Principles Of Engineering™ Part A
advertisement

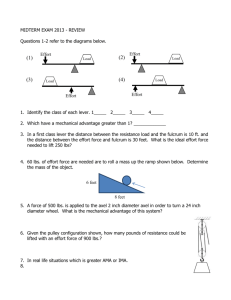
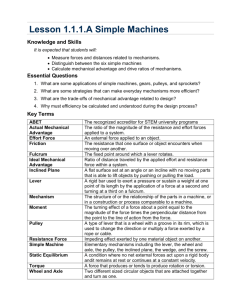
Principles Of Engineering™ Final Examination Part A Spring 2009 Student Name: ___________________________________ Date: _____________________ Class Period: _____________ Total Points: Converted points: ____________/50 _____________/40 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 1 of 11 Directions: This is a CLOSED BOOK/CLOSED NOTES exam. Select the letter of the response which best completes the item or answers the question. Then record your answer on the answer sheet provided for Part A. Reference Tables are available at the end of the document. 1. Which of the following engineering achievements occurred first? A. Development of the catapult C. Development of stone bridges that incorporated wood stringers B. Development of methods to D. Development of the water wheel create fire at will 2. An engineering technician would generally be more involved in ________ than would an engineer. A. researching a product idea C. conducting complex analysis B. the initial design of a product Figure 1a D. servicing and maintaining equipment Figure 1b 3. Figure 1a represents a(n) _____________ drawing and figure 1b represents a(n) _____________ drawing. A. isometric, orthographic C. cabinet oblique, orthographic B. orthographic, isometric D. isometric, cavalier oblique 4. _____________ is freehand drawing, which is done without the use of drafting equipment. A. CAD C. Sketching B. Dodging D. Board drafting 5. Given the total population of five counties, which visual representation would be most appropriate if you want to demonstrate percentages of people in each county? A. Pie chart C. Line graph B. X,Y scatter plot D. Spreadsheet Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 2 of 11 Figure 3 6. The wheelbarrow shown in Figure 3 represents what type of simple machine? A. Class 1 Lever C. Class 3 Lever B. Class 2 Lever D. Wheel and Axle Figure 4 7. Given the pulley configuration shown in Figure 4, how many pounds of effort force would a user have to exert on the rope to lift the 60 lb load? A. 15 lbs C. 25 lbs B. 30 lbs D. 20 lbs Figure 5 8. A POE student is using the ramp shown in Figure 5 to raise an object 4 feet above the ground. The mechanical advantage of the ramp is _____________. A. 0.316 C. 3.0 B. 1.05 D. 3.163 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 3 of 11 Figure 6 9. Study the gear train in Figure 6. The purpose of the center gear is to _____________. A. change the direction of C. maintain the direction of rotation from rotation from the input to the the input to the output gear output gear B. decrease the rotational output D. increase the rotational output Figure 7 10. Figure 7 represents a belt-driven system. Pulley B, which has a diameter of 16 inches, is being driven by pulley A, which has a diameter of 4 inches. If pulley A is spinning at 60 RPMs, then pulley B is spinning at _____________ RPMs. A. 240 C. 4 B. 15 D. 64 11. In a third class lever, the distance from the effort to the fulcrum is _____________ the distance from the load/resistance to the fulcrum. A. greater than C. less than B. less than or equal to D. greater than or equal to 12. Which of the following methods of heat transfer describes how heat from inside a home is lost to the outside through the walls on a cold day? A. Convection C. Radiation B. Conduction D. R-value Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 4 of 11 13. A pneumatic device is a machine that derives its mechanical advantage from _____________. A. compressed air C. gears B. compressed liquid D. pulleys 14. _____________ states that a force exerted on a fluid will be transferred equally against the walls of that fluid’s container. A. Pascal’s Law C. Boyle’s Law B. Bernoulli’s Law D. Charles’s Law 15. If one light bulb burns out in a string of lights and the rest stay lit, it is reasonable to assume that the lights are wired in _____________. A. series C. order B. line D. parallel Figure 8 16. Study the circuit in Figure 8. Which of the following electrical properties is being measured by the multimeter? A. Resistance C. Current B. Voltage D. RPMs 17. In a control system, _____________ provide feedback on the condition of the operating environment. A. sprockets C. gears B. 18. motors D. sensors Which of the following digital control devices processes the input information from sensors? A. Microprocessor C. Algorithm B. Variable resistor D. Flowchart program Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 5 of 11 Figure 9 19. If electrical wires are connected to ports 1 and 3 on the limit switch in Figure 9, then the switch will be wired normally- _____________. A. common C. closed B. open D. neutral 20. Which of the following is a light-sensitive input device? A. Lamp C. Phototransistor B. Reed switch D. Electromagnet 21. A sketch showing a single object with all of the surrounding parts removed to expose the external forces is called a _____________. A. stress-strain diagram C. system diagram B. load-deflection diagram D. free body diagram 22. The torque on an object, also known as its moment, is calculated using the formula _____________. A. Force / Area C. Mass * Acceleration B. 23. Force * Perpendicular Distance D. Weight * Area Figure 10 In the structural system shown in Figure 10, Member B is experiencing _____________. A. compression C. shear B. tension D. torque Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 6 of 11 24. Static equilibrium