The Thorax [8-31
advertisement

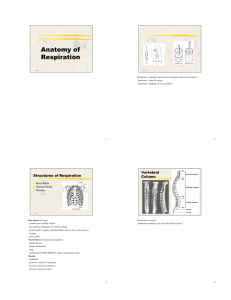
The Thorax Compartments: these compartments are completely separate from one another Compartment Right Pleural Cavity Boundaries Right root of neck (slightly above rib 1—therefore abnormal events in neck can affect it), right thoracic wall, mediastinum, diaphragm. It extends to rib 8 in the midclav. line and to rib 10 in the mid ax. line, crossing ribs 11 and 12 to reach T12 Sternum to thoracic vertebrae (A to P), and from the superior thoracic aperture to the inferior (S to I) Mediastinum T4/5 separates superior and inferior parts. The pericardium separates it into ant, post, and med parts Left root of neck (slightly above rib 1), left thoracic wall, mediastinum, diaphragm Left Pleural Cavity Contents Right lung and its recesses (costodiaphragmatic and costomediastinal recesses), right hilum and lung root, serous fluid in pleural cavity Heart, thymus, esophagus, trachea, major nerves (phrenic, vagus), and major systemic blood vessels (aorta, vena cavae, pulmonary arteries and veins, azygos vein), and thoracic duct Left lung and its recesses (costodiaphragmatic and It extends to rib 8 costomediastinal in the midclav. recesses), left hilum line and to rib 10 and lung root, in the mid ax. line, serous fluid in Description Clinical Points Double sided mesothelial membranes (pleura) with parietal and visceral layers Recesses allow accumulation and aspiration of fluids (hemothorax, pheumothorax, thoracocentesis Thick, flexible, soft tissue partition sitting longitudinally in the median sagittal position Double sided mesothelial membranes (pleura) with parietal and visceral layers Pericarditis (inflammation if the pericardium), Constrictive Pericarditis (look for Kussmaul’s sign), Pericardial effusion (excess fluid in the pericardial space) leading to Cardiac Tamponade, Pericardiocentesis Left lung is smaller to accommodate the heart (cardiac notch) crossing ribs 11 pleural cavity and 12 to reach T12 Bones of the Thorax: Vertebrae, discs, ribs, and sternum Bone (group) Thoracic Vertebrae True Ribs False and Floating Ribs Sternum Structures/Parts Bodies, spinous processes, pedicles, lamina, transverse processes, sup. And inf. articular processes Head (2 articular facets separated by a crest), neck, tubercle( rib 1 has scalene tubercle), angle, costal groove, costal cartilage Interchondral joints attach ribs to eachother in the anterior wall (7-10) Manubrium (jugular notch), body (transverse ridges from sternbrae), and xiphoid process Number 12 Ribs 1-7 Ribs 8-12 (11 and 12 are floating) 3 parts Articulations Ribs: superior (own rib) and inferior (rib below) costal demifacets, transverse costal facet (own rib) Exceptions: T1, T10-T12 Clinical Issues Disc protrusions, vertebral fractures and displacements T1-7 (costotransverse and with vertebral body), articulate directly with sternum Flail chest, cervical ribs (thoracic outlet syndromestress on brachial plexus and subclavian vessels) 8-10 articulate with T 8-10 and costal cartilage of the true ribs 11-12 only articulate with T11 and T12 Manubrium with clavicle and ribs 1 and 2, body with ribs 2-7, xiphoid with rib 7 Bone marrow samples Sternal angle used for reference to find T4/T5 level and 2nd rib Important Nerves: Nerve Vagus Phrenic Innervation Lung (parasympathetic: constricts bronchioles), visceral pleura, esophagus, stomach, cardiac plexus supplies heart, recurrent laryngeal nerve goes to larynx The entire Diaphragm, and the fibrous and parietal pericardium Breast (anterior and lateral cutaneous branches of Intercostals Spinal Nerves T1 to L2 the 2nd to 6th), Intercostal muscles, subcostales, transverses thoracis, dermatomes of thorax (4th: nipples, 10th: umbilicus, 12th: ASIS) and parietal pleura All preganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers (sympathetic system dilates the bronchioles. Greater, lesser and least splanchnic nerves branch from the lower 7 ganglia and supply the viscera of the abdomen and pelvis Muscles of the Thorax: Muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Subclavius External Intercostals Internal Intercostals Innermost Intercostals Attachments Medial clavical, sternum, and costal cartilages to lateral lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus anterior surface of ribs 3-5 to the coracoid process Anterior and medial aspect of rib 1 to the inferior clavicle Inferior margin of rib above to superior margin of rib below Lateral edge of costal groove of rib above to superior margin of rib below, deep to ext. intercostal Medial edge of costal groove of rib above to internal aspect of superior margin of rib below Internal surface Innervation Action Clinical Issues Medial and Lateral Pectoral nerves Flexes, adducts, and medially rotates the arm Directly underlies the breast, forms anterior wall of axilla Medial Pectoral nerve Pull tip of shoulder inferiorly Nerve to subclavius (C5, C6) Pull tip of shoulder inferiorly Intercostal Nerves (T1-T11) Most active during inspiration, moves ribs superiorly Intercostal Nerves (T1-T11) Most active during expiration, moves ribs inferiorly Intercostal Nerves (T1-T11) Act with internal intercostals Enclosed by clavipectoral fascia, forms anterior wall of axilla Enclosed by clavipectoral fascia, forms anterior wall of axilla Thoracotomy (incision through intercostal space), chest tubes Thoracotomy (incision through intercostal space), chest tubes Intercostal veins, arteries, and nerves run between this layer of muscle and the int. intercostals along inf. rib edge Subcostales Transversus thoracis near angle of lower ribs to internal surface of 2nd or 3rd rib below Int. surfaces of c. cartilages of 2nd to 6th ribs to deep sternum, xiphoid process and c. cartilages ribs 4-7 Related intercostal nerves May depress