ABG`s
advertisement

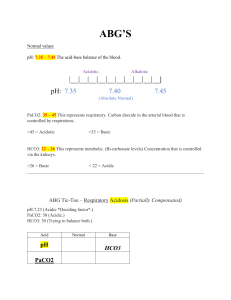
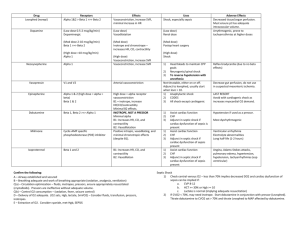
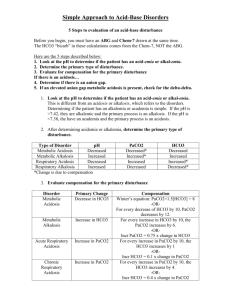
ABG’s • • • • • Indications Technique Complications Analysis Summary Indications • • • • Respiratory illness Critical illness Unwell patients Other circumstances Technique • • • • • • • • Right pt? Any artery : commonly radial Allens test Preparation pre test Monitoring Caution Don’t loose it Arterial lines and monitoring of IABP Complications • • • • • Bleeding Bruising Thrombosis AV fistula Complication of arterial lines Analysis • • • • • • • • pH PaCO2 PaO2 HCO3 O2 sats Electrolytes Lactate Hb, Meth Hb, Carboxy Hb Normal values • • • • • • pH: 7.35 – 7.45 PaCO2: 4.7 – 6 kPa PaO2: 11 – 13 kPa HCO3: 22 – 26 mEq/L Lactate: <2 O2 sats: >96% Step wise analysis • What is the pH? • Normal: 7.35 – 7.45 • Acidosis: < 7.35( more acid ie H+) • Alkalosis: > 7.45( less acid ie H+) What is the PaCO2 • Normal: 4.7 – 6.0 • Hypercapnoea: > 6 ( more CO2) • Hypocapnoea: < 4.7( less CO2) What is PaO2 • Normal? • High: > 13 on room air • Low: < 11 on room air What is the HCO3 • Normal: 22 – 26 • Low: < 22 • High: > 26 Is it metabolic or respiratory? Acidosis Respiratory pH PaCO2 Acidosis Metabolic pH PaCO2 Alkalosis Respiratory pH PaCO2 Alkalosis Metabolic pH PaCO2 Is there compensation? • Respiratory pathology the compensation is renal • Renal pathology the compensation is respiratory Is there compensation? Disorder pH Primary problem Compensation Metabolic acidosis in HCO3 in PaCO2 Metabolic alkalosis in HCO3 in PaCO2 Respiratory acidosis in PaCO2 in HCO3 Respiratory alkalosis in PaCO2 in HCO3 Anion gap • • • • Na – ( Cl+HCO3) Normal 12 Metabolic acidosis with normal anion gap Metabolic acidosis with increased anion gap Respiratory acidosis • • • • • • Airway obstruction - Upper - Lower: COPD, asthma CNS depression Sleep disordered breathing Neuromuscular impairment Ventilatory restriction Increased CO2 production: shivering, rigors, seizures, malignant hyperthermia, hypermetabolism • Incorrect mechanical ventilation settings Respiratory alkalosis • CNS stimulation: fever, pain, fear, anxiety, CVA, cerebral edema, CNS infection • Hypoxemia or hypoxia: lung disease, profound anemia, low FiO2 • Stimulation of chest receptors: pulmonary edema, pleural effusion, pneumonia, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolus • Drugs, hormones: salicylates, catecholamines, medroxyprogesterone, progestins • Pregnancy, liver disease, sepsis, hyperthyroidism • Incorrect mechanical ventilation settings Metabolic alkalosis • Hypovolemia with Cl- depletion • GI loss of H+Vomiting, gastric suction, villous adenoma, diarrhea with chloride-rich fluid • Renal loss H+Loop and thiazide diuretics • Renal loss of H+: edematous states (heart failure, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome), hyperaldosteronism, hypercortisolism, excess ACTH, exogenous steroids, severe hypokalemia bicarbonate administration Metabolic acidosis with elevated anion gap • • • • • • • • M U D P I L E S Metabolic acidosis with normal anion gap • GI loss of HCO3-Diarrhoea, ileostomy, proximal colostomy • Renal loss of HCO3-proximal RTA • carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (acetazolamide) • Renal tubular disease, ATN, Chronic renal disease, Distal RTA, NaCl infusion Metabolic acidosis with elevated anion gap • Methanol intoxication • Uremia • Diabetic ketoacidosis, alcoholic ketoacidosis, starvation ketoacidosis • Paraldehyde toxicity • Isoniazid • Lactic acidosis • Ethanol • Salicylate intoxication ABG’s pH: 7.38 PaCO2 8.0 PaO2 8.0 HCO3 32 Sats 88 O2 2L Lac 1.5 Na 138 Cl 99 • What is the abnormality? • What might this patient have? ABG’s pH: 7.50 PaCO2 3.0 PaO2 8.0 HCO3 22 Sats 88 O2 Room air Lac 1.5 Na 138 Cl 99 • What is the abnormality? • What might this patient have? ABG’s pH: 7.50 PaCO2 3.0 PaO2 13.0 HCO3 23 Sats 98 O2 Room air Lac 1.5 Na 138 Cl 99 • What is the abnormality? • What might this patient have? ABG’s pH: 7.20 PaCO2 12 PaO2 8.0 HCO3 30 Sats 88 O2 2L Lac 1.5 Na 138 Cl 99 • What is the abnormality? • What might this patient have? ABG’s pH: 7.10 PaCO2 3.0 PaO2 12 HCO3 10 Sats 96 O2 2L Lac 1.5 Na 138 Cl 99 • What is the abnormality? • What might this patient have? • What other blood tests may you want to do? ABG’s pH: 7.10 PaCO2 6.5 PaO2 9.0 HCO3 15 Sats 96 O2 2L Lac 4.5 Na 148 Cl 94 Summary • • • • • Systematic approach in analysis of ABG’s Can help you in difficult situations Always co relate clinically Should not be abused Get slick at it Thanks