Warm-up: (10-2-14) *Ch. 5-1 video lec notes, rubric, and Journal #2
advertisement

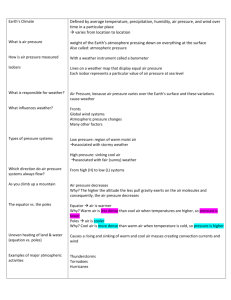
Warm-up: (10-2-14) *Ch. 5-1 video lec notes, rubric, and Journal #2 finch article out for stamp! 1. Explain how growing an herbicide resistant crop: Can increase your crop yield Increases your use of herbicide 2. The overuse of herbicides can cause weeds to become _____ to it. 3. The use of rBGH can lead to infections in cows. What will these cows need to be given in order to fight the infection? 4. How is GE different from artificial selection? How many giant convection currents (cells) does earth have? Contrast weather and climate. What are the 2 most important factors in determining climate? What other factors can affect climate? Why do the high and low temp of a coastal areas differ slightly, while an inland area can have a big difference between high and low temps? What is a heat island effect? Why is wind important? Give two pros and two cons In what layer of the atmosphere does weather happen? Troposphere What pattern do you see in Earth’s current climate zones? What is the rainshadow effect? Chapter 7-1: Climate Mrs. Boyd Global Air Circulation: Distributing Heat Global air circulation is affected by: uneven heating of the earth’s surface seasonal changes in temperature and precipitation What causes the seasons? Coriolis Effect Global air circulation is affected by the rotation of the earth on its axis. Convection Currents Global air circulation is affected by the properties of air, water, and land. What causes air to circulate on Earth? What is a high pressure area? Cool dense air that is dropping toward earth and warms, fair weather follows this if high stays put what is a low? Low density warm air spirals and rises, thus cooling and releasing moisture Weather on the move What is a cold front? When a mass of cold, dense air pushes up a warm mass causing thunder clouds And a warm front? Warm air strikes cold dense air and rises, thus cooling and releasing moisture (Rain) El Nino El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Normal winds keep warm water on west side of pacific, if winds weaken, warm water moves east and changes weather patterns worldwide Affects upwelling on Western side of Americas animation Other factors that influence climate: What is the greenhouse effect? Natural warming of the atmosphere depending upon the concentration of greenhouse gasses What are some greenhouse gases? Water carbon dioxide methane nitrous oxide (N2O) ozone Check for Understanding: 1. What influences climate? 2. In an El nino year, the surface ocean temperature is (warmer, cooler) and this causes an upwelling to (occur, be blocked). 3. What is the rain shadow effect? 4. Describe what happens in a high pressure area? Low pressure?