Problem Set 6
advertisement

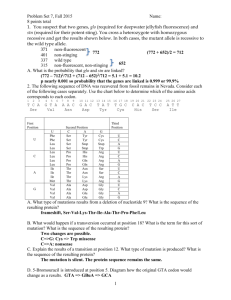
Problem Set 7, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 1. You suspect that two genes, glo (required for deepwater jellyfish fluorescence) and stn (required for their potent sting). You cross a heterozygote with homozygous recessive and get the results shown below. In both cases, the mutant allele is recessive to the wild type allele. 371 non-fluorescent 401 non-stinging 337 wild type 315 non-fluorescent, non-stinging A. What is the probability that glo and stn are linked? 2. The following sequence of DNA was recovered from fossil remains in Nevada. Consider each of the following cases separately. Use the chart below to determine which of the amino acids corresponds to each codon. 1 2 3 T C A Ser 4 5 First Position U C A G 6 G T A Val U Phe Phe Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Ile Ile Ile Met Val Val Val Val 7 8 9 A A C Asn 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 G A C Asp A T T Ile Second Position C A Ser Tyr Ser Tyr Ser Stop Ser Stop Pro His Pro His Pro Gln Pro Gln Thr Asn Thr Asn Thr Lys Thr Lys Ala Asp Ala Asp Ala Glu Ala Glu T A T Tyr T G C Cys C A C His T C C Ser Third Position G Cys Cys Stop Trp Arg Arg Arg Arg Ser Ser Arg Arg Gly Gly Gly Gly U C A G U C A G U C A G U C A G A. What type of mutations result from a deletion of nucleotide 9? What is the sequence of the resulting protein? B. What would happen if a transversion occurred at position 18? What is the term for this sort of mutation? What is the sequence of the resulting protein? C. Explain the results of a transition at position 12. What type of mutation is produced? What is the sequence of the resulting protein? D. 5-Bromouracil is introduced at position 5. Diagram how the original GTA codon would change as a results. 1 Problem Set 7, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 3. In analyzing a new compound as a suspected mutagen, you conduct the Ames test. Using strains 1 and 2, which contain a frameshift mutation or a base substitution, respectively, in a gene required for histidine biosynthesis, you find the results pictured below (all plates contain only enough histidine to permit a few cycles of cell division. A spot indicates formation of a colony of cells.) a. Why did you include strains 1 and 2 incubated without the suspected mutagen? Why are there a few colonies on each of those plates? b. Does your suspected mutagen actually function as a mutagen? If so, what type of mutagen is it? If not, why not? c. If you found only two or three colonies on each of the 4 plates using suspected mutagen that was not incubated with liver extract, what would you conclude? d. Why did you add enough histidine to permit only a few rounds of cell division? 4. A diploid strain of the unusual filamentous fungus A. farlowae is heterozygous for several genes as diagrammed. + + bt + c rd + ura gdin Mutations in c causes the colonies to be "clumpy" in appearance. Mutation in ura results colonies that can't grow without uracil added to the culture medium. bt results in colonies that cannot grow without added biotin and rd results in a reddish color. The black dot indicates the location of the centromere. The original colony was white, not clumpy and grew well on minimal plates lacking biotin or uracil. You treat cells with a mutagen and plate on minimal medium. You find colonies that display a number of phenotypes. What is the most likely explanation for each? a. Most colonies are still white and not clumpy. b. Several colonies are now red. These can be divided into two categories. i. Most of these colonies still are not clumpy. ii. Some of these colonies are now clumpy. c. Many cells simply didn't grow much. These were transferred to rich medium containing all nutrients required for growth. i. Some now grew to form colonies. ii. Some still did not grow. 2 Problem Set 7, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 5. Several Loch Ness Monsters have been captured recently, and have been subjected to careful genetic analyses. Three linked, recessive mutations were identified: tn mutants have tan body color scl mutants have large scales fla mutants have flat fins In a cross of triple heterozygous individuals (parent 1)with homozygous recessive (parent 2), you find: tan, large scales, flat fins tan, flat fins tan, large scales large scales, flat fins tan flat fins large scales all wild type 5 422 36 33 26 43 449 6 1020 total A. What is the order of the three linked genes? B. Calculate the map distances between all three pair-wise combinations of genes. tn to scl: scl to fla: fla to tn: C. What is the genotype of the two parents used in the cross? 3 Problem Set 7, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 6. Please compare the sequence at the top to each DNA sequence that appears below, and identify the type of mutation present. If it’s a substitution mutation, please identity as to whether it is a transition mutation or a transversion mutation. Starting with the ATG on the top strand, left hand side, please give the sequence of the resulting protein. 5’ATGGCATGGATAAGCTACGATCG3’ 3’TACCGTACCTATTCGATGCTAGC5’ 5’ATGGCATGAATAAGCTACGATCG3’ 3’TACCGTACTTATTCGATGCTAGC5’ 5’ATGGATGGATAAGCTACGATCG3’ 3’TACCTACCTATTCGATGCTAGC5’ 5’ATGGCATGCATAAGCTACGATCG3’ 3’TACCGTACGTATTCGATGCTAGC5’ 7. Provide the name of the mutagen, a brief description of its mode of action in the table below and the type of mutation that results. See the first line for an example. Name of compound Mechanism of action example: ultraviolet light causes pyrimidine dimers Type of mutation produced frameshift (other answers possible) name: name: name: 8. In your studies of three recessive corn genes, su, v and gl, you find that the three genes are linked. Recessive mutations in each produce: variable amounts of sugar in kernels (su), prominent leaf veins (v) and glossy leaves (gl). Two homozygous corn plants are crossed. The 4 Problem Set 7, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total resulting F1 progeny all have normal kernels, veins and leaves. Some of the F1 plants were test crossed to produce: 270 7 variable sugar, glossy leaves, prominent veins glossy leaves 48 glossy leaves, prominent veins 60 prominent veins 4 40 235 62 variable sugar, prominent veins variable sugar wild type variable sugar, glossy leaves a. What were the genotypes and phenotypes of the original homozygous parents used to produce the F1s? b. Calculate the map distance between: su and gl: gl and v: su and v: c. Another recessive mutation in corn is w, which gives wrinkled kernels. This gene is known to be 5.9 mu from v. A heterozygous plant with mutations in the trans orientation is test crossed to produce: 440 436 63 61 wrinkled glossy wrinkled, glossy wild type What is the genetic distance between gl and w? d. Draw a genetic map of the 4 linked genes. Show all distances. 5