Study Guide Biochemistry - Manhasset Public Schools
advertisement

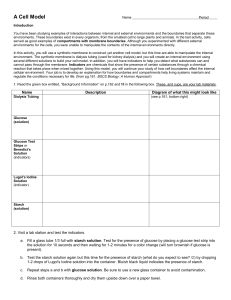
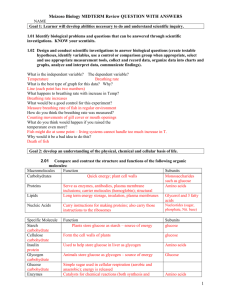
Name:_________________________________________ Study Guide: Test#3- up to Biochemistry Date:_______________________ A. Paramecium Lab Know parts (and functions) of the Paramecium- cilia, oral groove, food vacuoles, anal pore, and contractile vacuole Food vacuoles move around by cytoplasm Streaming (cyclosis) How does a paramecium (single-celled) carry out all of the life processes? ________________________________ B. Transport Passive = requires no energy- Osmosis and Diffusion (High → Low) – with gradient Active = requires energy (ATP) – ex. Pinocytosis, Phagocytosis – (Low → High) – against gradient C. Diffusion through a Membrane (NYS Mandated Lab) Hypertonic solution – cells placed in salt water will shrink (water diffuses out) Hypotonic solution – cells placed in distilled water will swell (water diffuses in) – Animal cells may burst, plant cells will not because of cell wall Isotonic solution – cells will maintain dynamic equilibrium = no change Starch (macromolecule) - does not diffuse across membrane Glucose (simple sugar) – does diffuse across the membrane Indicators: i. Iodine (Starch indicator)- Amber → Blue/Black in the presence of starch ii. Benedict’s solution (glucose indicator) – Blue → Orange in the presence of glucose when heated D. Biochemistry Organic Compound Elements found: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids CxH2xOx C, H, O C, H, O, N C, H, O, N, P 3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol Energy storage Amino acids Nucleotides Function: Simple sugars (monosaccharaides) Energy Example: Glucose, starch Fats, oils, waxes Subunits: Structural Heredity molecule compound Pepsin, hemoglobin, DNA, RNA lipase, sucrase Monomers – simple sugars, amino acids, nucleotides. (small, building blocks of macromolecules that can easily diffuse across the cell membrane) Polymers macromolecules- starches, proteins, nucleic acids Isotopes- atoms that differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus Inorganic Molecules- small and simple and usually do not contain C-H bonds (H2O, NaCl, CO2) Name:_________________________________________ Date:_______________________ Study Guide: Test#3- up to Biochemistry i. Water: extremely important to cells because it is the universal solvent and provides for the environment of the cell. It also has many properties because of its ability to hydrogen bond between water molecules: 1. Cohesive- water sticks to itself 2. Adhesive- water sticks to other substances (its container) 3. Polar (slightly + and – charges at opposite ends) E. F. G. Organic Molecules- large, complex and contain carbon and hydrogen (Glucose- C6H12O6) Carbohydrates- (end in –ose) monosaccharides (glucose), disaccharides (sucrose), polysaccharides (starch) o Animals- store excess carbs as glycogen in liver and muscles o Plants- store excess carbs as cellulose (fiber or roughage) in cell walls and as starch in cytoplasm (man can’t digest cellulose) o Glucose (monosaccharides) form disaccharides, which in turn forms polysaccharides (starches) like cellulose in plants and glycogen in animals Proteins – long chains of amino acids (polypeptides bonded together by peptide bonds) o Enzymes – Organic catalysts-speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy; proteins-formed in the ribosomes; end in –in or –ase Enzyme + Substrate = Enzyme-substrate complex for a brief moment in time (during a reaction), then the enzyme goes on its merry way to catalyze other reactions. They can be reused!!! Shape is very important to a protein’s ability to function. A protein’s shape (active site) is determined by many factors- one of which is the sequence of amino acids (controlled by DNA code!) If a protein is denatured, its structure is altered. It can no longer work. This can be caused by changes in pH, temperature, or heavy metals like mercury or lead Enzyme activity is affected by the following factors: pH, temperature, concentration of substrate, concentration of enzyme Lock and Key Model- Every reaction in the body is catalyzed by a specific enzyme, just like every lock as a key that will unlock it Induced Fit Theory- enzyme may change its shape to fit its substrate Dehydration Synthesis: Combining molecules by removing water Glucose + Glucose → Maltose + Water Hydrolysis: Separating molecules by adding water Starch + Water → Simple Sugars pH measure of acidity and basicity Scale: 0 – 14 (acids (0-6), bases (8-14), water is neutral (7)). pH indicators change color in different pH’s i. Congo Red- turns blue with acids ii. pH paper- best indicator because it turns a specific color associated with a specific number on the pH scale Name:_________________________________________ Study Guide: Test#3- up to Biochemistry Review Questions: Date:_______________________ 1. Which substances may pass through a cell membrane by simple diffusion? a. Carbon dioxide and Water c. Carbon dioxide and Starch b. Protein and Fat d. Starch and Protein Explain your answer to #1:___________________________________________________________ 2. Which compound is inorganic? a. Stearic acid (C18H36O2) b. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) c. Ethane (C2H6) d. Glucose (C6H12O6) Explain your answer to #2:___________________________________________________________ 3. Most organisms contain a. Both organic and inorganic compounds b. Inorganic compounds only c. Neither organic nor inorganic compounds d. Organic compounds only Explain your answer to #3:___________________________________________________________ 4. Which percentage would explain the net movement of water into a cell through the process of osmosis? a. Water and protein was equal inside and outside the cell b. Water was 90% inside the cell and 95% outside the cell c. Water was 95% inside the cell and 90% outside the cell d. Protein was 30% inside the cell and 35% outside the cell Explain your answer to #4:___________________________________________________________ 5. Which of the following substances plays a major role in most of the chemical reactions that occur in a living cell? a. Water b. Maltose c. Glycogen d. Glycerol Explain your answer to #5:___________________________________________________________ 6. The enzyme amylase will affect the breakdown of carboydrates, but it will not affect the breakdown of proteins. The ability of an enzyme to interact with specific molecules is most directly determined by a. Number of molecules involved c. Shapes of the molecules involved b. Sequence of bases present in ATP d. Amount of glucose present in the cell Explain your answer to #6:___________________________________________________________ 7. Which substance should be used to determine if a solution is basic? a. pH paper b. methylene blue c. Benedict’s solution d. Lugol’s iodine Explain your answer to #7:___________________________________________________________ Name:_________________________________________ Study Guide: Test#3- up to Biochemistry Date:_______________________ 8. Which organic molecule is correctly paired with an end product of its digestion? a. Lipid- amino acid b. Protein- glycerol c. Nucleic acid- nucleotide d. Carbohydrate-fatty acid Explain your answer to #8:___________________________________________________________ 9. A neutral solution has a pH of: a. 1 b. 7 c. 9 d. 14 Explain your answer to #9:___________________________________________________________ 10. The arrows in the diagrams below represent the direction of movement of a certain type of molecule through the cell membrane of two different cells. The dots represent the relative concentrations of this molecule. Which processes are illustrated in the diagrams? a. phagocytosis and diffusion b. pinocytosis and osmosis c. active transport and diffusion d. dehydration synthesis and circulation Explain your answer to #10:_______________________________________________________