat Using PPFs and CPFs Product Market Consumption expenditures Goods and services Net taxes Net taxes Government Households Public goods and services Firms Public goods and services Land, labor, capital. entrepreneurial ability Rent, wages, interest, profits Resource Market Circular Flow Model P S P1 D Q1 Q Perfectly Competitive Market Demand Supply Changes in: Changes in: •Taste and preference •Income •Marketsize (# of buyers) •Consumer expectations •Price of related goods complements or substitutes •Resource prices •Technology •Number of sellers •Producer expectations •Taxes and subsidies •Price of alternative goods Non-price determinants S$ Yen/$ $/Yen SYen D$1 SYen1 D$ DYen USD Yen Currency Markets Supply and Demand Changes in any of the following: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Relative real interest rates Relative price levels Relative national income Taste for imports Speculation Determinants of Exchange Rates LRAS PL SRAS PL1 AD=C+Ig+G+Xn Yf RGDP Aggregate Supply and Demand LRAS – changes in technology, productivity, and the quantity or quality of land, labor, capital SRAS – changes in input costs and inflation expectations AD – changes in personal consumption spending, gross private domestic investment, government purchases and net exports Determinants RIR (As compared to the expected rate of return) •As RIR changes the quantity of Investment demanded changes •Other determinants shift the ID curve: • costs of capital •business taxes •Technology ID •expectations Q Investment Demand MS NIR •MS – affected by actions of the Federal Reserve i1 MD Q1 •MD – •Transaction demand determined by GDP •Asset demand determined by NIR Q Money Market RIR S LF r1 D LF Q1 •Supply of Loanable Funds: personal savings and financial capital from abroad •Demand for Loanable Funds: firms demand for funds for capital and interest sensitive consumption Q Loanable Funds Market Inflation rate LRPC 4% 2% SRPC (assumes 4 % expected inflation at each UR) SRPC (assumes 2% expected inflation at each UR) Natural rate of unemployment Unemployment rate Phillips Curve – LR and SR