Optics Unit Review
advertisement

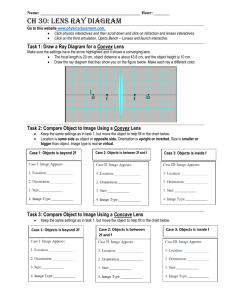
SNC 2D Name: ______________ Optics Unit Review Be familiar with… Properties of light – what is light, how light moves, the different sources of light (bioluminescence or chemiluminescence) Parts of the electromagnetic spectrum (longer/shorter wavelengths, lots vs. little energy) – what the different types are and what they are used for Law of reflection Parts of a ray diagram: how do we draw a light ray, wha is an incident ray, reflected ray, angle of incidence, angle of reflection Reflection in a plane: relationship between incident ray and reflected ray concave and convex mirror: the different types of rays that will reflect of the curved mirrors, Locating images in plane, concave and convex (know the definitions associated with curved mirrors – e.g. – centre of curvature, radius of curvature, vertex, focal point, focal length, principal axis) mirrors --- and their characteristics (SALT). Know how to find an image in all cases Know the alternative names for concave and convex mirrors Divergent and convergent Why do we see reflections (luminous vs. non-luminous, opaque, translucent, transparent, reflected, absorbed, transmitted, diffuse reflection, regular reflection) Be able to locate images convex lenses and describe their characteristics (SALT) as well as know the definitions associated with the lenses Be able to recognize the patterns for lenses in terms of location of the object versus characteristics and location of the image Be able to use the THIN LENS EQUATION to be able to determine di, do, f Magnification of Images – know the two equations (one using the ratio of heights and the other using the ratio of distances). Know how to solve for different variables in the equations Know when to use positive or negative numbers when using these equations and be able to describe the image characteristics (SALT) given numbers Be able to work your SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR correctly Refraction of light (what is it? why does it occur? When does it occur?) What is the index of refraction and how is it determined (know both equations)? What does a low ‘n’ value vs. a high ‘n’ value mean? Be able to solve for different variables What is total internal reflection – give examples Know the eye, be able to label a diagram of the eye and describe how it works (for e.g. – how is an image formed on the retina) What is the difference between rods and cones What is the difference between far-sightedness, near-sightedness and astigmatism. What lenses are used to correct each 1. For the following converging lens system, measure the focal length. Label the principal axis and the lens axis. Use the rules for drawing ray diagrams (Parallel Ray, Centre Ray and Focal Ray) for converging lenses to find the resulting image. Describe the image using SALT (Size, Altitude, Location, Type). 2f f f 2f SNC 2D Diagram – Sketch the Image using 2 Characteristic Rays Name: ______________ Concave, Convex or Plane? Mirror or Lens? SILT