Snork DNA
advertisement

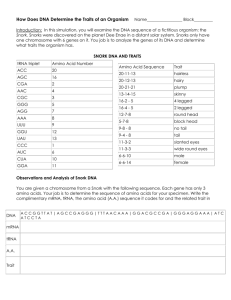
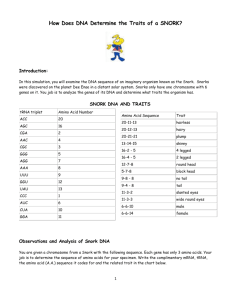
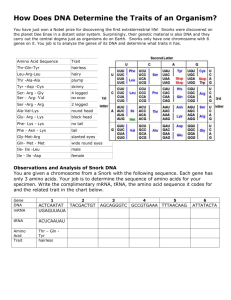
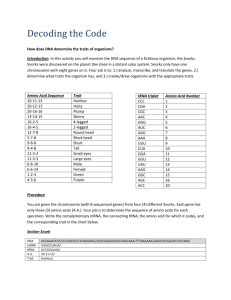
Name _________________________________________ Period _____ Date __________ SNORKS Today, you will examine the organism known as the Snork. Snorks were discovered were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. Your job is to analyze the genes of its DNA and determine what traits the organism has. SNORK DNA AND TRAITS mRNA ACC AGC CGA AAC CGC GGG AGG AAA UUU GGU UAU CCC AUC CUA CCA Amino Acid Number 20 16 2 4 3 5 7 8 9 12 13 1 6 10 11 Amino Acid Sequence 20-11-13 20-12-13 20-4-4 13-6-1 16-2-5 16-4-5 12-7-8 5-7-8 9-8-8 9-4-8 11-3-2 11-3-3 6-6-10 6-6-12 Trait Hairless Hairy Plump Skinny 4 legged 2 legged Round head Block head No tail Tail Squinty eyes Wide round eyes Male Female Observations and Analysis of Snork DNA You are given a chromosome from a Snork with the following sequence. Each gene has only 3 amino acids. Your job is to determine the sequence of amino acids for your specimen. Write the complimentary mRNA, tRNA, and the amino acid (a.a.) sequence it codes for, and the related trait in the chart below. DNA mRNA a. a Trait TGG-CCT-ATA ACC-GGA-UAU ATA-TAG-GGG TCG-TTG-CCC CCC-TCC-TTT AAA-TTG-TTT GGT-GCG-GCT TAG-TAG-GAT 20-11-13 hairless SOME HUMAN PRACTICE! Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA). Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling the production of a protein. In this case, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person cannot digest sugars the same way others can, and they have a disease called diabetes. PROCEDURE: 1. Using the DNA sequence given in table 1, make a complimentary RNA strand for the human. Write the mRNA strand directly below the DNA strand. 2. Repeat step 1 for the cow. 3. Use the codon table to determine what amino acids are assembled to make the insulin protein in both the cow and the human. Write your amino acid chain directly below the mRNA sequence. HUMAN DNA CCATAGCACGTTACAACGTGAAGGTAA mRNA Amino Acids COW DNA CCGTAGCATGTTACAACGCGAAGGCAC mRNA Amino Acids ANALYSIS 1. The DNA sequence is different for the cow and the human, but the amino acid chain produced by the sequence is almost the same. How can this happen? 2. Diabetes is a disease characterized by the inability to break down sugars. Often a person with diabetes has a defective DNA sequence that messes up the code for making insulin. Suppose a person has a mutation in their DNA, and the first triplet for the gene coding for insulin is CCC (instead of CCA). Determine what amino acid the new DNA triplet codes for. Will this person be diabetic? 3. What if the first triplet was CAA? 4. DNA sequences are often used to determine relationships between organisms. DNA sequences that code for a particular gene can vary widely. Organisms that are closely related will have sequences that are similar. Below is a list of sequences for a few organisms. Based on the sequences, which two organisms are most closely related? Human CCA TAG CAC CTA Pig CCA TGG AAA CGA Chimpanzee CCA TAA CAC CTA Cricket CCT AAA GGG ACG 5. An unknown organism is found in the forest, and the gene is sequenced. It is found to be CCA TGG AAT CGA. What kind of animal do you think this is?