The Urinary System
advertisement

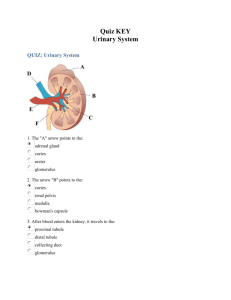
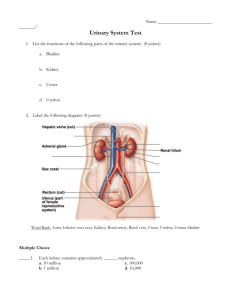
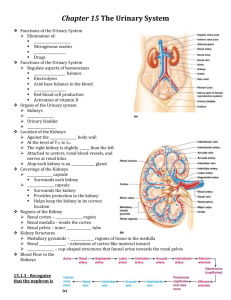
The Urinary System Source: http://www.the-human-body.net/urinary-system.html The Urinary System 2|Page The Kidneys The KIDNEY is one of two BEAN-SHAPED ORGANS behind the abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal) on either side of the spine in the lumbar region. A cushion of adipose (fatty) tissue and fibrous connective tissue surrounds each kidney for protection. The kidneys consist of an outer CORTEX region and an inner MEDULLA region. The HILUM is a depression on the medial border of the kidney. Blood vessels and nerves pass through the hilum. Combining Forms Kindey ren/o, nephr/o Medical Terms Paranephric pt. to near the kidney Nephropathy disease of the kidney Nephroptosis downward displacement or drooping of a kidney Nephrolithotomy Incision into the kidney to remove a stone Hydronephrosis an abnormal condition of fluid (urine) in the kidney Nephrostomy surgical opening to outside of the body (from the renal pelvis) Renal ischemia blood held back from the kidney Renal colic pain resulting from calculi in the kidney or ureter Source: http://www.babble.com/CS/blogs/strollerderby/archive/2008/02/18/girl-asks-to-donate-extrakidneys.aspx Inside the Kidneys The Glomeruli Each arteriole in the cortex of the kidney leads into a mass of tiny, coiled, and intertwined smaller blood vessels called GLOMERULI (plural). Each glmerulus (singular) is a collection of tiny capillaries formed in the shape of a small ball. There are about 1 million glomeruli in the cortex region of each kidney. The kidneys produce urine by FILTRATION. As bold passes through the many glomeruli, the thin walls of each GLOMERULUS (the filter) permit water, salts, sugar, and urea (with other nitrogenous wastes such as creatinine and uric acid) to leave the bloodstream. These materials collect in a tiny, cup-like structure, a GLOMERULAR (BOWMAN) CAPSULE, that surrounds each glomerulus. Combining Forms Glomerulus glomerul/o Medical Terms Glomerular capsule capsule that surrounds the glomerulus Source: http://science-naturalphenomena.blogspot.com/2009/11/glomerulus.html The Urinary System The Renal Tubule Attached to each glomerular capsule is a long, twisted tube called a RENAL TUBULE. The combination of a glomerulus and a renal tubule forms a unit called a NEPHRON. Each kidney contains about 1 million nephrons. As water, sugar, salts, urea, and other wastes pass through the RENAL TUBULE, most of the water, all of the sugar, and some of salts return to the bloodstream. This process is called TUBULAR REABSORPTION. TUBULAR REABSORPTION ensures that the body retains essential substances such as sugar, water and salts. The final process in the formation of urine is TUBULAR SECRETION. In secretion waste products such as acids, potassium, and drugs leave the body in urine. URINE is composed of 95% water, 5% wastes (urea, creatinine), salts, acids, and drugs. All collecting tubules lead to the RENAL PELVIS, a basin-like area in the central part of the kidney. Small, cup-like regions of the renal pelvis are called CALYCES or CALICES (singular). Combining Forms Calyx cali/o, calic/o Renal pelvis pyel/o Medical Terms Caliectasis stretching of the calyx Caliceal pt. to the calyx Pyelolithotomy to cut into the renal pelvis. Usually this is to remove large calculus (stones) The Urinary System The Ureter, the Urinary Bladder, the Urethra The renal pelvis narrows into the URETER, which carries urine to the URINARY BLADDER. The bladder, a muscular sac, temporarily stores urine. Sphincter muscles control the exit area of the bladder to the URETHRA. As the bladder fills and pressure increases at the base of the bladder, an individual notices a need to urinate and voluntarily relaxes sphincter muscles. Combining Forms Ureter ureter/o Urinary bladder cyst/o, vesic/o Medical Terms Ureteroplasty surgical repair of the ureter Ureteroileostomy a pouch from a segment of the ileum, used in place of the bladder to carry urine from the ureters to outside of the body Cystitis inflammation of the urinary bladder Cystectomy removal of the urinary bladder Cystostomy an opening made into the urinary bladder from the outside of the body. A catheter is placed in the bladder for drainage. Intravesical within the urinary bladder Vesicoureteral reflux urine is passed backwards from the bladder into the ureters Source: http://healthguide.howstuffworks.com/uterine-fibroids-and-hysterectomy-in-depth4.htm The Urinary System