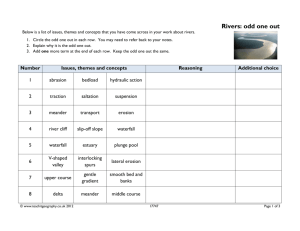
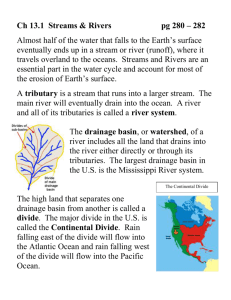
Scheme of Work - geographylwc.org.uk
advertisement
grs09/02/16 Water on the land Aims: To demonstrate an understanding of the fluvial processes and the landforms associated with them Demonstrate an understanding of the work of a river in eroding, transporting and depositing. Reference should be made to the erosional processes of hydraulic action, corrasion, corrosion (solution) and attrition. River transport should include the processes of traction, saltation, suspension and solution. Reasons why and where in a river’s course deposition takes place should be studied. It should be realised that the effectiveness of the river processes concerned will vary according to the volume and velocity of the running water and the nature of the load (boulders, pebbles, sand and silt) which, in turn, will be affected by the bedrock along the course of the river. • Describe and explain the landforms associated with these processes. A study should be made of the following: Forms of river valleys – long profile and shape in cross section, rapids, waterfalls, potholes, meanders, oxbow lakes, deltas, levées and flood plains. GEOACTIVE FILES FOR RIVERS Key Questions Suggested Pupil activities/methods How do rivers, through erosion and transportation, develop characteristic landforms? IT EX ON DRAINAGE BASIN AND WATER Text 66 CYCLE Discuss the processes of transportation ; traction, saltation, suspension and solution; and vertical and lateral erosion; attrition, abrasion, solution and hydraulic action. Relate processes to velocity. Hjulstrom curve? Rivers stores and flows river from source to mouth Resources DVD Misc Rivers GinP 2 P7 http://www.lalc.k12.ca.us/tar get/units/river/riverweb.html Time 1 grs09/02/16 How does the profile of the river change downstream? How are deltas formed? Draw the long (graded) profile and discuss reasons for knick points. Discuss the reasons for the changes in cross section map of Niagara Examine the formation of V shaped valleys and how they appear on maps. Rapids, potholes Explain with examples the formation of waterfalls. Case study: High Force and Niagara Discuss the formation of a meander, showing the areas of deposition and erosion and also the position of maximum velocity. Identify river cliffs and slip off slopes and the type of deposits found. Note how the meander “scrolls” across the valley and how the slip off deposits “smear” the valley floor. Discuss how ox bow lakes develop from a meander, relate to areas of deposition and erosion and maximum velocity. Describe the processes, include cross section Nile and Mississippi ASSESSMENT Sample question marks scheme What processes cause landforms in highland rivers? How do rivers form meanders and ox bow lakes? 68 Rivers Use AS material 1 GeoA 16330 Und Geog Act P 43 2 2001 Arran map Skills Paper 2010 23 qu 4 Und Geog 3.1 70 GinP HC 12 B River channels and floodplains Key Act 1.2 Und Geog Act P 44 Und Geog 3.2 1 2003 Perth Map 73 ½ Key assess 1.2