ribs Related intercostal nerves Depresses costal cartilages Secure the internal thoracic vessels to the anterior chest wall The Diaphragm Attachments The diaphragm attaches peripherally to the xiphoid process, costal margin of the thoracic wall, ends of ribs 11 and 12, vertebrae of lumbar region, and ligaments that span the posterior abdominal wall and the fibers converge to form the central tendon Innervation Right and Left Phrenic nerves (C3, C4, C5) Action Clinical Significance Contraction of the diaphragm flattens its structure and increases thoracic volume, essential to normal inspiration Structures passing through the diaphragm: aorta (T12), Thoracic duct (T12), Azygos and hemiazygos veins (T12), Inferior vena cava (T8), esophagus (T10), vagus nerve (T10) The Lungs: Right Lung Left Lung Features 3 lobes separated by the oblique and horizontal fissures, hilum and pulmonary ligament 2 lobes separated by the oblique fissure, cardiac notch and lingual to accommodate the heart, hilum Related Structures Heart, inferior vena cava, superior vena cava, azygos vein, esophagus Heart, aortic arch, thoracic aorta, esophagus Root Contents Right pulmonary artery, right pulmonary veins, right main bronchus, bronchial vessels, nerves, lymphatics Left pulmonary artery, left pulmonary veins, left main bronchus, bronchial vessels, Clinical Issues Right lung is more likely to receive aspirated objects because the right primary bronchus is wider, shorter, and more vertical Lung cancer, chest wounds, pneumothorax, hemothorax, pneumonia and pulmonary ligament nerves, lymphatics The Heart: Chamber Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle Features Forms right border of heart, receives blood from venae cavae and coronary sinus, Crista terminalis, right auricle, interatrial septum with fossa ovalis Forms most of anterior surface, receives blood from the right atrium, infundibulum, papillary muscles, trabeculae carneae, chordate tendineae, moderator band (carries right bundle branch) Forms most of base of heart, receives the 4 pulmonary veins, interatrial septum with fossa ovale, left auricle, Forms the apex, and contributes to the anterior surface, has fine and delicate trabeculae carneae, anterior and posterior papillary muscles, Interventricular septum (membranous and muscular) Membranous aspect of septum is most common site of VSDs Valves Right AV valve (tricuspid) delivers blood to right ventricle Right AV valve (tricuspid), Pulmonary Semilunar Valve delivers blood to pulmonary trunk Left AV Valve (Mitral Valve)delivers blood to left ventricle Left AV Valve (Mitral Valve) Aortic Semilunar Valve delivers blood to aorta and coronary arteries (right and left) Clinical Significance Contains SA node Valve disease usually caused by infection Valve disease usually caused by infection Mitral Valve Disease (stenosis and regurgitation) leads to hypertrophy of left ventricle and atrium Thickest walled chamber Mitral Valve Disease leads to hypertrophy of left ventricle and atrium Mitral is Most commonly diseased! Coronary Vasculature: The Coronary Arteries and Cardiac Veins Vessel Right Coronary Artery Left Coronary Artery Branches Sinu-atrial nodal branch, Right Marginal branch, Posterior Interventricular branch (PDA) Location Passes anteriorly and to the right between the right auricle and the pulmonary trunk and then descends vertically in the coronary sulcus Supplied Area of Heart Right atrium and right ventricle, SA and AV nodes, interatrial septum, and portions of the left atrium, IV septum, and left ventricle Anterior Interventricular branch (LAD) which gives off 1 or 2 Diagonal Branches Passes between pulmonary trunk and the left auricle before Most of the Left atrium and ventricle and the IV septum (including the entering the coronary sulcus Circumflex Branch which gives off the Left Marginal Branch An enlargement of the Great Cardiac Vein Coronary Sinus Great Cardiac Vein Middle Cardiac Vein Small Cardiac Vein Posterior Cardiac Vein Posterior coronary sulcus Begins at apex of the heart, ascends in the anterior interventricular sulcus, then the coronary sulcus where it turns left onto the base of the heart and enlarges to form the coronary sinus Begins at apex of heart and ascends in the posterior interventricular sulcus to the coronary sinus Begins in the lower anterior coronary sulcus between the right atrium and ventricle and goes to coronary sinus Lies on the posterior surface of the left ventricle and shunts to coronary sinus or great cardiac vein bundle of His and its branches) Receives four main tributaries (great, middle, small, and posterior) drains into the right atrium Drains the anterior apex of the heart Drains the posterior apex of the heart Drains inferior right portion of heart Drains posterior left ventricle Autonomic Nervous System: Monitor and regulate function and blood flow to viscera Preganglionic: inside the CNS, Postganglionic: outside of CNS Posterior Root: sensory (afferent), Anterior Root: motor (efferent) Parts/Divisions GVAs Neurons Utilized Do NOT synapse 1 cell body in sensory ganglia 2 cell bodies Signal Type Origins Sensory (receptors) Preexisting pathways (same levels as GVEs) [SAME DAVE] Locations ANS GVEs (one in CNS and one in periphery, or ganglia) Secretory and Motor (smooth muscle) Preexisting pathways (same levels as GVAs) ANS IML Fight or flight Sympathetic Motor and sensory Rest and digest Parasympathetic Motor and sensory Arise from T1-L2 (white rami)and the axons go everywhere (superficial and deep) Arise from craniosacral CNS (CNs 3,7,9,10 and S2-4) regions Paravertebral sympathetic trunk extends from base of skull to coccyx, connected to anterior rami by white (preganglionic) and gray (post ganglionic) rami communicans IML-like area in sacral region and only go deep, NOT to skin