Regions Study Guide - Tangipahoa Parish Schools
advertisement

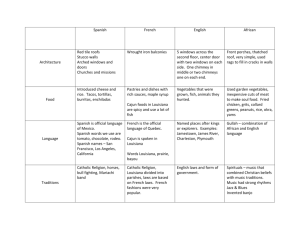
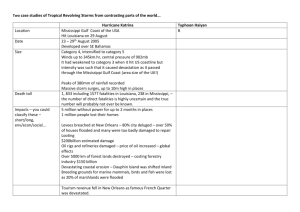
8th Grade Name___________________ LA regions study guide Section _________________ Regions are areas that have unique characteristics that make them separate from other areas. Regions can be in different categories such as location, physical characteristics, human characteristics, climate, political, and cultural characteristics. Here are some relevant regions of Louisiana: Culture: Components of culture include: religion, food, music, language, and ethnicity Music that is unique of Louisiana culture are Jazz, blues, zydeco, gospel, and spirituals. The religious purpose of Mardi Gras is the festive time before Lent. Lent begins Ash Wednesday. Mardi Gras means “fat Tuesday”. Regions: Sportsman Paradise: north LA. Many lakes, hills, and forests, home to hunting and fishing. Crossroads: center of the state small towns, farming, rural areas Cajun Country: southwest LA small towns that are 10 miles apart Cajun culture Prairie Cajun and Wetland Cajun. Prairie Cajun is mostly agriculture and livestock. Wetland Cajun is fishers and trappers Plantation Country: South central LA Home to Louisiana’s greatest plantations along the Mississippi River, Baton Rouge is at the center of this region Greater New Orleans Region: Southeastern LA New Orleans is focal point. Described as the cosmopolitan an American City that is more like a European one. The Florida Parishes is different than other southern regions because it was once part of the colony of West Florida. It includes the following parishes: Washington, St. Tammany, Tangipahoa, Livingston, East Feliciana, West Feliciana St. Helena, and East Baton Rouge. People: An ethnic group is a group of people who share the same traditions, beliefs, and patterns of living including language, religion, customs, and food. Acadians: When English took control of Novia Scotia they forced the Acadians to believe in their king and follow their rules. The Acadians did not want to so the British exiled them from Nova Scotia African Americans: Came to Louisiana several different ways. One was by the slave trade from West Africa. Another way was by being a slave from the West Indies. Free people of color came from the West Indies as well. French-African people born in Louisiana is referred to as Creole. Today Creole means native of Louisiana. American Indians have been in Louisiana for centuries. Some Native tribes include Chitimacha, Choctaw, Coushatta, Tunica-Biloxi, and Houma. Anglo culture developed in the British Colonies on the eastern coast of the United States. Scots-Irish established farms in North Louisiana. Culture is Upland South and the accent is Southern. The religion is Protestant. Germans immigrated in the early colonial period. They blended with the dominant French culture. On December 6, a procession celebrating the religious feast of St. Nicholas goes from House to house Hispanics: Islenos are the oldest and best preserved Hispanic culture in Louisiana. They descended from the Canary Islands. Most reside in St. Bernard Parish. The Hispanics in Sabine Parish comes from Texas. Cuban community developed in New Orleans. The most recent Hispanic immigrants have come from Mexico. Italians: Farmers who raised vegetables and strawberries. Largest group lives in Independence. Custom of St. Joseph Altar is now a Louisiana culture; it is a feast for friends. Croatians: Came from the Adriatic Sea and brought sailing skills and developed the oyster industry. Most live in Plaquemines Parish. Filipino: Shrimpers Vietnamese: Fishermen in Louisiana’s coastline. Rivers, Lakes, and Bayous: Three largest rivers in Louisiana are The Mississippi, The Red, and the Atchafalaya Waterways that serve as boundaries of Louisiana are: The Mississippi between Mississippi and Louisiana, The Pearl River between lower Louisiana and Mississippi, The Sabine River and Toledo Bend between Louisiana and Texas, and the Gulf of Mexico in the South. The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway extends from the Panhandle of Florida to Brownsville, TX. It provides a channel for ships. Because of this channel Lake Charles is Louisiana’s third largest port. Rivers Mississippi River is a vital part of Louisiana. The Great River, or River of the Holy Spirit. The basin of the Mississippi is the body of the nation. It drains at least part of 31 states. Atchafalaya River means long river. It gets the water from the Red River as well as 30% of the volume from the Mississippi River. Lakes: The largest manmade lake is Toledo Bend. It is also the nation’s fifth largest water reservoir. Lake Pontchatrain is the largest natural lake. Lake Borgne and Lake Maurepas are lagoonal lakes that open into the lake. It has brackish water (a mixture of salt water and fresh water). An interesting cutoff lake is Cane River Lake. It formed when the Red River took a shortcut and left the town without a river. Bayou comes from Choctaw language means creek. The French called it Sleeping Water because of the slow moving currents. Some are long and deep while others are less than a mile and shallow enough to walk across. Bayou Lafourche is called the longest main street in the world because so many people live there. Bayou Teche offered navigation route fro steamboats. Natural Regions: Elevation: the height of a place above se level Relief: the difference between the highest point and lowest point in a given region. Mississippi Flood Plain Region Mississippi Flood Plain: follows the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico. the level land along a river that is likely to flood. The soil is alluvial (deposited by the river). The soil is fertile and produces natural vegetation and agricultural crops. Cotton is one of those crops. The Natural Levee: Natural riverbanks built up over time by the silt deposited by flooding. About 10-15 feet high. Trees that grow there are usually willows, cottonwoods, and sycamores. Swamp: lowest part of the river basin. Cypress and tupelo gum trees live in the swamp. Swamp is water with trees. The Passes: routes the Mississippi River takes to merge with the Gulf of Mexico. Can be called a Delta because it is triangular shaped. The estuary (where the river meets the sea) the water changes from freshwater to saltwater. The vegetation is marsh grasses. Terraces Region Terraces Region is the old Mississippi Floodplain. Three divisions Blufflands, Prairies, and Flatwoods. Blufflands: are the old natural levees and are the highest points They have vertical slopes on high bluffs. Magnolia trees, dogwood, holly, ash and oak trees along with ferns, green mosses, and wildflowers. Prairies: Flat part of the old natural levees Grasses and wildflowers grow there. Common plants are broom sedge, bluestem sedge. Flatwoods: Drains well allows trees to grow. Pine and hardwood forests called pineywoods Marsh Region: wet, treeless prairie covered with water and grasses. Marsh is found along the coast. Migrating birds return to feed on the marsh. 180 species have been seen from Canadian geese to hummingbirds. The region closest to the Gulf of Mexico is called the salt whose waters are brackish. Freshwater marsh has different plants such as cattail and iris marsh Salt Domes: Found in the salt marsh. They have mineral treasures such as sulphur, petroleum and salt. 5 islands include: Avery Island, Weeks Island, Jefferson Island, Cote Blanche, and Belle Isle. Avery Island Tabasco Factory because of the amount of salt. Weeks Island store petroleum part of the emergency reserve supply maintained by the Department of Energy Red River Valley Region: Northwestern corner to central part of Louisiana. Single stream with natural levees and low-lying areas. Red fertile soil comes from Oklahoma and Texas. Trees such as willow, cottonwood, sweet gum, and sycamore. Hills Region: Much of North Louisiana as well as the toe of the boot Refers to rock formation Ridges formed in the uplift as erosion wore down the surrounding rock. These ridges are called wolds. Contains the highest point of Louisiana called Driskill Mountain 535 feet. Iron lakes the soil reddish color and is not fertile.