Chapter 15 The Urinary System
advertisement
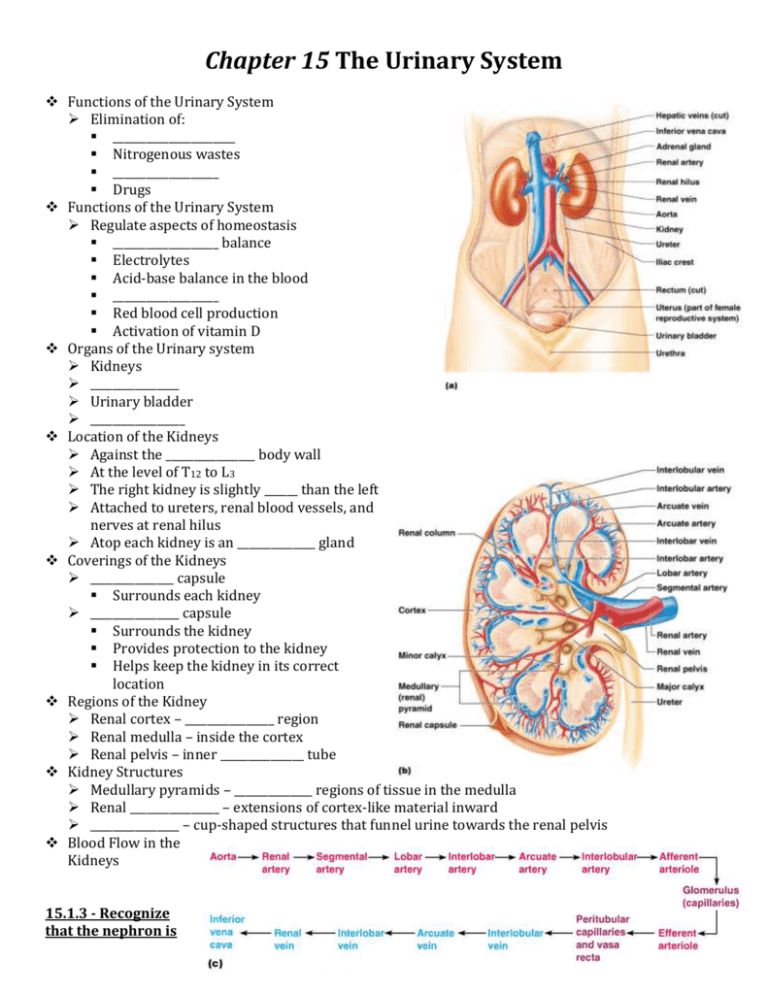
Chapter 15 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of: ______________________ Nitrogenous wastes ___________________ Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis ___________________ balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood ___________________ Red blood cell production Activation of vitamin D Organs of the Urinary system Kidneys ________________ Urinary bladder _________________ Location of the Kidneys Against the ________________ body wall At the level of T12 to L3 The right kidney is slightly ______ than the left Attached to ureters, renal blood vessels, and nerves at renal hilus Atop each kidney is an ______________ gland Coverings of the Kidneys _______________ capsule Surrounds each kidney ________________ capsule Surrounds the kidney Provides protection to the kidney Helps keep the kidney in its correct location Regions of the Kidney Renal cortex – ________________ region Renal medulla – inside the cortex Renal pelvis – inner _______________ tube Kidney Structures Medullary pyramids – ______________ regions of tissue in the medulla Renal ________________ – extensions of cortex-like material inward ________________ – cup-shaped structures that funnel urine towards the renal pelvis Blood Flow in the Kidneys 15.1.3 - Recognize that the nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney and describe its anatomy. Nephrons The structural and ____________________ units of the kidneys Responsible for forming ____________________ Main structures of the nephrons ____________________ Renal tubule Glomerular capsule (Bowman’s capsule) - The closed end of the ____________________ is enlarged and cup-shaped and completely surrounds the glomerulus. Glomerulus A specialized ____________________ bed Attached to arterioles on both sides (maintains high pressure) ____________________ afferent arteriole Narrow efferent arteriole Glomerulus Capillaries are covered with ____________________ from the renal tubule Podocytes form a porous, membrane around the glomerulus The glomerulus sits ____________________ a glomerular capsule (the first part of the renal tubule) Renal Tubule Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of ____________________ Distal convoluted tubule Types of Nephrons Cortical nephrons Located entirely in the ____________________ Includes most nephrons Juxtamedullary nephrons Found at the ____________________ of the cortex and medulla Glomerulus Capillaries Each nephron is associated with ____________________ capillary beds, glomerulus and peritubular. Glomerulus Unlike any other capillary in the body Fed and ____________________ by arterioles High-resistance vessels Blood pressure is very ____________________ High Pressure Forces fluid and solutes out of blood ____________________ is reclaimed and returned to blood Peritubular Capillaries Arise from ____________________ arteriole of the glomerulus Normal, ____________________ pressure capillaries Attached to a venule Cling close to the renal tubule Reabsorb (reclaim) some substances from ____________________ tubes 15.1.4 - Describe the process of urine formation, identifying the areas of the nephron that are responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Urine Formation Processes ____________________ Reabsorption Secretion Filtration Nonselective ____________________ process Water and solutes smaller than proteins are forced through ____________________ walls Blood cells cannot pass out to the capillaries Filtrate is collected in the glomerular capsule and leaves via the renal tubule Reabsorption The peritubular capillaries reabsorb several materials Some water ____________________ Amino acids Ions (ex _____________________________ ) Some reabsorption is passive, most is active Most reabsorption occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule Materials Not Reabsorbed Nitrogenous waste products Urea ____________________ Creatinine Excess water Secretion – Reabsorption in Reverse Some materials move from the peritubular capillaries into the renal tubules ____________________ and potassium ions Creatinine Materials left in the renal tubule move toward the ____________________ 15.1.8 Describe the composition of normal urine. Characteristics of Urine Used for Medical Diagnosis Colored somewhat yellow due to the pigment urochrome (from the destruction of ________________) and solutes _________________ Slightly aromatic Normal pH of around ______________ Specific gravity of 1.001 to 1.035 15.2.1 - Describe the general structure and function of the ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the ______________ Continuous with the renal _____________ Enter the posterior aspect of the bladder Runs behind the peritoneum _______________ aids gravity in urine transport Urinary Bladder ________________ , collapsible, muscular sac Temporarily stores urine ____________ – three openings Triangular passageway Very sensitive to _________ Two from the ureters One to the urethrea Urinary Bladder Wall ____________ layers of smooth muscle (detrusor muscle) Mucosa made of transitional epithelium Walls are thick and folded in an empty bladder Bladder can expand significantly without increasing internal _______________ Urethra Thin-walled tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body by peristalsis Release of urine is controlled by two _______________ Internal urethral sphincter (involuntary) External urethral sphincter ( ________________ ) 15.2.2 - Compare the course and length of the male urethra to that of the female. Urethra Gender Differences Length ____________ – 3–4 cm (1 inch) Males – 20 cm (8 inches) Location Females – along _________ of the vagina Males – through the ____________ and penis Function Females – only carries urine Males – carries urine and is a passageway for _____________ cells Micturition (Voiding) __________ sphincter muscles must open to allow voiding The internal urethral sphincter is relaxed after __________ of the bladder Activation is from an impulse sent to the ______________ and then back via the pelvic splanchnic nerves The external urethral sphincter must be voluntarily ____________