This is not an all-inclusive list of what will be on the test. This is
advertisement

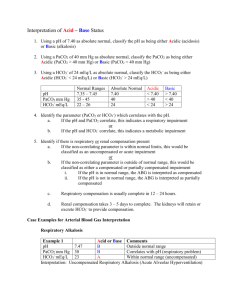
Metropolitan Community College NURS 2140 Final Review Fall 2013 Concepts I Would Review Types of burns - Thermal, scald, electrical, radiation, chemical, inhalation Shock syndromes Rule of Nines Nursing management of shock Burn depth - First, second, third/fourth degree MODS Fluid resuscitation for clients with burns Labs used in the evaluation of fluid status Pain management for clients with burns Overhydration Nursing care in each phase of burn treatment Dehydration SIRS Electrolyte imbalances Four categories of acid/base abnormalities Role of the lungs in acid/base balance Hypercarbic drive Role of the kidneys in acid/base balance Hypoxic drive Interpreting ABGs Complications of infusion therapy Central lines PICC lines Implanted ports Adventitious breath sounds Lower airway disorders Airway obstruction Intubation Tracheostomy Mechanical ventilation *This is not an all-inclusive list of what will be on the test. This is however, a great place to start studying.* Normal pH – 7.35-7.45, PaCO2 – 35-45, HCO3 – 22-28 Uncompensated Phase – 2 abnormal, one still normal pH Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory Alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic Alkalosis PaCo2 HCO3 Normal Normal Normal Normal Partially Compensated – All three are abnormal pH PaCo2 HCO3 PaCo2 HCO3 Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory Alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic Alkalosis Fully Compensated Phase – pH is normal Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory Alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic Alkalosis pH Normal Normal Normal Normal 1. The nurse is caring for a client with 3rd degree burn injuries over 45% of his body. The client’s wife asks the nurse “Why does he need those intravenous fluids?” What is the best response by the nurse? A. B. C. D. So he can receive his antibiotics So we can be sure he keeps enough blood volume So we have an open line in case his heart stops So we can rapidly administer his pain medications 2. The client has been running in a long-distance marathon on a very warm day. The client complains of dizziness and nausea. She is taken to the hospital where she becomes lethargic. The serum sodium level is 125 mEq/L. What will be the best plan for this client? A. B. C. D. Administer normal saline IV Administer 0.45% NaCl Encourage the client to drink fluids Provide a diet high in sodium 3. When planning care for a client with a partial airway obstruction, which nursing intervention has the greatest priority? A. B. C. D. Ensuring advanced airway equipment is at the bedside Ensuring the resuscitation team is on standby Keeping the client calm and relaxed Providing pain medication around the clock 4. A client diagnosed with active tuberculosis is in a negative pressure room for respiratory airborne isolation. How long should the nurse maintain the client in this type of isolation? A. B. C. D. Until the Mantoux test converts from positive to negative Until the client has orders for discharge Until the chest x-ray is normal Until three consecutive sputum specimens for acid fast bacilli are negative 5. The nurse is caring for a client who was admitted in respiratory distress. What is the nurse’s priority action based on this ABG: pH: 7.32, PaCO2: 52, HCO3: 20 A. B. C. D. Document and continue to monitor Place the client on oxygen via mask Call the healthcare provider to report the results Suction the client using a yankeur 6. During the immediate postburn period, the nurse assesses the client for injuries other than burns. Which of the following assessments indicates a potential problem? A. Urine output of 30ml/hour B. Presence of eschar C. Presence of edema D. Coughing 7. The nurse is caring for a client with papillary muscle rupture. When assessing the client, the nurse is alert to the development of symptoms related to _________ shock? A. B. C. D. Septic Anaphylactic Cardiogenic Neurogenic 8. The family of a client in shock asks why the client’s hands are cold. The nurse’s best response is which of the following? A. “Blood vessels constrict in shock, which takes blood away from the hands and feet” B. “We keep the intensive care unit cool to reduce clients’ metabolic rate” C. “Your family member has developed a fever and chills” D. “This happens frequently to clients in shock states” 9. While flushing a central vascular access device, the nurse meets resistance. The nurse should: A. B. C. D. Apply force to the syringe Report the findings to the physician Check the clamp on the catheter Pull the catheter back slightly 10. When caring for a group of patients, which of the following individuals is at risk for metabolic alkalosis? A. B. C. D. A patient with bulimia A patient undergoing dialysis A patient with a venous stasis ulcer A patient with COPD Answers 1. B Rationale: Clients with burn injuries lose a great deal of fluid from the injured area. A net loss of fluids from the body can result in dehydration and shock. IV fluid therapy is used to maintain blood volume and support blood pressure. 2. A Rationale: The client is experiencing hyponatremia with lethargy. She needs an isotonic IV fluid. Oral intake of fluid and food is contraindicated due to her altered mental status. 0.45% NaCl is hypotonic and will further lower her sodium level. 3. A Rationale: Whenever a client has the potential to quickly lose the airway, advanced airway tools such as intubation equipment and tracheotomy supplies should always remain at the bedside. The resuscitation team, keeping the client calm, and providing pain medication are needed, but maintaining the airway is priority. 4. D Rationale: The client should remain in isolation until three consecutive sputum cultures have tested negative. Until that time and in spite of treatment, there is no certainty that the client is not infectious. A positive PPD indicates that an individual has been exposed to tuberculosis and has developed antibodies, so the PPD will not convert back to negative. The chest x-ray validates the amount of lung involvement; the client may experience chronic changes, such as nodules. The client should not be discharged without evidence that he or she is no longer infectious. 5. B Rationale: In blood gases, normal pH: 7.35−7.45; normal PaCO2: 34−45 mmHg; normal HCO3: 22−26 mEq/L; so respiratory acidosis occurs when the pH drops below 7.35, the PaCO2 is >45 mmHg, and the HCO3 is < 22 mmHg. Thus, this client requires oxygen. Once placed, the nurse can report the results. Suctioning is not indicated. The nurse should continue to document and monitor, but not until the patient has been placed on oxygen. 6. D Rationale: Coughing could indicate either an inhalation injury or a cold. Urine output of 30 ml/hour is a normal finding. The presence of eschar and edema are normal manifestations of burn injuries. 7. C Rationale: The papillary muscle holds the valves in place and may be damaged during MI, the most common reason for cardiogenic shock. Anaphylactic shock develops from hypersensitivity reactions. Neurogenic shock results from spinal cord injury or vasodilatation below the level of spinal anesthesia, and septic shock results from overwhelming infection. 8. A Rationale: Vasoconstriction results from catecholamine release, which is a compensatory mechanism in shock. Cooling measures are used in shock for fever; the ICU is not purposefully chilled. There is no indication that the client has developed fever and chills. Stating that cold hands happen frequently does not answer the family member’s question. 9. C Rationale: The nurse would check the clamp on the catheter because the catheter is clamped when not in use; unclamping the catheter is necessary to initiate flushing of the catheter. Applying force to the syringe could result in damage to the catheter or could dislodge a clot. Pulling the catheter back could result in misplacement of the catheter in the vena cava. The physician should not be called unless an occlusion is certain. 10. A Rationale: Metabolic alkalosis is caused by vomiting, diuretic therapy, or NG suction, among others. A bulimic client may engage in vomiting or indiscriminate use of diuretics. A client undergoing dialysis has kidney failure, which causes metabolic acidosis. A venous stasis ulcer does not result in an acid−base disorder. The client with COPD typically has hypercapnea and respiratory acidosis.