Multiple Choice * Using a scantron form, bubble in the
advertisement

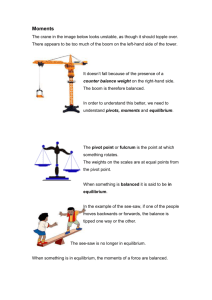
MIDTERM EXAM 2013 - REVIEW Questions 1-2 refer to the diagrams below. (1) (3) Effort Load (2) Effort Load (4) Load Load Effort Effort 1. Identify the class of each lever. 1_____ 2_____ 3_____ 4_____ 2. Which have a mechanical advantage greater than 1? _____________ 3. In a first class lever the distance between the resistance load and the fulcrum is 10 ft. and the distance between the effort force and fulcrum is 30 feet. What is the ideal effort force needed to lift 250 lbs? 4. 60 lbs. of effort force are needed are to roll a mass up the ramp shown below. Determine the mass of the object. 6 feet 8 feet 5. A force of 500 lbs. is applied to the axel 2 inch diameter axel in order to turn a 24 inch diameter wheel. What is the mechanical advantage of this system? 6. Given the pulley configuration shown, how many pounds of resistance could be lifted with an effort force of 900 lbs.? 7. In real life situations which is greater AMA or IMA. 8. 1/3 12 NC 8. How much resistance can be overcome using a 10 inch wrench, and an effort force of 25 lbs. on the bolt shown. 9. Calculate the WORK needed to move the 800 lb. piano to the top of the 6 ft. high inclined plane plain. 10. Find the effort required to move the piano. 6 ft 8 ft 11. What are advantages and disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells? 12. How is Resistance, Voltage, Current measured with a multimeter? Gear A is the driver and is turning clockwise at 100 RPM’s. 13. What is the direction of gear B and C? 14. What is the speed of gear B and C (measured in RPM’s) 15. What is the total gear ratio of this system? 16. If gear A has a torque of 20 ft lbs, what is the torque of gear B? 17. If gear A rotates 50 times, how many times will gear C rotate? Gear B 50 Teeth Gear A 25 Teeth Gear C 40 Teeth 18. In the belt-driven pulley system below, pulley A has a diameter of 5 cm, and pulley B has a diameter of 9 cm. Pulley A is spins at 80 RPM, what is the speed of pulley B? B A Questions 19 -21 are based on the following. A motor running a winch system can lift a 5 N load 2 meters in 6 seconds while running at an average of 12 volts and drawing 0.25 A. 19. What is the mechanical power (output) produced by the winch? 20. What is the electrical power (input) used by the winch? 21. What is the percent efficiency of a system which runs on 30 watts of electricity and outputs 22. Use Ohm’s law to calculate the amount of current (in Amps) in the diagram on the right. R=8Ω 5 Volts Questions 23 and 24 relate to the series circuit below. 23. Calculate the total resistance RT in the circuit below. 50 Ω 12 V 30 Ω 24. What is the voltage drop across the 20 ohm resistor? 20 Ω Questions 25 - 27 refer to the parallel circuit below. 25. What is the voltage drop across the 20 ohm resistor? 12 V 10 Ω 20 Ω 26. How much current is flowing through the 30 ohm resistor? 27. Calculate the total resistance RT in the circuit. 28. Find the Moment of Inertia, and beam deflection, given a load of 200 lbf, Modulus of Elasticity of 1,200,000 psi, and a span of 144 inches. Moment of Inertia = ________________ 2 inches 8 inches Max (beam deflection) = ______________ 29. Draw a free body diagram of the middle book in the pile below. 30 Ω Use the diagram below to answer questions 30 and 31. Use the bottom left corner as the reference point (0,0). 1 in. 30. Find the x direction centroid. 6 in. 31. Find the y direction centroid. 2.5 in. 2.5 in. 2 in. 6 in. 32. What is the force of the vector in the y direction? Round answer to 2 decimal places. A few other things on the midterm… Determine effort force moments acting on the lever. Determine the reaction forces at roller and pin joints. Determine the magnitude of the forces on truss members. Some terms you need to know. Conduction Convection Radiation R-Value U-Value Geothermal Energy Renewable Energy Inexhaustible Energy Nonrenewable Energy Biomass fuel Hydrogen fuel cell Scalar Vector Moment Resultant Power Resistance Voltage Current Work Energy Series Parallel Solar cell Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics Second Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Equilibrium Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s Second Law of Motion Newton’s Third Law of Motion Resultant Force