Japanese Literacy
advertisement

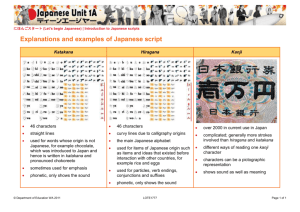
S e c o n d G r a d e C u r r i c u l u m — 2 0 1 4 Japanese Literacy We expect students coming into Second Grade to be able to do the following: Recognize Hiragana letters (names and sounds) Write Hiragana letters Read First Grade high -frequency words in the target language Read a First Grade text fluently Quarter 1 (Main Idea/ Sequences) Review Hiragana alphabet , Japanese phonetics Katakana Recognition Review Start handwriting of Katakana Theme: Back to School/All about me Reading Theme: Mom, get well with salad (Fiction) Grammar (Nouns, Verbs, Sequence of writing, Transition words ) Quarter 2 (Compare/ Contrast, Drawing Conclusions) Continue Katakana recognition and writing The concept of Kanji Reading Theme: Various ships (Non-fiction, Fact) Japanese phonetics Grammar (Particles, Nouns, Verbs, A djectives) Writing workshop Quarter 3 (Opinion, Cause & Effect) Katakana word writing Kanji recognition Reading Theme: My little brother, Chiro (Fiction) Japanese phonetics Grammar (Past tense, Cause & Effect words ) Writing workshop Quarter 4 (Classifying) Continue Katakana word writing Kanji recognition & writing Reading Theme: My Discovery (Non-fiction, Fact) Grammar (Sentences with more various details) Writing workshop S e c o n d G r a d e C u r r i c u l u m — 2 0 1 4 We use a variety of the following methods to help students acquire the target language: Songs or poems are used for themes and/or holidays studied. Music is a great tool to help all of us remember things. Games (bingo, puzzles, skits, cheers, Total Physical Response) are also helpful as students get to interact with others i n the target language. Picture walks—looking at the only drawings before we actually read the text—are used. This allows students to become acquainted with the theme before focusing on the decoding and reading of new vocabulary. The more students have knowledge and command of the spoken language, the easier they can read and write the written language. Listening centers where students can hear recorded text (studied themes, spelling words, poems) and follow along in the written text help improve their com prehension. Stories are beneficial as they help students observe drawings, listen to text that is read, and follow a story line from beginning to end. Visuals (drawings, photos, internet websites, real objects, graphic organizers) are a necessity to help s tudents relate the word with the object or idea itself. Children’s films are often available in the target language and can come in handy. Technologies such as computer, smart interactive board, i -Pad and etc are used for any aspects of their literacy lear ning.