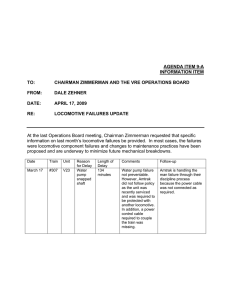
Locomotives
advertisement
CE 515 Railroad Engineering Rolling Stock: Locomotive Source: Armstrong Ch 4 AREMA Ch. 2.6 “Transportation exists to conquer space and time -” What is a Locomotive? • A Vehicle which Provides the Motive Power to the Train • Almost All Trains Use One or More Types of Locomotives • • • • • Steam Diesel-Electric Electric Hybrid This Discussion will Focus on Diesel-Electric http://www.brookvilleequipment.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=80 Tractive Effort • The ability to Overcome Resistance – Starting – Grade – Wind – Curve – Rolling • Is Discussed Further in REES #3 Tractive Effort Adhesion Control • Grip Rail without Slipping • Dependant on weather, rail conditions • Controlled automatically in modern locomotive • Sanding http://science.howstuffworks.com/diesel-locomotive3.htm Power to Pull Train • Not all Engine Power Pulls Train • Powering Auxiliary Devices, Efficiency Losses, Pulling Locomotive Itself • On Average, 82% of Power Left to Pull Train Locomotives Today • Used Today on Class I – Endcab Switcher (5%) – Four-Axle Road Switcher (20%) – Six Axle Medium Horsepower Road Switcher (15%) – High Horsepower SixAxle Road Switcher (55%) Prime Mover (Engine) • V-8 to V-20 Diesel Engine • Idle at 300 rpm, Full Power 900-1050 rpm • Alternator Converts into Electrical Energy for Traction – AC produced, converted to DC (and converted back for AC) http://www.vistacorpofva.com/images/engine1.jpg What Locomotive Carries • • • • Engine Cooling Water: 325 gallons Engine Lube Oil: 450 gallons Diesel Fuel: 5000 gallons Sand: 1.5 tons Traction Power System • • • • DC is used for 80% of Fleet What Actually Drives the Wheels Since 1990’s AC is Gaining Ground AC Offers Greater Power – However, Most Have Gone Back to Regular Power – Used Mainly in Heavy Haul Emissions • 1998-EPA Issues Final Emission Standards – Applies to Newly Manufactured and Remanufactured Locomotives After January 1, 1973 • Tier Based on Manufacture Date • Plus Tiers for Remanufacture http://www.epa.gov/oms/regs/nonroad/locomotv/420f09025.pdf Locomotive Controls • Minimum Levers, but Connected to Circuitry • “Microprocessor” Control • Display Screens • Interfaces with Primary Operator Four vs. Six Axles • Why Have 6 Axles when 4 can Haul More Tonnage? – Adhesion at Higher Speeds and Grades – Starting up? Maintenance and Life Span • Most New Locomotives can Self-Diagnose Problems • Different Inspections Mandatory at Daily, 92days, Annual, and Biennial Periods • Remote Diagnostics • Average Locomotive Service is 20-25 Years • Used to be Returned to Manufacturer, but Now Sold to Smaller Railroads Videos / Websites • How Diesel-Electric Locomotive Works: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L8MxASJoC4M • Modern Marvels: Freight Trains (go to 5:00 for Sand Operations) (Evan Vencil): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h6ozfxDeXII&feature=rela ted • http://science.howstuffworks.com/diesel-locomotive3.htm (Nicole Oneyear) • http://www.thedieselshop.us/DS.html (Ben Hucker) • http://www.nrm.org.uk/OurCollection/LocomotivesAndRollin gStock.aspx?ipp=12&cat=All&comp=All (Na Ning)