File
advertisement
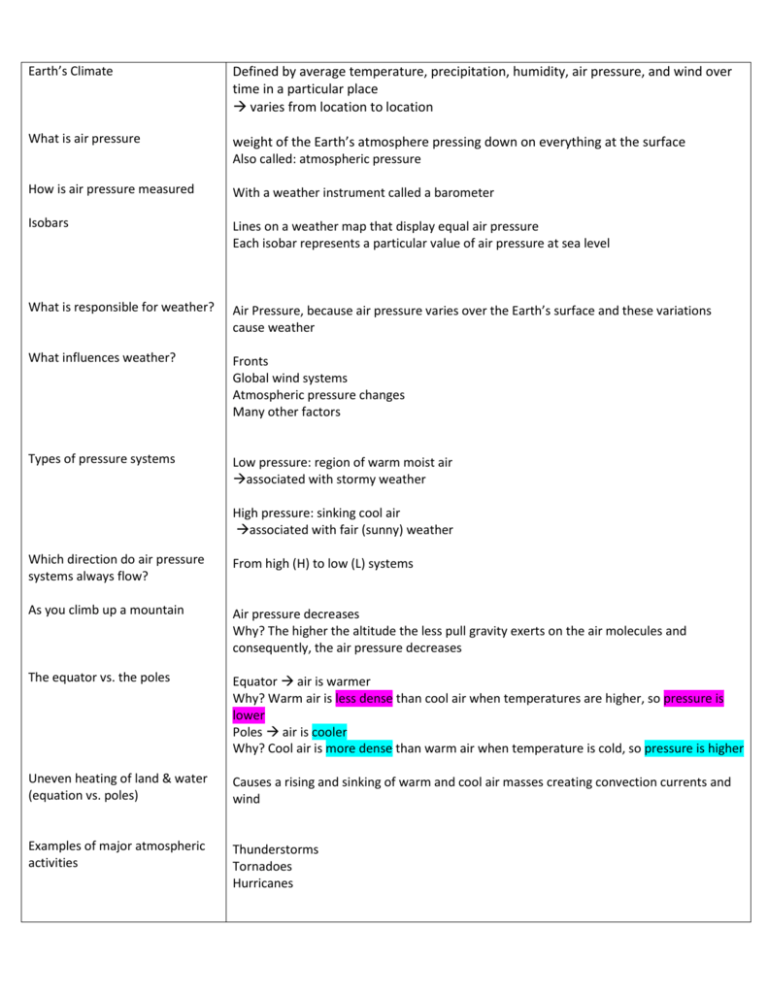
Earth’s Climate Defined by average temperature, precipitation, humidity, air pressure, and wind over time in a particular place varies from location to location What is air pressure weight of the Earth’s atmosphere pressing down on everything at the surface Also called: atmospheric pressure How is air pressure measured With a weather instrument called a barometer Isobars Lines on a weather map that display equal air pressure Each isobar represents a particular value of air pressure at sea level What is responsible for weather? Air Pressure, because air pressure varies over the Earth’s surface and these variations cause weather What influences weather? Fronts Global wind systems Atmospheric pressure changes Many other factors Types of pressure systems Low pressure: region of warm moist air associated with stormy weather High pressure: sinking cool air associated with fair (sunny) weather Which direction do air pressure systems always flow? From high (H) to low (L) systems As you climb up a mountain Air pressure decreases Why? The higher the altitude the less pull gravity exerts on the air molecules and consequently, the air pressure decreases The equator vs. the poles Equator air is warmer Why? Warm air is less dense than cool air when temperatures are higher, so pressure is lower Poles air is cooler Why? Cool air is more dense than warm air when temperature is cold, so pressure is higher Uneven heating of land & water (equation vs. poles) Causes a rising and sinking of warm and cool air masses creating convection currents and wind Examples of major atmospheric activities Thunderstorms Tornadoes Hurricanes