Lab - Molecular Models
advertisement

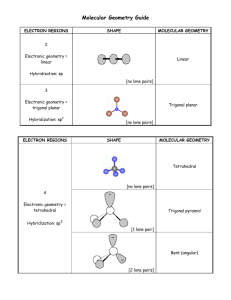
Name: _________________________________ Date: _____________ Period: ____ Lab – Molecular Models Introduction: Lewis structures can be used to predict molecular and ionic geometries (shapes), as well as polarity. Generally, atoms have eight electrons in their outer shell (octet rule). In addition, valence electrons exist in electron domains around atoms in either bonded pairs or non-bonded (lone) pairs. These electron domains can be used to predict the overall geometry of a molecule because electrons repel each other. This method is termed valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. Each electron pair occupies as much space around the nucleus and inner electron shells of the atom as it can, and excludes other electrons from occupying the same space, a consequence of the Pauli Exclusion Principle. In addition to VSEPR theory, orbital hybridization can be used to predict overall electron domain geometry (includes atoms and electron domains) as well as molecular geometry. A hybridization (blending) of s and p orbitals can occur when low energy electrons are promoted to higher energy levels, resulting in a blended orbital of the participating orbitals (i.e., sp, sp2, sp3). In this lab, you will construct molecules from Lewis structures, and correlate molecular shapes with orbital hybridizations. Materials: molecular models kits Methods and Analysis: Construct each of 24 molecular species, and then complete a data table including the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Total valence electrons Lewis structure Total # of electron domains # of non-bonded (lone) electron pairs ABmEn category Predicted overall electron domain geometry Predicted molecular geometry (shape) Predicted bond angle(s) Orbital hybridization (if applicable) Symmetry (symmetrical or asymmetrical) Polarity (polar or nonpolar) Resonance (yes or no) Tips for Modeling Kit: (refer to these tips frequently throughout the lab) -Yellow wood spheres are H and any atom forming only one bond (like F, Cl, etc.). -Red wood spheres are usually O, but not when O is central (2 lab groups will use red clay spheres). -Black wood spheres can be any atom with 4 domains: 4 bonds, 3 bonds and 1 E pair, 2 bonds and 2 E pairs. -Purple or Orange wood spheres are for lone E pairs on the central atom (other e– need not be modeled). -If more 3, 5, or 6 domains (bonds and E pairs) are needed, choose a clay sphere as the central atom. 1 Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: H2 O 8 OR Total # of Electron Domains: 4 # of Lone Electron Pairs: 2 ABmEn: AB2E2 Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: HCN Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: NH3 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: CCl4 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Electron Domain Geometry: tetrahedral Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): bent Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): 109.5o (or 104.5o) Hybridization (or N/A): sp3 Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): 2 Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: CF2Cl2 (CFC or chlorofluorocarbon) Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: BF3 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: SCl4 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: SF6 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): 3 Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: SO2 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: PCl5 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: XeF4 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: IF5 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): 4 Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: CO2 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: NO2 – Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Total Lewis Structure: Valence Electrons: BrF3 Total # of Electron Domains: ___ # of Lone Electron Pairs: ___ ABmEn: ______ Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Electron Domain Geometry: _____________ Symmetrical or Asymmetrical Molecular Geometry (Shape): _____________ Polar Molecule/Ion or Nonpolar Molecule/Ion Bond Angle(s): Resonance (more than one identical structure): Yes or No Hybridization (or N/A): Conclusion: Write a brief conclusion describing what you have experienced regarding VSEPR theory and molecular geometry. Include related concepts like number of domains and hybridization, and symmetry and polarity. 5