exam outline and unit review
advertisement

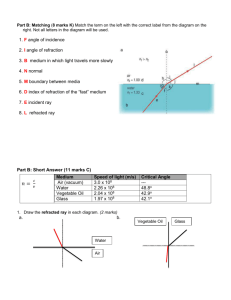
Physics Unit Review: pages 590 – 594 # 1-16, 18-24, 26-27, 29-34, 36, 39, 40, 42-47, 51-60, 63, 65, 68-70 Physics Self Quiz Unit Review: pages 596-597 # 1-14, 16-18, 20-23 Chemistry Unit Review: pages 302-307 # 1-17, 19, 20, 22-27, 32-37, 39-45, 47-49, 51-55a,b, 56-57a-d, 59, 60 Chemistry Self Quiz Unit Review: pages 596-597 # 1-14, 16-18, 20-23 SNC 2D Biology Unit Review The Cell (cell parts and their function) - Characteristics of living things and cell theory Plant and animal organelle diagrams (structure and function) Differences between plant and animal cells The Need for Cell Division and the Cell Cycle - 3 functions of cell division 5 main phases of the cell cycle (G1, S and G2 phases, mitosis and cytokinesis) Programmed Cell Death and Cancer - Apoptosis – programmed cell death What is cancer? Causes of cancer, diagnosis, and treatment Compare and contrast normal and cancer cells Microscopes - Parts of a compound light microscope and their functions electron microscopes ( SEM and TEM ) uses measuring the field of the field of view and estimating cell size Cell Specialization - How do cells become specialized? What happens to the DNA in these specialized cells? The Animal Body – Levels of Organization - What is a tissue? Levels of organization (hierarchy) …organelles – cells – tissues – organs – organ systems – organism Animal tissue types: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nerve tissue Stem Cells and Cellular Differentiation - What is a stem cell? How stem cells different from specialized cells? Examples of stem cells What is regeneration? Examples of regeneration Regeneration research and its applications Animal Systems - Digestive system Major organs and their functions - mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestine Circulatory system Major organs and their functions - blood, heart, blood vessels Respiratory system Major organs and their function - mouth, trachea, lung ( bronchus, bronchioles, alveoli) Respiration processes – gas exchange, breathing Nervous system Parts of a nerve cell (neuron) Parts of a nervous system: central nervous system and peripheral nervous system Interactions of Systems Describe the interdependency of organ systems within an organism Plant Systems - Plant systems – their parts and function within the plant root and shoot systems Plant Tissues - Cellular differentiation and specialization in plants – tissues in plants … dermal tissue, vascular tissue, ground tissue Frog Dissection Identify frog organs and their functions Terminology: mitosis, chromosomes, sister chromatids, interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis, homologous chromosomes, apoptosis, carcinogen, mutation, tumour, benign, malignant, metastasize, magnification, resolution, contrast, differentiation, meristematic cells, stem cells, totipotent, cellular differentiation, meristematic cells, SNC 2D Physics Unit Review What is a wave? Parts of a wave: crest, trough, rest position, wavelength, amplitude, frequency The relationship between frequency and wavelength and energy Be able to draw a wave with specific measurements What is electromagnetic radiation? the 7 types of electromagnetic radiation on the electromagnetic spectrum (compare frequency of wavelengths of each type of electromagnetic radiation to visible light and describe the uses of each type of radiation) Describe the wave model of light Sources of light (how they work and applications of each) What is the ray model of light? Describe materials that allow light to be transmitted, absorbed or reflected How do bright and dim lights differ? What are an umbra and a penumbra? How are they created? What is a regular reflection? Diffuse reflection? How are they created? What is geometric optics? What is an image? An optical device? Draw a ray diagram for a plane mirror, indicating the normal, incident ray, angle of incidence, angle of reflection Describe the law of reflection Find an image in a plane and curved mirror (concave or convex) and describe the image using SALT Describe the focal point, vertex, focal length, hi, ho, di and do in both concave and convex mirrors by drawing ray diagrams for curved mirrors Describe practical uses of concave and convex mirrors and what properties make them suitable for these applications Calculate magnification Describe refraction; Describe the index of refraction and be able to calculate n or v using n = c/v Be able to predict the angle of refraction and draw a diagram showing the incident ray, angle of incidence, refracted ray, refracted angle, n1 and n2 Calculate the angle of refraction or a refractive index using Snell’s law n 1sinØ1 = n2 sinØ2 Draw an image in a convex or concave lens and describe it using SALT Use the thin lens equation to calculate di, do or f Describe the parts of the human eye and their functions (including the blind spot). Describe the three main types of vision problems and how they are corrected. SNC 2D Chemistry Unit Review o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o classifying matter - pure substances & mixtures physical and chemical properties and changes atomic theory (electrons, protons, neutrons) drawing Bohr – Rutherford diagrams families /groups and periods ionic charges within chemical families predicting ionic charges cations and anions ionic compounds (metals with one charge, multivalent metals, polyatomic ions, binary acids, oxyacids, and bases) names and formulas for molecular compounds, including diatomic molecules molecular models word equations (reactants and products) counting atoms, the conservation of mass and balancing chemical equations types of chemical reactions (synthesis, decomposition, single displacement and double displacement reactions, combustion and neutralization reactions) identifying acids and bases and interpreting the pH scale