Thorax, Pleural Cavity
advertisement

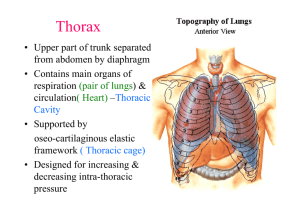
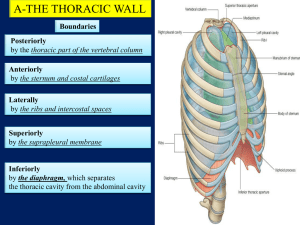
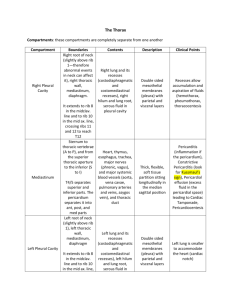
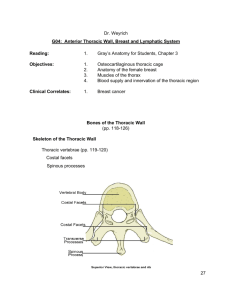
Thorax, Pleural Cavity Bones • sternum - all landmarks • 12 ribs, costal cartilages - all landmarks • 12 thoracic vertebrae - all landmarks Borders • 1. superior thoracic aperture ( thoracic inlet) - opening to neck, – superior borders of: manubrium, 1st pair ribs, costal cartilages, 1st thoracic vertebrae • 2. inferior thoracic aperture / thoracic outlet - opening to abdomen – inferior borders of: T12 vertebra; ribs 12, 11; costal cartilages #10, 9, 8, 7, xiphoid Diaphragm • muscle + fibrous connective tissue separates thoracic & abdominal cavities • domed in center Pleural sacs • a continuous serous membrane folded back on itself to form a double layer – 1. visceral pleura - inner layer - forms external surface covering of lung – 2. parietal pleura - outer layer - forms inner lining of thoracic wall – 3. both layers meet at root Pleural sacs • Pleural cavities: potential space - contains thin serous fluid layer, slight negative pressure • Regions of parietal pleura are named by surrounding structures: – cervical/apical, costal, diaphragmatic, mediastinal • Recesses: narrow clefts at edges of pleura, where lungs don't extend – costodiaphragmatic - most inferior, between costal & peripheral border of diaphragm, first place to find fluid accumulation in X-ray – costomediastinal - most anterior, medial, in front of mediastinum Thoracocentesis Mediastinum • central structures between two pleural sacs, sternum & vertebral bodies – Heart: pericardium, chambers, blood supply, pulmonary vessels, ligamentum arteriosum vagus nerve, recurrent laryngeal nerve – Trachea – Esophagus – Phrenic nerve: in mediastinal pleura -- to pericardium Blood Vessels • Intercostal arteries - anterior & posterior, + subcostal (12th) • 1st and 2nd posterior intercostal artery branch off supreme (superior) intercostal artery, which branches off costocervical trunk of subclavian artery • 3d - 11th posterior intercostal, & subcostal artery - are branches of thoracic aorta Blood Vessels • 1st- 5th (or 6th) anterior intercostal artery: = branches of internal thoracic artery • 6th (or 7th) - 9th anterior intercostal arteries are branches of musculophrenic artery - anterior & posterior intercostal arteries terminate by anastomosing with each other • There are no anterior intercostal arteries in the most inferior two intercostal spaces. These areas are provided by posterior intecostal arteries only. Blood Vessels • internal thoracic artery (branch of subclavian): divides behind #6 costal cartilage: – a. superior epigastric artery – b. musculophrenic artery Nerves • Intercostal nerves = ventral rami of thoracic nerves 1-11 – to intercostal muscle, skin – travel in costal grooves, between internal & innermost intercostal muscle. Herpes Zoster • Shingles • Viral infection of Chicken pox virus • Affect along intercostal nerve Muscles • • • • • External intercostalis Internal intercostalis Innermost intercostalis Subcostalis Transversus thoracis External intercostalis • ORIGIN Inferior border of ribs as far back as posterior angles • INSERTION Superior border of ribs below, passing obliquely downwards and backward • ACTION Fix intercostal spaces during respiration. Aids forced inspiration by elevating ribs • NERVE Muscular collateral branches of intercostal nerves Internal intercostalis • ORIGIN Inferior border of ribs as far back as posterior angles • INSERTION Superior border of ribs below , passing obliquely downwards and backwards • ACTION Fix intercostal spaces during espiration. Aids forced inspiration by elevating ribs • NERVE Muscular collateral branches of intercostal nerves Innermost intercostalis • ORIGIN Internal aspect of ribs above and below • INSERTION Internal aspect of ribs above and below • ACTION Fix intercostal spaces during respiration • NERVE Muscular collateral branches of intercostal nerves Subcostalis • ORIGIN Internal posterior aspects of lower six ribs • INSERTION Internal aspects of ribs two to three levels below • ACTION Depresses lower ribs • NERVE Muscular collateral branches of intercostal nerves Transversus thoracis • ORIGIN Lower third of inner aspect of sternum and lower three costosternal junctions • INSERTION Second to sixth costal cartilages • ACTION Depresses upper ribs • NERVE Muscular collateral branches of intercostal nerves