Click to Design Project II Report
advertisement

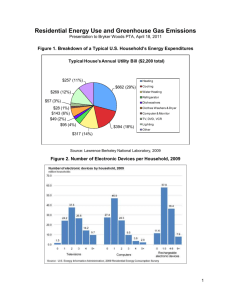
GE LOCOMOTIVE PROJECT 2 Engineering Design 100 Submitted to: Mr. Wallace Catanach Sec. 004 Group 7: Fantastic Four Group Members: Gabriel Shope---------------------------gds5164@psu.edu Ziyang Fang------------------------------zkf5009@psu.edu Hongbo Li--------------------------------hfl5026@psu.edu Ruixi Sun---------------------------------rms5921@psu.edu 1 Table of Contents Executive Summary……………………………………………..…………. 3 Introduction…………………………………………………..……………….. 4 Needs………………………………………………………………………………. 4,5 Research……………………….…………………………..……………………. 5-9 Concept Generation………………………………………………………...9,10 Concept Selection……………………………………………………………11 Cost Model………………………………………………………………………..12 Design……………………………………………………………………………….14,15 Model………………………………………………………………………………..15 Conclusion…………………………………………………………………………16 References………………………………………………………………………..16 2 Executive Summary Pittsadelphia has a need for the design of a cost-effective transportation solution that reduces emission and meets the new EPA requirements. It’s going to maintain or increase transportation ability between the port cities. Every day approximately 165,000 tons of raw materials travel via rail into and out of the Pittsadelphia. The train emissions generated from engine-emitted NOx is a key complaint of city residents. Tier 2 locomotives used to haul freight are approaching age for overhaul, at which investments will be required to meet EPA Tier 3 (or higher) requirements. We are going to upgrade the locomotive fleet to meet more recent emissions guidelines set by the EPA. A few options may exist to meet the new standards. We are implementing a combination of methods to reduce the locomotive’s emissions and its effect on smog in the city. Using a combination of a an ammonia based after treatment and exhaust gas recirculation we successfully reduce the amount of NOx produced and hydrocarbons emitted into the atmosphere. GE Transportation is going to be our Sponsor. GE Transportation, is a unit of GE (NYSE: GE), they solve the world’s toughest transportation challenges. GE Transportation builds equipment that moves the rail, mining, and marine industries. GE designs and builds fuel-efficient and reduced-emission freight and passenger locomotives; diesel engines for rail; marine and stationary power applications; signaling and software solutions; drive systems for mining trucks; and value-added services to help customers grow. GE Transportation is headquartered in Chicago, IL, and employs approximately 13,000 employees worldwide. 3 Introduction In today’s society, the government is enforcing stricter and stricter regulations on companies to control their emissions. The automobile industry was hit first but now the locomotive industry is getting the attention. The locomotive industry is no exception to this problem. The industry is constantly developing new ways to reduce their carbon footprint and develop new ways to cut down on the harmful emissions produced from their locomotives. Specifically, General Electric has tasked us to develop a model for a new locomotive to add to their fleet. It must meet the new EPA requirements for NOx emissions and must also reduce the emissions that contribute to the smog in the urban area. This can be achieved through a number of different methods such as after treatment, upgraded combustion design etc. Needs Customer Statement Needs Statement Smog from locomotive is a key complaint of city residence Smog is generated from engine emitted NOx Tier 2 locomotives used to haul freight are approaching age of overhaul EPA requires locomotive to reach tier three requirements Reduce smog emissions within Pittsdelphia Decrease NOx emissions from engines of locomotive Upgrade the locomotive fleet Meet EPA requires for NOx 4 Needs Upgrade metrics locomotives from tier 2 to tier 2+, or even higher Reduce smog emissions within the city Decrease x NOx emissions from engines Upgrade the x locomotive Meet EPA x requirements NOx Cost efficient design Add after treatment on locomotive engines Add Use emissions alternative recirculation fuels x x x x x Pick the comparative low cost solution x x x X Research Freight 15 Freight trains/day 2 Locomotives/freight trains Coal 5 Minerial trains/day 3 Locomotives/coal train 45 Locomotives/day 50 total locomotives in fleet 5 Mileage for Teir 2 locomotive 1 Ton freight 470 miles/gallon 165000 Tons/day Emmissions for Teir II Locomotive 0.2 g/hp-hr 5.5 NOx/hp-hr Diesel Particulates NOx Assumptions 500 50 143 117 26 miles/trip into the city mph tons tons tons 215000 lbs 30 tons 110 tons average speed tons/loaded coal car Weight of coal Weight of coal car Freight Lading Capacity Freight car weight empty Freight Lading Capacity $2.50 $/gallon 500 miles Diesel fuel One way trip 12000 gallons 470 miles 500 miles need 12000 gallons to go 470 miles need 12000 gallons to go 470 miles Miles per trip to city Coal train full 6 Coal/freight into city (tons) Total # of cars in a train Weight of empty cars Weight of locomotives Total weight of loaded train Total power @50 mph level grade Power fraction (tons) Fuel used per