10th December 2012 Tom Salter FY1 Cardiology SWFT Diabetes
advertisement

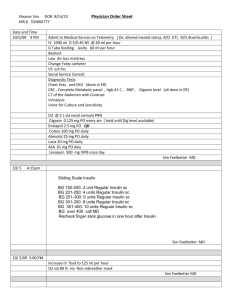
10th December 2012 Tom Salter FY1 Cardiology SWFT Diabetes Mellitus Handout Type 1 Diabetes (~15%) A condition of insulin deficiency Autoimmune destruction of Beta cells in the Islets of Langerhans Genetic component (30% concordance in identical twins), associated with HLA DR3 and DR4 Type 2 Diabetes (~85%) An acquired condition of gradual onset insulin insensitivity Risk factors include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history and high refined-sugar diet History Weight loss (T1DM), polyuria, polydipsia, lethargy, pruritus or frequent, recurrent or prolonged infections Diabetic Ketoacidosis in T1DM (abdominal pain, dehydration, hyperventilation) Assess for compliance with lifestyle advice and medication as well as signs of complications (e.g. retinopathy, neuropathy etc) Assess risk factors, smoking status ?Previous Gestational Diabetes (risk factor for T2DM) Family History of Diabetes Investigations Bedside: Urine dipstick (Ketones, protein and glucose) ECG (?hyperkalaemia in DKA/HONK) 10th December 2012 Tom Salter FY1 Cardiology SWFT Bloods/Urine: Urine PCR (usually done yearly for signs of CKD) FBC (WBC ?infection causing DKA/HONK), U+Es (CKD), LFTs (Fatty liver), Glucose/HbA1c (depending on the situation i.e. ED /clinic) Radiological: CXR (?LRTI in HONK/DKA) USS Kidneys (to rule out other causes of kidney damage) Special Tests: Slit lamp examination for retinopathy Management “A chronic condition that needs to be managed by a multidisciplinary team” Lifestyle advice on: Diet – low refined sugar Foot care – sensible well-fitting shoes Smoking cessation Encourage physical activity and weight loss Consider MedicAlert bracelet Contact DVLA Medical: Metformin (Suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis, Increases insulin sensitivity) Sulfonylurea (Increase insulin secretion by Beta cells, need underlying insulin production) DPP-4 inhibitor (Reduce circulating glucagon levels ) Thiazolidinediones/glitazones (Activates nuclear receptors called PPARs effecting gene transcription) 10th December 2012 Tom Salter FY1 Cardiology SWFT Insulin: Long acting OD (e.g. Glargine) Can be used OD as first line in T2DM if patient has difficulty injecting Or as part of the Basal-Bolus usually seen in T1DM (or advanced type 2) Intermediate (e.g NPH insulin) Often used BD as a first line insulin regimen in T2DM (once tablet control has become insufficient) Biphasic (e.g. Novomix 30) A premixed solution of 70% intermediate and 30% rapid acting insulin that is also used as an early insulin treatment regimen for T2DM Other varieties are also available Short acting (e.g. Actrapid & Humulin S) Given approximately 20-30 minutes before a meal to mimic the body’s natural prandial insulin bolus Fast/Rapid acting (e.g. aspart/Novorapid) Even faster than Short acting they are also given as bolus insulin with meals, usually as part of a basal-bolus regimen The General Diabetic consultation Usually three-monthly during first year and then six-monthly, check: Patient concerns lifestyle assessment (alcohol, smoking etc) current health, medication and compliance history of hypo- and hyperglycaemic episodes BP pulse weight and BMI (& height if no record) blood or urine testing diary if appropriate blood tests: U+E creatinine, lipids, glucose and 6-monthly HbA1c urine protein test: o if positive, check for microalbuminuria on three occassions 10th December 2012 o Tom Salter FY1 Cardiology SWFT if persists, start ACE inhibitor and investigate for non-diabetic cause feet o Sensation(especially vibration sense as often 1st sensation to go) o Signs of ulceration visual acuity and fundoscopy with dilated pupils macrovascular examination (i.e. heart, carotids, peripheral circulation) General advice for FPE Try to have a structure for each section of the clinical exam to hang your answers on, for example, Investigations “The simple/bedside tests I would perform on this patient would be X to look for or rule out...Y” Then move on to bloods, radiological and special tests Management “In the acute setting I would manage this patient in an A-E approach ensuring the airway was patient by...” “This patient could be managed conservatively, medically or surgically. The conservative options are...” For the written exams just get plenty of practice with online services (OnExamination, PasTest, PassMedicine etc) each have their own advantages and disadvantages find the one that works for you or use several! The PasTest multiple choice/SBA/EMQ books are good too.