Two case studies of Tropical Revolving Storms from contrasting
advertisement
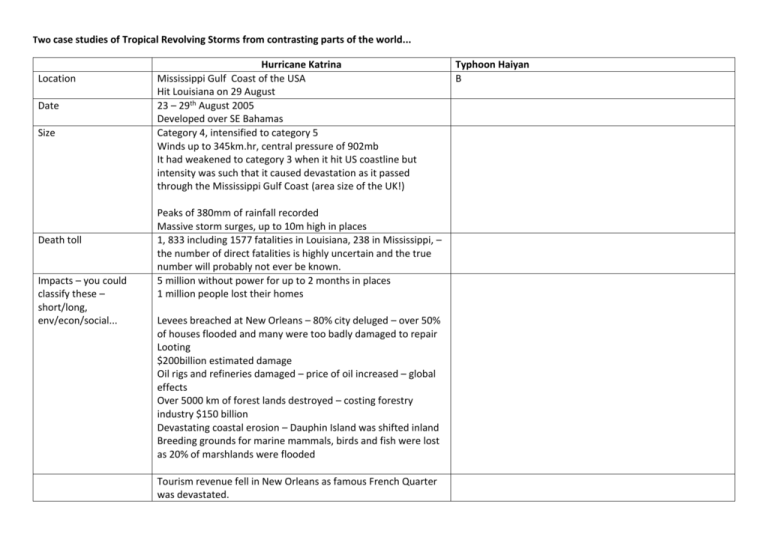
Two case studies of Tropical Revolving Storms from contrasting parts of the world... Location Date Size Death toll Impacts – you could classify these – short/long, env/econ/social... Hurricane Katrina Mississippi Gulf Coast of the USA Hit Louisiana on 29 August 23 – 29th August 2005 Developed over SE Bahamas Category 4, intensified to category 5 Winds up to 345km.hr, central pressure of 902mb It had weakened to category 3 when it hit US coastline but intensity was such that it caused devastation as it passed through the Mississippi Gulf Coast (area size of the UK!) Peaks of 380mm of rainfall recorded Massive storm surges, up to 10m high in places 1, 833 including 1577 fatalities in Louisiana, 238 in Mississippi, – the number of direct fatalities is highly uncertain and the true number will probably not ever be known. 5 million without power for up to 2 months in places 1 million people lost their homes Levees breached at New Orleans – 80% city deluged – over 50% of houses flooded and many were too badly damaged to repair Looting $200billion estimated damage Oil rigs and refineries damaged – price of oil increased – global effects Over 5000 km of forest lands destroyed – costing forestry industry $150 billion Devastating coastal erosion – Dauphin Island was shifted inland Breeding grounds for marine mammals, birds and fish were lost as 20% of marshlands were flooded Tourism revenue fell in New Orleans as famous French Quarter was devastated. Typhoon Haiyan B Immediate Response Long Term Response Businesses, especially insurance companies. issued profit warnings to shareholders thousands of lost jobs and millions of dollars in lost tax revenues for the impacted communities and states Pollution – e.g. Lake Pontchartrain was used as a store for the polluted water from New Orleans – containing raw sewage, heavy metals, pesticides and oil. The official track forecasts for Katrina issued within about two and a half days of landfall of the center in Louisiana were exceptionally accurate and consistent. 2 days prior to landfall President Bush declared state of emergency in Louisiana, Alabama and Mississippi FEMA made preparations, including providing refrigerated trucks for anticipated dead. 1 day before landfall Mayor ordered that New Orleans should be evacuated – 150000 remained.- they were offered the Louisiana Superdrome as a protective shelter and food supplies for 3 days were delivered National Guard deployed to secure New Orleans from looting Provision of clean water, medical care and food supplies Criticism of the government’s role – many believed poorer, black people were perceived as lower status and government has responded slowly $10 billion of aid from the US government and another $51 million form Federal funds were made available for repair Public donated $1.8 billion International aid from 70 countries – e.g. Kuwait donated $500m Rehousing – 75% stayed within 400km, tens of thousands of refugees were relocated over 1000km from home People returned to New Orleans, by Jan 2006 its population was still less than half. Insurance premiums rose or became unavailable in some areas The forecasting of the National Hurricane Center was reviewed.