occurs in a truss system when the sum of the _____________ is equal to zero. A. velocities C. member lengths B. scalars D. forces and moments 25. When comparing different support beams (made of the same material) for stiffness, it is best to compare their _____________. A. cross-sectional areas C. Modulus of Elasticity B. height-to-width ratio D. weights 26. __________ materials would be attracted to a magnet. A. Ferrous C. Non-ferrous B. Polymer D. Organic 27. Which of the following materials is considered synthetic? A. Oil C. Plastic B. Wood D. Iron Figure 11 28. Figure 11 shows a 100 lb normal force being applied to a 10 in. diameter cylinder. What is the resulting compressive stress in the cylinder? A. 10 psi C. 0.88 psi B. 8.33 psi D. 1.27 psi 29. Which one of the following manufacturing tools is used to create parts from heated plastic? A. Milling machine C. Injection molder B. Lathe D. Drill press 30. Which one of the following manufacturing processes is used to form a piece of metal into a predetermined shape through the application of pressure? A. Turning C. Annealing B. Forging D. Threading Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 7 of 11 31. Using a dial caliper, the following seven diameters were obtained for a dogbone aluminum tensile test sample: 0.120, 0.123, 0.121, 0.122, 0.118, 0.122, and 0.119. What is the median value for this group of numbers? A. 0.119 C. 0.121 B. 0.120 D. 0.122 Figure 12 32. The dial caliper in Figure 12 is showing a measurement of _____________ inches. A. 0.875 C. 0.757 B. 0.750 D. 0.775 33. The process of loading a material to the point of failure for the purpose of collecting data on that material’s physical properties is known as _____________. A. the offset method C. statistical process control B. destructive testing D. non-destructive testing 34. A material that experiences very little plastic deformation prior to rupture or fracture would be referred to as a _____________ material. A. brittle C. tensile B. chip-forming D. ductile 35. The probability of satisfactory operation of a product in a given environment over a specified time interval is referred to as _____________. A. reliability C. system failure B. liability D. redundancy 36. _____________ provide a means for analyzing documented events such as engineering disasters and the ethical dilemmas associated with them. A. Resumes C. Free body diagrams B. Design briefs D. Case studies Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 8 of 11 37. 38. A free-falling object will experience a constant increase in speed per unit time. This is referred to as _____________ due to gravity. A. velocity C. acceleration B. displacement D. force Figure 13 Which of the four launch angles of the ballistic device shown in Figure 13 will the ping pong ball theoretically (no air resistance) go the farthest? A. 20° C. 60° B. 40° D. 80° 39. When a projectile is thrown, the _____________ component of its initial velocity will remain constant throughout its flight. A. horizontal C. vertical B. Y D. Z 40. Neglecting air resistance, the path that is formed by a projectile with a horizontal component velocity will take the shape of a(n) _____________. A. circular curve C. hyperbolic curve B. elliptical curve D. parabolic curve Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 9 of 11 POE Exam Reference Tables Circular Shapes Formulas C = π×D A = π×r2 Variables C = Circumference π = 3.14 D = Diameter A = Area r = Radius Electrical Systems Formulas Variables E = Voltage I = Current R = Resistance E = I×R Simple Machines Formulas MA = R ÷ E Lever MA = LE ÷ LR Wheel and Axle MA = rw ÷ ra Pulley MA = Total number of strands supporting the load Inclined Plane or Wedge MA = L ÷ H Screw MA = C ÷ Pitch Pitch = 1 ÷ TPI Variables MA = Mechanical advantage R = Resistance force E = Effort force LE = Length from fulcrum to effort LR = Length from fulcrum to resistance L = Slope length H = Inclined plane height or wedge thickness C = Circumference Pitch = Screw pitch TPI = Threads per inch rw = Wheel radius ra = Axle radius Statics Formulas M = ⊥F×D ΣFX = 0 = X (right) + X (left) ΣFY = 0 = Y (up) + Y (down) SM = 0 = CCW + CW Variables M = Moment about a point ⊥F = Perpendicular force D = Perpendicular distance Σ= sum of CCW = Counter-clockwise moment CW = Clockwise moment Right Triangle Ratios Formulas Variables sin θ = Opposite ÷ hypotenuse cos θ = Adjacent ÷ hypotenuse θ = Angle tan θ = Opposite ÷ adjacent Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 10 of 11 Properties of Materials Formulas Variables δ = Deformation σ = Stress ∈ = Strain E = Modulus of elasticity, Young’s Modulus P = Axial force Ao = Original area Lo = Original test length Δ = Change in σ = P ÷ Ao ∈ = δ ÷ Lo δ = (P×L) ÷ (Ao×E) E = Δσ ÷ Δ∈ E = ((P1-P2)×Lo) ÷ (( δ 1-δ2)×Ao) Kinematics Formulas Variables VI = Initial velocity VIX = Initial horizontal velocity VIY = Initial vertical velocity θ = Initial trajectory angle g = Acceleration due to gravity X = Range Note: θ is measured from the horizontal plane Gear Ratios Formulas GR = Input Rate ÷ Output Rate GR = Nout ÷ Nin SR = Win ÷ Wout Win / Wout = Dout ÷ Din Tin / Tout = Din ÷ Dout Variables GR = Gear ratio Nin = Number of teeth on driver gear Nout = Number of teeth on driven gear Din = Driver gear diameter, in Dout = Driven gear diameter, in Win = Driver gear speed, rpm Wout = Driven gear speed, rpm Tin = Torque of driver gear, ft lbs. Tout = Torque of driven gear, ft lbs. SR = Speed ratio Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2009 Page 11 of 11