train Fuel cost per train Particulate emissions per train NOx emissions per train Coal Train Coal Train Freight Freight In Out Train In Train Out 12,000 0 7,000 5,000 103 103 64 64 (tons) 2,678 2,678 1,920 1,920 (tons) 648 648 432 432 (tons) 15,326 3,326 9,352 7,352 (hp) 10,230 2,220 6,242 4,907 0.76 0.16 0.69 0.55 (gal) ($) (kg) 10,883 27,208 20 2,362 5,905 4.4 6,641 16,602 12 5,221 13,052 10 (kg) 563 122 343 270 ANNUAL TOTALS Fuel used Fuel cost Particulate emissions NOx emissions (kgal) (M$) (tonnes) (tonnes) 19,862 49.7 18.7 513 4,310 10.8 4.1 111 36,359 90.9 34.2 940 28,583 71.5 26.9 739 GRAND TOTAL 89,114 223 83.8 2,304 7 Alternative Fuel Emissions: D1 D2 NG M100 E85 NOx(g/mile) 32 31.8 30 14.7 18.2 CO(g/mile) 9.7 16.5 15.3 19.9 31.9 HC(g/mile) 2.6 2.1 14.8 14.7 10.5 PM(g/mile) 0.96 1.48 0.03 0.26 0.49 D2 2.498 NG 2.331 M100 2.512 Alternative Fuel Price D1 Price(d/gal) E85 1.89 Locomotive Diagram (Size Relativity): 8 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a technique of reducing nitrogen oxide emissions in petrol/gasoline and diesel engines. It works by recirculating a portion of an engine's exhaust gas back to the engine cylinders. This dilutes the Oxygen in the incoming air stream and provides gases inert to combustion to act as absorbents of combustion heat to reduce peak in-cylinder temperatures. NOx is produced in a narrow band of high cylinder temperatures and pressures. Picture from www.aa1car.com A High Pressure Injection Pump is the device pumps diesel (as the fuel) into cylinders of a diesel engine. Traditional injection pump is driven indirectly from the crankshaft by gears, chains or a toothed belt (often the timing belt) that also drives the camshaft. It rotates at half crankshaft speed in a conventional four-stroke diesel engine. Its timing is such that the fuel is injected only very slightly before top dead center of that cylinder's compression stroke. It is also common for the pump belt on gasoline engines to be driven directly from the camshaft. 9 Picture from www.enginebuildermag.com A diesel particulate filter is the device designed to remove diesel particular matter or soot from exhaust gas of a diesel engine. Usually its type varies in cordierite wall flow filter, Silicon carbide wall flow filter, Ceramic Fiber Filters, Metal fiber flow-through filters, and paper filter. Picture from http://www.ironmanparts.com/?id=emi3&sub=products 10 Ammonia based after-treatment is a technique of converting nitrogen oxides, with a catalyst into diatomic nitrogen, and water. A gaseous reductant, typically anhydrous ammonia, aqueous ammonia or urea, is added to a stream of flue or exhaust gas and is adsorbed onto a catalyst. Carbon dioxide, is a reaction product when urea is used as the reductant. Picture form http://www.mathworks.com/company/newsletters/articles/optimizing-a-diesel-engine-aftertreatmentsystem-with-matlab-and-gt-suite.html Concept Generation 11 12 Concept Selection REACH EPA REQUIREMENTS REDUCE HARMFUL EMISSION ECONOMICAL LOW MAINTENAN CE SUM OF + CONTINUE? UPGRADE ENGINE EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION PISTON DESIGN + + _ 0 2 Yes + + 0 + 3 Yes 0 0 + + 2 Yes HIGH PRESSURE INJECTION 0 0 0 0 0 Yes DIESEL PARTICULATE FILTER AMMONIA BASED + + + - 3 Yes + + + - 3 Yes USE ALTERNATIVE FUEL 0 + - + 2 yes WEIGHING REACH EPA REQUIREMENTS REDUCE HARMFUL EMISSIONS WITHIN THE CITY ECONOMICAL LOW MAINTENANCE SUM CONINUE? 35% UPGRADE EXHAUST GAS PISTON HIGH ENGINE RECIRCULATION DESIGN PRESSURE INJECTION 5 5 4 4 DIESEL AMMONIA USE PARTICULATE BASED ALTERNATIVE FILTER FUEL 5 5 5 25% 5 5 3 3 5 5 4 25% 15% 3 4 3 5 4 5 3 5 4 3 4 3 4 5 4.35 YES 4.5 YES 3.65 NO 3.65 NO 4.45 NO 5.5 YES 4.5 NO 13 Cost Model TierII to Tier III locomotive upgrade cost Number of locomotives upgrade cost 750k After Treatment Cost 100k Exhausted Gas Recirculation 100k 50 50 50 37,500,000 5,000,000 5,000,000 total cost 47,500,000 Design 14 Our designed entailed upgrading each locomotive from tier II to tier III. We added an after treatment system to each locomotive. The ammonia based after treatment will significantly reduce the amount of NOx emitted into the atmosphere. To combat against the carbohydrates not burned in the combustion process we also implemented an exhaust gas recirculation. Both of these solutions will significantly reduce the harmful emissions of the locomotive and reduce smog in Pittsdelphia. Model 15 Conclusion Modern technology is constantly being advanced. Society is demanding for bigger and better machines. Our use of technology does have negative effects that are not always accounted for economically. This is why the EPA sets these regulations. The locomotive industry is behind the curve when it comes to these regulations. These advanced designs need to be implemented into the new locomotives being produced. These new locomotives are just another stepping stone to reducing our carbon footprint and our impact on our planet. References http://www.mathworks.com/company/newsletters/articles/optimizing-a-diesel-engine-aftertreatment-system-withmatlab-and-gt-suite.html http://www.ironmanparts.com/?id=emi3&sub=products www.aa1car.com www.enginebuildermag.com 16