How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism?
advertisement
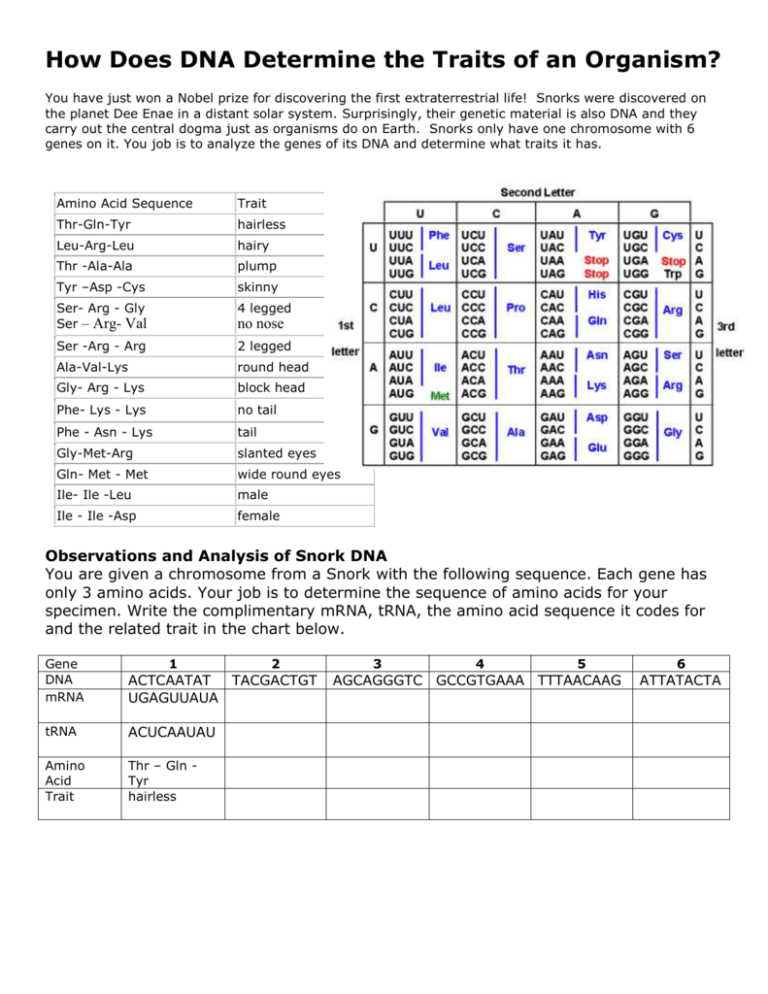
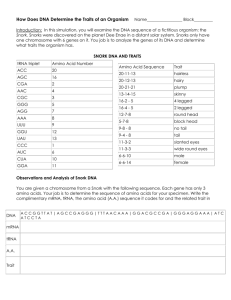
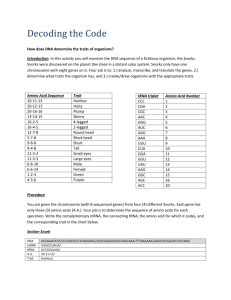
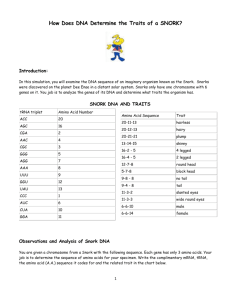
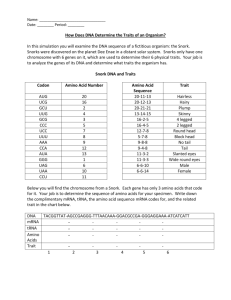
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? You have just won a Nobel prize for discovering the first extraterrestrial life! Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Surprisingly, their genetic material is also DNA and they carry out the central dogma just as organisms do on Earth. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. You job is to analyze the genes of its DNA and determine what traits it has. Amino Acid Sequence Trait Thr-Gln-Tyr hairless Leu-Arg-Leu hairy Thr -Ala-Ala plump Tyr –Asp -Cys skinny Ser- Arg - Gly Ser – Arg- Val 4 legged Ser -Arg - Arg 2 legged Ala-Val-Lys round head Gly- Arg - Lys block head Phe- Lys - Lys no tail Phe - Asn - Lys tail Gly-Met-Arg slanted eyes Gln- Met - Met wide round eyes Ile- Ile -Leu male Ile - Ile -Asp female no nose Observations and Analysis of Snork DNA You are given a chromosome from a Snork with the following sequence. Each gene has only 3 amino acids. Your job is to determine the sequence of amino acids for your specimen. Write the complimentary mRNA, tRNA, the amino acid sequence it codes for and the related trait in the chart below. Gene DNA mRNA ACTCAATAT TACGACTGT UGAGUUAUA 1 2 tRNA ACUCAAUAU Amino Acid Trait Thr – Gln Tyr hairless 3 4 5 AGCAGGGTC GCCGTGAAA TTTAACAAG 6 ATTATACTA Now, what would happen if there were mutations (changes) in the Snork’s DNA (gene 2, 3, 5, and 6)? Fill in the table below using the changes described: Gene DNA Mutation mRNA 1 2 3 4 5 6 ACTCAATAT TTACGACTGT AGCAGGGGC GCCGTGAAA TTCAACAAG ATATACTA tRNA Amino Acid Trait Draw your Snorks! BEFORE MUTATION AFTER MUTATION Questions 1. What is the name of the step that copies the information in DNA into a strand of mRNA? Where does it take place in the cell? 2. What is the name of the step that uses mRNA to make protein? Where does it take place in the cell? 3. How does DNA provide instructions for life? (DNA provides instructions to make proteins? How do proteins control life?) 4. Some proteins need to leave the cell. What organelle processes proteins before they are secreted? 5. How are proteins affected by DNA mutations? 6. Does a mutation always change the protein? If not, give an example of a mutation that would not change the protein.