Algorithm
advertisement

ALGORITHMS
To make a computer do anything, you have to write a computer program.
To write a computer program, you have to tell the computer, step by step, exactly
what you want it to do. The computer then "executes" the program, following
each step mechanically, to accomplish the end goal.
When you are telling the computer what to do, you also get to
choose how it's going to do it. That's where computer algorithms come in. The
algorithm is the basic technique used to get the job done.
An algorithm is a set of instructions designed to perform a specific task. This
can be a simple process, such as multiplying two numbers, or a complex
operation, such as playing a compressed video file.
Language in Algorithms
• Natural language : For people, we use a natural language like English
Before writing an algorithm for a problem, one should find out what is/are
the inputs to the algorithm and what is/are expected output after running the
algorithm.
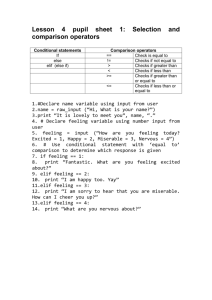
we will use following symbol for different operations:
‘+’ for Addition
‘-’ for Subtraction
‘*’ for Multiplication
‘/’ for Division and
‘’ for assignment.
For example A X*3 means A will have a value of X*3.
Example of Algorithm
Problem 1: Find the area of a Circle of radius r.
Inputs to the algorithm:
Radius r of the Circle.
Expected output:
Area of the Circle
Algorithm:
Step1: Read\input the Radius r of the Circle
Step2: Area PI*r*r // calculation of area
Step3: Print Area
Problem2: Write an algorithm to read two numbers and find their sum.
Inputs to the algorithm:
First num1.
Second num2.
Expected output:
Sum of the two numbers.
Algorithm:
Step1: Start
Step2: Read\input the first num1.
Step3: Read\input the second num2.
Step4: Sum num1+num2 // calculation of sum
Step5: Print Sum
Step6: End
Problem 3: Convert temperature Fahrenheit to Celsius
Inputs to the algorithm:
Temperature in Fahrenheit
Expected output:
Temperature in Celsius
Algorithm:
Step1: Start
Step 2: Read Temperature in Fahrenheit F
Step 3: C5/9*(F32)
Step 4: Print Temperature in Celsius: C
Step5: End
Problem 4: write algorithm to find the greater number between two numbers
Step1: Start
Step2: Read/input A and B
Step3: If A greater than B then C=A
Step4: if B greater than A then C=B
Step5: Print C
Step6: End
Problem 5: write algorithm to find the result of equation: ( ) {
Step1: Start
Step2: Read/input x
Step3: If X Less than zero then F=-X
Step4: if X greater than or equal zero then F=X
Step5: Print F
Step6: End
Problem 6: A algorithm to find the largest value of any three numbers.
Step1: Start
Step2: Read/input A,B and C
Step3: If (A>=B) and (A>=C) then Max=A
Step4: If (B>=A) and (B>=C) then Max=B
Step5:If (C>=A) and (C>=B) then Max=C
Step6: Print Max
Step7: End
Example 1: Write an algorithm to determine a student’s final grade and
indicate whether it is passing or failing. The final grade is calculated as the
average of four marks.
Detailed Algorithm
Step 1:
Input M1,M2,M3,M4
Step 2:
GRADE (M1+M2+M3+M4)/4
Step 3:
if (GRADE < 50) then
Print “FAIL”
else
Print “PASS”
endif
Example 2:
Write an algorithm that will read the two sides of a rectangle and calculate its
area.
Input the width (W) and Length (L) of a rectangle
Calculate the area (A) by multiplying L with W
Print A
Algorithm
Step 1:
Input W,L
Step 2:
AL x W
Step 3:
Print A
Example 3:
Write an algorithm that reads two values, determines the largest value and prints
the largest value with an identifying message.
ALGORITHM
Step 1:
Input VALUE1, VALUE2
Step 2:
if (VALUE1 > VALUE2) then
MAX VALUE1
else
MAX VALUE2
endif
Step 3:
Print “The largest value is”, MAX
The taxi algorithm:
1. Go to the taxi stand.
2. Get in a taxi.
3. Give the driver my address.
The call-me algorithm:
1. When your plane arrives, call my cell phone.
2. Meet me outside baggage claim.
The rent-a-car algorithm:
1. Take the shuttle to the rental car place.
2. Rent a car.
3. Follow the directions to get to my house.
1.
2.
3.
4.
The bus algorithm:
Outside baggage claim, catch bus number 70.
Transfer to bus 14 on Main Street.
Get off on Elm street.
Walk two blocks north to my house.
All four of these algorithms accomplish exactly the same goal, but each algorithm
does it in completely different way.
Assignment
For this project you need to pick an everyday or interesting task and create an
algorithm that explains how to do it.
You need to specify what (if anything) is input (like ingredients in a recipe)
The process by which you operate on that input to produce or accomplish a
task
What the output of the algorithm is
What (if any) assumptions are made in the algorithm
What to turn in
Type your algorithm up using the following example as a template.� Name the
task your algorithm describes, the input and output, and then list the steps
involved, numbering each, followed by what your algorithm assumes.
Example
Algorithm: Calling a friend on the telephone
Input: The telephone number of your friend.
Output: None
Steps:
1. Pick up the phone and listen for a dial tone
2. Press each digit of the phone number on the phone
3. If busy, hang up phone, wait 5 minutes, jump to step 2
4. If no one answers, leave a message then hang up
5. If no answering machine, hang up and wait 2 hours, then jump to step 2
6. Talk to friend
7. Hang up phone