Bio 1 Unit 1 Answers
advertisement

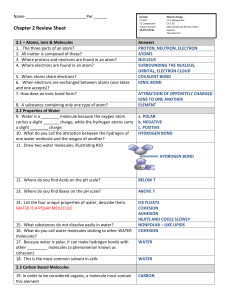
Unit 1 Test: Introduction to Biology What is Biology Objective 1.1: I can recognize some possible benefits from studying biology. What are some important reasons for studying biology? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Answer: Studying biology allows you to learn about living things around you. Biologists study the interactions of life, the interactions of the environment, the problems and propose solutions. Biologists study the diversity of life. Objective 1.2: I can summarize the characteristics of living things. List the characteristics you would check to see if a pine tree is a living thing. Give an example that shows how the tree exhibits each characteristic. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Answer: 1. Organization, 2. Homeostasis, 3. Response to a Stimulus, 4. Growth and Development, 5. Reproduction Methods of Biology Objective 1.3: I can compare different scientific methods. Use the lab procedure below to answer questions A.) and B.) A group of scientists wishes to see if using a new, environmentally friendly pesticide is effective in preventing insect damage to soybeans. Three different soybean plots are planted. The first plot contains soybeans treated with the traditional pesticide. The second plot is treated with the new environmentally friendly pesticide. The third plot is left untreated. A.) Which pot is the control group? a. the first plot with traditional pesticide b. the second plot with the new pesticide c. the third pot with no pesticide d. there is no control group Answer: C B.) What could be concluded if the plot treated with the new pesticide has damage similar to the control plot? a. The experiment is a failure. b. The new pesticide may not be effective. c. The control plot was problematic. d. The new pesticide should be used. Answer: B Describe a controlled experiment you could perform to determine whether ants are more attracted to butter or to honey. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Answer: Answers may vary. The same number of ants must be set up in the same environment, which is divided into two spaces. In one space there will be butter and there will be honey in the other. You will observe and count the number of ants that are at the butter and honey and compare. The one with the most ants is the one the ants are more attracted too. Objective 1.4: I can differentiate among hypothesis, theory, and principle. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. experimental results experiment(s) hypothesis laws scientific journals theory valid verify When (1) ___________________________ are reported in (2) ___________________________ , other scientists may try to (3) ___________________________ the results by repeating the (4) ___________________________ . Usually when a(n) (5) ___________________________ is supported by data from several scientists, it is considered (6) ___________________________ . Over time, a hypothesis that is supported by many observations and experiments becomes a (7) ___________________________ . Some well-established facts of nature, such as gravity, are recognized as (8) ___________________________ . Answer: (1) experimental results (2) scientific journals (3) verify (4) experiment(s) (5) hypothesis (6) valid (7) theory (8) laws The Nature of Biology Objective 1.5: I can compare and contrast quantitative and qualitative information. Complete the chart by checking the more correct column for each example. Example Quantitative Research Numerical data X Thermometer, balance scale, stopwatch X Measurements from controlled laboratory experiments X Purely observational data Binoculars, tape recorder, camera Qualitative Research X X Objective 1.6: I can explain why science and technology cannot solve all problems. Technology has helped increase the production of food, reduced the amount of manual labor needed to make products and raise crops, and aided in the reduction of wastes and environmental pollution. However, technology has also resulted in some serious problems. Name one way that technology has been more harmful than helpful. _____________________________________________________________________________________ Answer: Answers may vary. Harmful chemicals have entered the environment and caused contamination of water sources. Atoms and Their Interactions Objective 1.7: I can relate the structure of an atom to the identity of elements. Label the parts of the atom. Use these choices: energy level electron neutron proton nucleus If at atom has 6 protons and 6 electrons, what element is it? ________________________ carbon Answer: 7.) proton 8.) neutron 9.) energy level 10.) nucleus 11.) electron Objective 1.8: I can relate the formation of covalent and ionic chemical bonds to the stability of atoms. Complete the table by checking the correct column for each description. Statement Found in the compound NaCl Increases the stability of atoms Results in the formation of a molecule Is formed when atoms share electrons Ionic Bond(s) X Covalent Bond(s) X X X Objective 1.9: I can distinguish mixtures and solutions. This results when a multiple substances are combined, with each substance keeping its individual properties. a. A mixture d. An atom b. A solution e. A polar molecule c. An ion Answer: A Objective 1.10: I can define acids and bases and relate their importance to biological systems. Substances such as lemon and tomato, with a pH __________, are considered acidic. a. below 7 d. equal to 14 b. above 7 e. equal to 7 c. equal to 0 Answer: A Water and Diffusion Objective 1.11: I can relate water’s unique features to polarity. Define a polar molecule. ________________________________________________________________ Answer: A polar molecule is a molecule with an unequal distribution of charge. Each molecule has a positive end and a negative end. Describe two properties of water. _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Answer: (1) Water can dissolve many ionic compounds, such as salt, and many other polar molecules, such as sugar. (2) Water molecules attract other water molecules forming a weak hydrogen bond. (3) Water has capillary action where it can creep up thin tubes. (4) Water resists changes in temperature. (5) Water expands when it freezes. Objective 1.12: I can identify how the process of diffusion occurs and why it is important to cells. Define diffusion: _______________________________________________________________________ Answer: Diffusion is the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Summarize three factors that affect diffusion by describing each one in the organizers below. Answer: The more concentrated the substance, the more rapidly diffusion occurs because there are more collisions between the particles of the substances. An increase in temperature and pressure increases energy and will cause more rapid particle motion, increasing diffusion. Life Substances Objective 1.13: I can classify the variety of organic compounds. Description Made up of nucleotides Most consist of three fatty acids bonded to a glycerol molecule DNA and RNA Contain peptide bonds Produce proteins Commonly called fats and oils Made up of amino acids Used for long-term energy storage, insulation, and protective coatings Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids X X X X X X X X X Objective 1.14: I can describe how polymers are formed and broken down in organisms. Explain why carbon atoms are important in organic molecules. Include information about the kinds of bonds carbon can form. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Answer: A carbon atom has four electrons available for bonding and thus can form single, double, or triple bonds. When carbon atoms bond to each other, they can form straight chains, branched chains, or rings. The ability to bond in so many ways makes a huge number of carbon structures possible. Objective 1.15: I can compare the chemical structures of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, and relate their importance to living things. Which of the following pairs is unrelated? a. sugar – carbohydrate b. fat – lipid c. amino acid – protein d. starch – nucleic acids Answer: D Objective 1.16: I can identify the effects of enzymes. Enzymes serve as catalysts. Explain what this means. _____________________________________________________________________________________ Answer: Enzymes speed up the rate of a reaction.