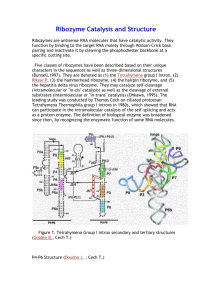
Splicing Lab
advertisement

Splicing Lab Purpose: To understand that RNA is genetic material and also an enzyme. To understand that genes are spliced together at the RNA level. Background: RNA is genetic information, it serves as a message to make proteins. It is important that the RNA message is put together correctly in order to make the right protein. In order to do this, RNA messages are cut and pasted together, a process known as splicing. Splicing is a way to cut and paste genes together. Why do genes need to be spliced? Splicing removes part of genes that do not code for protein. It also adds variety to genes, since they can be spliced (put) together in different ways. The parts of genes that code for proteins are called exons, the part of genes that do not code for proteins and are cut out are called introns. Introns are usually spliced (or cut) out of a gene. How does splicing occur? Splicing occurs with the help of enzymes. Enzymes are molecules that speed up a reaction. Some enzymes are proteins, but RNA can also be an enzyme. An RNA that is an enzyme is a ribozyme. Some ribozymes are capable of splicing. Ribozymes can cut out introns and splice their own gene. The ribozyme is in the RNA message itself, located in the intron. In this lab you will be make and splice RNA. RNA is made from DNA in a process called transcription. You will transcribe (make) RNA from DNA, the RNA we will make has a ribozyme. The ribozyme will splice the RNA message itself, and we will visually see the RNA before and after splicing. 1 PRE-LAB questions What is an enzyme? Some enzymes are proteins, but enzymes can also be ______. Splicing is a way to ____ and _____ genes together. Materials DNA of Ribozyme Centrifuge tubes Agarose gel 37 degree incubator Transcription kit Sybr gold Electrophoresis gel box Electrophoresis Power supply UV Light source PART A – Transcribe DNA to RNA Each station has a tube labeled DNA and T (for Transcription). 1. Add 1uL of from tube T to the tube labeled DNA. PART B - Incubation 1. After 1uL from tube T is added to the tube DNA, place the DNA tube in a 37°C incubator for a certain amount of time depending on what group you are in. Label your tube with what group you are in. Group 1- 5 minutes Group 2 – 10 minutes Group 3 – 15 minutes Group 4 – 20 minutes 2 PART C – Visualize splicing 1. After your time is up hand your teacher or resident scientist your tube. Make sure it is labeled with your group number. 2. The tube will be run on a gel. Draw an image of the gel after the gel is done running. Indicate where your group is on the gel. *Your teacher will run a control in the first lane. The control has not been incubated at all. How many bands should you see in the control #___? Questions 1. A ribozyme is an example of an______________________. 2. What is an intron? What is an exon? 3. After RNA is made and spliced, what does it code for? 3 4. What is the function of the ribozyme in splicing? 5. On a gel, a single piece RNA that does not splice will contain #___ bands, while an RNA that splices once will contain #____ bands. 4