solutions notes filled in ws
advertisement

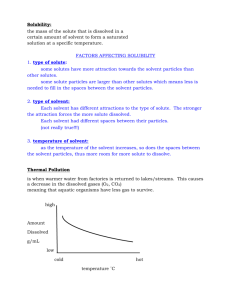
Name_______________________________________ date__________________ period______ SOLUTIONS 1. Mixtures=2 or more substances together that retain their properties Heterogeneous=not uniform throughout, not evenly mixed (suspensions) Homogeneous=uniform, same composition throughout (colloids, solutions) 2. Solutions=homogeneous mixture whose particles are molecules, ions, or atoms 3. Properties: Solutions= 1. Homogeneous 2. Will not separate 3. clear and transparent 4. Will not filter 5. Single phase 4. Parts: solute= substance being dissolved/dissolved substance solvent= substance in which solute dissolves solubility= maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a specific amount of solvent at a specific temperature soluble/insoluble= ability or inability of a solute to dissolve under specific conditions miscible= 2 liquids that will dissolve in one another 5. Types tinctures= solvent= alcohol aqueous= solvent= water hydration= solute particles surrounded by water molecules dissociation= (+) and( –) ions separated in water by hydration CaCl2 –> Ca+2 + 2Cl- Na2SO4 –> 2Na+ + SO4-2 solid= rare as solvent, solutes usually solids or gases alloys= one or more solids evenly mixed with a metal amalgams= solvent= Hg liquid= most common solvent, solutes=any phase gas= solutes=other gases or vapors 6. Factors affecting solubility: 1. Nature of solvent and solutes(“like dissolves like”) a) ionic and polar solutes dissolve in polar solvents b) non-polar solutes dissolve in non-polar solvents 2. temperature - solid and liquid solutes= solubility increases with heat - gas solutes = solubility decreases with heat 3. Pressure (gases only) -Henry’s Law= greater pressure increases solubility of gases 4. amount of substances already dissolved 7. Factors affecting rate of dissolving: 1. Size of solute particles 2. Stirring 3. Temperature of solvent 4. Amount already dissolved 8. Energy changes during dissolution: solid into liquid: (usually) requires energy(endothermic) gases into liquid: releases energy(exothermic) 9. Characteristics describing solutions: saturated=maximum amount dissolved solute@specific temp. unsaturated=less than maximum supersaturated= more than max. under normal conditions dilute= relatively low amount solute concentrated=relatively high amount solute molarity(M)=moles solute per liter solution = moles solute =M, M=#moles , or Liters solution L L=#moles , or , #moles=M X L M (Also) :Finding a new Volume or Molarity for a new solution made from a solution of already known Molarity: M1 X V1=M2 X V2 molality(m)= moles solute Kilogram solvent 10. Colligative properties= properties of a solvent affected only by amount of solute 1. Freezing point depression: solvent freezes @ lower temp. with more solute -Tf = m X Kf than normal freezing point 2. Boiling point elevation: solvent boils @ higher temp. with more solute Tb = m X Kb than normal boiling point