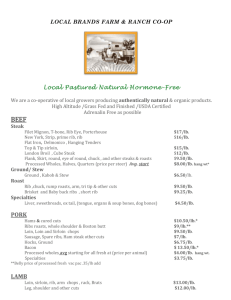
Region 10: Thoracic Wall and Cavity Thoracic Wall -
advertisement

Region 10: Thoracic Wall and Cavity Thoracic Wall --Sternum: 3 parts a. manubrium, body, and ziphoid process *manubrium and body meet at the sternal angle b. articulations *first rib articulates with manubrium below sternoclavicular articulation, usually c/n be palpated *2nd rib articulates at junction of manubrium and body at sternal angle --Ribs *first seven ribs: articulate with sternum through their costal cartilages (TRUE ribs) *5 remaining ribs are FALSE ribs and articulate with the rib above through their costal cartilage *ribs 11 and 12 d/n articulate w/ anything anteriorly (FLOATING ribs) *Articulations with the Sternum a. 1st rib articulates via primary cartilaginous joint b. 2-10th articulates via synovial joints *costal cartilages of ribs 7-12 form costal margin *first rib: shortest, broadest, most curved a. superior surface of its body has scalene tubercle bounded by groove for subclavian vein anteriorly and groove for subclavian artery posteriorly *Parts of the Rib a. Head of rib: part of the rib articulating with the body of vertebrae b. neck of the rib: joins the body of the rib c. junction of the neck and body of the rib there is a tubercle that articulates with TPs d. typical ribs have an angle distal to tubercles that correspond to most posterior aspect of thoracic cavity *lower border of typical ribs is groove that contains intercostal VAN *jugular notch: at top of sternums, horizontal plane passes through IVD b/w T2 and T3 *sternal angle: horizontal plance passes through IVD b/w T4 and T5 --Thoracic Vertebrae *posteriorly the ribs articulate with vertebrae, usually with body and TP a. first rib articulates with upper part of body of T1 near pedicle b. head of 2nd rib articulates with lower part of body of T1, the disc b/w T1 and T2, and upper part of body of T2//its tubercle articulates with TP of T2 c. ribs 3-10 have similar articulates with their vertebrae d. ribs 11 and 12 usually only articulate with their corresponding vertebrae --Intercostal Spaces *External Intercostal Muscle O: lower border of the rib above Act: stabilizes the ribs and aids in inspiration Not: terminates anteriorly as anterior intercostal membrane which can be considered to be a continuation of the epimysium of the muscle *Internal Intercostal Muscle O: upper border of rib below Act: aids in expiration Not: ends posteriorly as posterior intercostal membrane *Innermost Intercostal Muscle Not: those fibers of internal intercostal muscle separated apart from itself by intercostal nerve and vessels *Transversus Thoracis Muscle a. thin muscle on inner surface of ventral chest wall *Levatores costarum a. 12 pairs in number *Intercostal Nerves a. exit intervetebral foramina pass to inferior surface of neck of corresponding rib runs under the rib b. bulk of anterior primary ramus of T1 goes over 1st rib to contribute to brachial plexus (small first intercostal nerve supplies intercostal muscles in 1st intercostal space) c. anterior primary ramus of T2 is nearly identical (lateral cutaneous branch becomes intercostobrachial nerve) d. anterior primary rami of T3-T11 are typical nerves *Intercostal spaces a. posterior intercostal arteries --1st and 2nd intercostal spaces receive BS from highest/supreme intercostal branch of costocervical trunk of subclavian a. --remaining interspaces receive BS directly from aorta b. anterior intercostal arteries --first 5-6 interspaces receive BS from internal thoracic branch of subclavian a. --remaining interspaces receive BS from musculophrenic branch of internal thoracic a. *Intercostal Veins: accompany arteries a. posterior intercostal veins: drain azygos system of veins --Superior thoracic aperture bounded by: *first thoracic vertebrae *first pair of ribs *top of sternum --Inferior thoracic aperture bounded by: *T12 *12th rib *anterior extremities of 11th and 12th ribs *costal cartilages of 7-10 ribs and xiphoid process Mediastinum --Structures making up the mediastinum: a. thymus b. heart and its pericardium c. great vessels d. trachea and primary bronchi e. esophagus f. nerves and lymphatics Lungs and Pleura --Lungs *enclosed in double layer of pleura a. inner layer: visceral pleura b. outer layer: parietal pleura *pleural cavity: serous, potential space b/w parietal and visceral pleura *parietal pleura: consists of portions (cervical/cupula) *Reflections of the parietal pleura a. costomediastinal reflection: contains costomediastinal recess b. costodiaphragmatic reflection: junction of costal and diaphragmatic portions, contains costodiaphragmatic recess c. reflections of 2 parietal pleura: left reflection diverges laterally at rib 4 and becomes cardiac notch *parietal and visceral pleurae are continuous at root of the lung and pulmonary ligament Mediastinum --thick partition of tissue and structures b/w the lungs --extends from superior thoracic aperture --horizontal plane extending through the sternal angle anteriorly and b/w the disc of T4 and T5 divides mediastinum into superior and inferior mediastinum --inferior mediastinum is further divided into: anterior, middle, and posterior --Contents of Superior mediastinum a. Thymus *BS: pericardiophrenic vessels b. brachiocephalic veins and superior vena cava *brachiocephalic veins are formed by confluences of the subclavin and internal jugular veins *superior vena cava: just before it enters the pericardial sac, it receives azygos vein c. aortic arch (and its branches) *arches backwards over left primary bronchus *ligamentum arteriosus (obliterated ductus arteriosus) connects the inferior surface of arch to left pulmonary artery *brachicephalic trunk: first brach of the arch, ends by dividing into R subclavian and R common carotid aa. *L common carotid and L subclavian arise independently from arch d. trachea: behind great vessels and immediately anterior to esophagus e. Esophagus: most posterior structure f. thoracic duct *above T6, lies on left side of vertebral column *arches over left subclavian a. from behind to reach the left subclavian vein at its junction with internal jugular vein g. phrenic nerves: pass anterior to both subclavian aa. and roots of lungs h. vagus nerves: pass anterior to subclavian aa. but posterior to root of the lungs *right recurrent laryngeal nerve: passes under R subclavian a. ascends to larynx *left recurrent laryngeal nerve: passes under aortic arch immediately to left of ligamentum arteriosum to ascend to larynx --Contents of Anterior mediastinum a. fat and connective tissue --Contents of Middle Mediastinum a. pericardial sac and the heart b. parietal pericardium consists of: *fibrous outer layer *inner serous layer c. pericardium fused to the diaphragm d. parietal pericardium continuous with visceral pericardium/epicardium e. b/w visceral and parietal layers is pericardial cavity Pericardium --Pericardial Sac a. fibrous pericardium: stout external layer b. serous pericardium *parietal *visceral: covers the heart itself (also called epicardium) --Reflections of the Pericardium a. Transverse pericardial sinus: space posterior to both the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk but anterior to superior vena cava b. oblique pericardial sinus: blind recess on the posterior aspect of the heart formed by pericardial reflections off the pulmonary veins and inferior vena cava




![The Breathing System Key Terms [PDF Document]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008697551_1-df641dd95795d55944410476388f877c-300x300.png)