Art of Ancient Egypt
advertisement

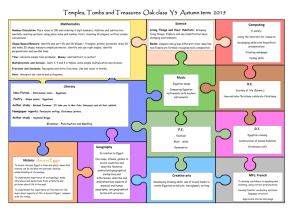
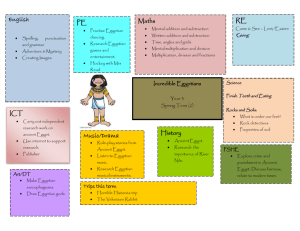
Art of Ancient Egypt Art of Ancient Egypt By Phuong Anh By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt -Content Symbolism Painting Art forms: - Architecture - Music - Pottery - Sculpture By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt -IntroductionAncient Egypt was one of the greatest civilizations in the ancient history, but besides all of the great things that ancient Egyptians have done in the past, have you ever even think about the ART of ancient Egypt ? Besides the amazing things that makes ancient Egypt great, the history of art in Egypt is also quite remarkable, although not much, that’s why some people have difficulties looking for the right book when it comes to art of ancient Egypt, but that’s not such a trouble anymore, correct? You have technology and computers now, so it should be easy, right? But try looking for all that information on the internet; it is any easier than looking for a book? In this book, you will read about the basic information about the art of ancient Egypt. Ancient Egypt is about symbolism, paintings and art forms like architecture or sculpture. Although you may not find many details for adults, but this book is a fine book for any young people who want to know about the history of art of ancient Egypt… By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt Symbolism By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt -SymbolsSymbolism also played an important role in establishing a sense of order. Animals are also often seen in symbolic figures in Egyptian art. Colors are also used: red skin implied strong tanned youth, where as yellow skin was used for women or man who worked indoors; blue or gold indicated divinity because of its unnatural appearance and association with precious materials; and black for royal figures expressed the fertility of the Nile from which Egypt was born. Stereotypes were used to indicate the origins of foreigners. By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt *Some of ancient Egyptian common symbols* -AnkhThis is the symbol of eternal life. Many of the Egyptian gods and goddess are often seen holding the Ankh, sometimes holding it to someone’s lip; this is considered to be an offering of “The Breath of Life”. The Breath of Life is believed to be the breath that the dead will need in the afterlife. -UdjatThis symbol is the eye of Horus. The legend about this symbol was once in an argument, Horus’s eye was tore off by his brother, though it was restored later on. Even though after restoration, Horus offered his eye as a present to the God of Underworld, Osiris, to help him rule the underworld, so it is believed that the eye of Horus became the moon. Apart from this legend, this symbol is also known as the symbol of healing and restoration. -Winged DiskThe Winged Disk was the form that the God Horus Behudety takes in a battle with Seth. According to the Egyptian mythology, God Thoth used his magic and turns God Horus into a disk with magnificent wings, and then Goddess Nekhbet and Uazet joined him in snakes form at his sides in the battle. The disk with magnificent wings, you can also see two snakes on the sides, which is Goddess Nekhbet and Uazet. By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt -Feather of MaatThis is a very common Egyptian symbol and the ‘Maat’ can be seen in Egyptian paintings and art since the Pharaoh also wore it. It was a common belief that this feather was kept on the heart of a person after they died. If the heart weighed more than the feather, it meant that the heart was filled with sin and as a punishment; it will be bait for Ammit. If the heart weighed less than the feather, it meant that the heart was free of sin and that person’s soul would have access to the world of Osiris. Feather of Maat also meant morality, stability, balance and justice. See that the person is wearing what looks like wings, which is the ‘Maat’ and also wearing the ‘Feather of Maat’ on their head. By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt Painting By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt -PaintingAlthough painting remained an accessory to architecture, sculpture and relief, all of the Egyptian reliefs were painted, and less prestigious works in tombs, temples and palaces were just painted on a flat surface. Many ancient Egyptian paintings have survived due to Egypt's extremely dry climate. The paintings were often made with the intent of making a pleasant afterlife for the dead. The themes included journey through the afterworld or protective deities introducing the dead to the gods of the underworld, such as Osiris. Some tomb paintings show activities that the dead were doing when they were still alive and wished to carry on doing for eternity. By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt Art forms -ArchitectureBy Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt People tend to think that Egyptian building styles stayed the same for the whole period of Egyptian history, but that’s not true. Ancient Egypt architecture was the noblest of the ancient arts, although Ancient Egypt architecture began humbly in the adornment of tombs and the decoration of homes. In the early part of the Old Kingdom, the Egyptians built mainly mastabas, a kind of tomb with a flat roof which looks just like a house. Then throughout most of the Old Kingdom, the Egyptians built the pyramid tombs, which are very well known now. And of course they also built smaller buildings like houses and butcher shops. In the Middle Kingdom, the mastaba tomb came back again, but they didn't build any more pyramids. Then in the New Kingdom there was a lot of building that was not tombs like palaces for the pharaohs and especially temples for the gods too. -MusicBy Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt People in Egypt have probably been playing music since the early Stone Age, long before there is any definite evidence of it. The earliest definite evidence of music from Egypt comes from about 3100 BC, at the beginning of the Old Kingdom. Because there wasn't any way of recording music or writing down notes in ancient Egypt, we don't know what Egyptian music sounded like, from pictures, we do know what kind of instruments the Egyptians had used like guitars and harps. And by the New Kingdom period, there were bronze trumpets too. As some picture shows, a lot of Egyptian musicians were women, and music was a good opportunity for women to work at a skilled job. But sometimes Egyptian women musicians had to wear thin or revealing clothes, and dance as well as singing. And some musicians were probably slaves. Musicians often performed at religious festivals, and they also played at private parties as well. -PotteryBy Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt Ancient Egyptians were among the first people to make pottery, beginning at about 4000 BC. Probably Egyptians started making clay pots in order to keep wheat and barley in so it wouldn’t get wet. The earliest Egyptian clay pots have geometric designs on it at first, and were made by hand. By about 3500 BC, Egyptian pottery has designs on it that are very much like the designs on earlier rock carvings. They show people, boats, and animals, and sometimes look like later Egyptian paintings too. Some Egyptians has always thought of pots as being like people in their shape. The part the pot stands on is the foot, the main part is the body, the part where the pot curves in is the shoulder, the narrow part near the top is the neck, and the very edge is the lip. -SculptureBy Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt Egyptians began to carve sculptures in Egypt about 4500 BC, about the same time as in West Asia or the other parts of Africa. These early sculptures are small figurines, mostly of women, but nobody knows why Egyptian artists started making these sculptures. By the time of the Old Kingdom, about 2900 BC, Egyptian artists began to carve life-size stone sculptures. Initially these statues were sitting down, which is a lot easier to carve. Picture gallery By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt Symbolism Painting By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt Architecture By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt Music Pottery By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange Art of Ancient Egypt Sculpture By Phuong Anh / 7 Orange