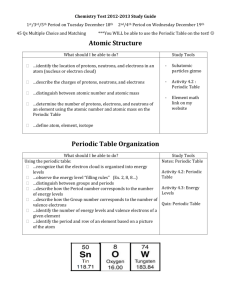
5.1 Review an Reinforce Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table 1
advertisement

5.1 Review an Reinforce Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table 1. 7 2. 7 3. 5 4. It is reactive because it needs three valence electrons to become stable. 5. Nonmetal 6. Valence electrons have the highest energy and are most loosely held by the atom 7. chemical bond 8. Electrons may be transferred or shared between atoms. 9. If atoms of an element have less than eight valence electrons, the element will likely react with other elements. 10. the same number of valence electrons 11. lose 12. gain; share 5.2 Review and Reinforce Ionic Bonds 1. An atom becomes a positive ion by losing an electron. An atom becomes a negative ion by gaining an electron. 2. Oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other. When ionic bonds form, the ions come together in a way that balances out the charges on the ions. 3. Solid ionic compounds typically form hard, brittle crystals and have high melting points. They conduct electricity well when dissolved in water or melted. 4. As solids, the ions are tightly bound in ionic bonds. The ions are free to move when the compound is dissolved in water. Then electricity can flow. 5. Two. A sulfide ion has a charge of 2 . Since potassium ions only have a charge of 1+, two potassium ions are needed to balance the charge. 6. CaCl 2 ,K 3 PO 4 7. Magnesium sulfide, ammonium chloride, and potassium oxide 8. Ammonium and phosphate are polyatomic. 9. An atom or group of atoms that has an electrical charge 10. The attraction between oppositely charged ions 11. In a crystal, positive and negative ions alternate, forming an orderly three-dimensional arrangement. 5.3 Review and Reinforce Covalent Bonds 1. Students should have drawn one circle around the shared electrons in each diagram (two electron pairs shared in O 2 and three pairs in N 2 ). 2. The bond in O 2 3. The bond in N 2 4. N 2 ,O 2 , and F 2 have nonpolar bonds. 5. The polar bond is a result of the fluorine atom pulling more strongly on the shared electrons than the hydrogen atom. 6. Compared to ionic compounds, molecular compounds have lower melting and boiling points. Most molecular compounds are poor conductors of electricity when melted or dissolved. 7. nonpolar 8. polar 9. polar 10. Nonpolar 5.4 Review and Reinforce Bonding in Metals 1. Ability to conduct heat and electricity, ability to change shape easily, and luster 2. An alloy is a mixture made of two or more elements that has the properties of metal. 3. Alloys can be harder and less likely to react with air and water than pure metals. 4. metallic bond 5. Point a represents positively charged metal ions. Point b represents freely moving valence electrons. 6. Striking or hammering a metal to make it change shape 7. In metallic bonding, metal ions are attracted to the freely moving electrons all around them and not to other metal ions. The ions can be pushed away from one another, but the metallic bonds hold the ions close enough together so that the metal does not break.