strong electrolytes
advertisement

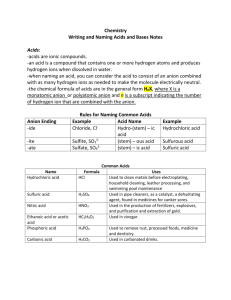
Name ____________________________________________ Date _________________________ Period__ Sample Problems for Chapter 14: Acids and Bases 14.1 Acids and Bases 1. (Read pgs. 442-446 in the chemistry textbook) (a) What does it mean to say a solid substance has dissolved in water? (b) What does it mean for a chemical to dissociate (ionize) in aqueous solution? 2. (a) What is an electrolyte? b) What are strong electrolytes? (c) What are weak electrolytes? (d) what is a nonelectrolyte? 1 3. (a) Fill in the following table of electrolytes: Summary of Electrolytic Behavior of Common Soluble Ionic and Molecular Compounds Compound Strong Electrolyte Weak Electrolyte Nonelectrolyte Ionic Molecular (b) What happens if an ionic substance is insoluble in water? 4. Identify each of the following as a strong, weak, or nonelectrolyte based on their chemical formulas. i. CO2 vi. NH4CH3COOH ii. KNO3 vii. LiBr iii. C2H6 viii. XeF2 iv. Mg(OH)2 ix. PbSO4 v. NaCl x. Ca3(PO4)2 5. Identify the non-, strong, and weak electrolytic solutions below. Explain your choices. 2 6. (a) What is the hydronium ion? (b) What is the symbol for the hydronium ion? 7. (a) What is the hydroxide ion? (b) What is the symbol for the hydroxide ion? 8. What is an acid? 9. What is a base? 10. The table of electrolytes from Question 3(a) identifies strong acids as strong electrolytes. What are the strong acids? 3 11. Write a dissociation equation for the following strong and weak acids. STRONG ACIDS: (a) HCl(aq) (b) HNO3(aq) (c) H2SO4(aq) WEAK ACIDS: (a) HF(aq) (b) HNO2(aq) (c) H2SO3(aq) 12. All the strong bases are ionic compounds and, therefore, strong electrolytes. What are the strong bases? 4 13. Write a dissociation equation for the following strong and weak Bases. STRONG BASES: (a) LiOH(s) (b) Ca(OH)2(s) WEAK BASES: (a) Mg(OH)2(s) (b) Sr(OH)3(s) 14. The ammonium polyatomic ion, NH4+(aq), dissociates weakly to increase the [H+] in aqueous solution. Write an equation to show the dissociation of the ammonium polyatomic ion. 15. The ammonia molecule, NH3(aq), reacts in an equilibrium reaction with water to increase the [OH−] in aqueous solution. Write an equation to show the dissociation of the ammonia molecule. 5 ACID NOMENCLATURE 16. (a) What is a binary acid? (b) How are binary acids named? 17. What are the common binary acids? 6 18. (a) What is an oxy-acids? (b) How are oxy-acids named? 19. What are the “trendsetter” oxy-acids? Polyatomic Anion Polyatomic Name Acid Name Chemical Formula 7 20. How can the “Trendsetter” oxy-acids be changed? EXAMPLE Change Made Change in Name Name Formula 21. Practice changing the name or formula of the trendsetters Acid Name a) Chemical Formula H3PO3 b) sulfurous acid c) nitrous acid d) H3PO2 e) H3CO2 f) pernitric acid g) hyposulfurous acid h) i) H2CrO3 Permanganous acid 8 PRACTICE QUESTIONS 22. Identify each of the following compounds as either and acid (A) or a base (B). a. NaOH d. H3PO4 g. HNO3 j. Cu(OH)2 b. HCl e. Al(OH)3 h. Ca(OH)2 k. Ba(OH)2 c. HCN f. KOH i. LiOH l. HI 23. Write dissociation equations for each of the following acids or bases. Keep in mind whether or not it is a strong or weak electrolyte. a) barium hydroxide b) nitrous acid c) aluminum hydroxide d) lead (IV) hydroxide e) calcium hydroxide f) lithium hydroxide g) chloric acid h) copper (II) hydroxide 9 24. Name each of the following as an acid (A) or a base (B): a. hydrochloric e. sulfurous j. potassium hydroxide b. calcium hydroxide f. lithium hydroxide k. ammonium c. carbonic h. aluminum hydroxide l. ammonia d. nitric i. hydrobromic 25. Write chemical formulas for each of the following and classify each as an acid (A) or a base (B): Chemical Formula Acid/ Base a) magnesium hydroxide b) hydrofluoric c) nitric acid d) lithium hydroxide e) ammonium hydroxide f) chromic acid g) barium hydroxide 26. Write the chemical formula for each of the following and then identify each of the following as a strong electrolyte (SE), weak electrolyte (WE), or nonelecrtrolyte (NE). The solubility chart would be helpful! Chemical Formula Electrolyte (a) potassium hydroxide (b) sodium carbonate (c) silver chloride (d) dinitrogen pentoxide 10