Mutations - David Brotherton CCCMC
advertisement

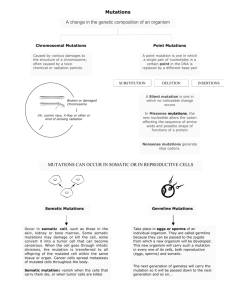
Biology Class Notes Lesson 24 Mutations and Genetic Variation Objective: 3.1.3 *DNA codes for amino acids, which comprise proteins, via mRNA. *Each protein is made of a few to several amino acids, and if only one is changed, an altered protein may form. Mutation: A change in the normal DNA sequence resulting from random error or the effect of a mutagen. Mutagen: Any agent that changes the DNA of an organism. Ex: X-Rays, Ultraviolet Radiation, Ionizing Radiation, certain chemicals, and viruses. Ex: Ethidium bromide (EtBr): An agent commonly used as a fluorescent tag in agarose gel electrophoresis because it will fluoresce when exposed to ultraviolet light. Types of Mutations 1. Base Pair Substitution: A mutation in which one nucleotide base replaces another. 2. Base Insertion: The addition of one or more bases into a nucleotide sequence. 3. Base Deletion: The removal of one or more bases from a nucleotide sequence. 4. Nondisjunction: A chromosomal mutation that produces an offspring with an incorrect number (more or less) of chromosomes. Ex: Nondisjunction of sex chromosome causes Kleinfelter Syndrome (XXY). Ex: Turner Syndrome (X_, or XO) Ex: Down Syndrome (three copies of chromosome 21). Effects of Mutations *Recall that cells can be categorized as somatic cells or gametes. Somatic cell mutations are not inherited, but germ/gamete mutations are inherited via the sex chromosomes. Somatic Mutations Usually result in cancerous or uncontrolled growth of cells. Can be caused by chemical or viral mutagens. Ex: Chemicals in asbestos and tobacco can cause uncontrolled cell growth in lungs. Ex: Human Papillomavirus (HPV) causes cervical cancer by attaching to the DNA of cells in the cervix. The cells eventually rupture causing copies of the virus to be release to infect other cells. Germ Mutation: Can be passed from parent to offspring. Can effect survival of the offspring and change the traits of descendants. Ex: Hemophilia: A disorder that slows blood clotting. Ex: Color blindness: A disorder that hinders the ability to distinguish different colors. Key Words: Mutation Mutagen Base-pair substitution Base insertion Base deletion Nondisjunction Autosome Somatic mutation Germ mutation