SL Enzymes KEY
advertisement

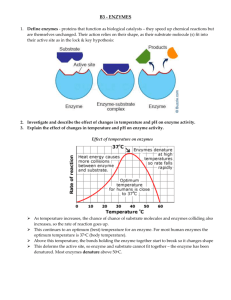
1. C 2. C 3. B 4. E 5. A 6. B 7. C 8. C 9. D 10. A (c) Outline how enzymes catalyse reactions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Enzymes increase rate of (chemical) reaction; Enzymes remains unused/unchanged at the end of the reaction; Enzymelower activation energy of the chemical ; The activation energy of a chemcial is energy needed to overcome energy barrier that prevents reaction; The substrate/ chemical reactant joins with enzyme at active site; When the substrate bonds with the active site of the enzyme they form enzyme-substrate complex; 7. The active site/enzyme (usually) specific for a particular substrate/ chemical reactant as described by the lock and key model; 8. Enzyme binding with substrate brings reactants closer together to facilitate chemical reactions (such as electron transfer); High level Stuff 9. The induced fit model shows how the substrate initiates a change in enzyme conformation (when enzyme-substrate/ES complex forms); 10. This change in enzyme conformation makes the substrate more reactive 11. Students may have an annotated graph showing reaction with and without enzyme; IB Questionbank Biology 1 (a) The activity of enzymes determines the rate at which chemical reactions occur in living organisms. Outline the effects of two factors that can both increase and decrease enzyme activity. Award marks only for the first two factors outlined. (a) temperature; -- 3 Points Max. 1. Rate of reaction increases as temperature increases / rate of reaction decreases as temperature decreases. 2. When temperatures are higher molecules have more kinetic energy / faster movement of molecules means more collisions between enzyme / active site and substrate; 3. Optimum temperature is temperature at which rate of enzyme-catalyzed reaction is fastest; 4. At high temperatures above the optimum temperature for a given enzymes, enzyme will be denatured and stop working; 5. Denatured means change of structure in enzyme / protein resulting in loss of its biological properties / no longer can carry out its function; 6. High temperatures denature an enzyme because too much kinetic energy / vibrations breaks bonds that give enzyme specific shape which change the shape of the active site and therefore decrease the rate of reaction. pH; -- 3 points max 1. 2. 3. 4. enzyme activity is highest at the optimum pH / graph to show this; different optimum pH with different enzymes; Optimum pH is the pH where enzyme activity/ reaction rate is the highest Denaturation of enzymes by high and low pH / extreme pHs because bonds are made and IB Questionbank Biology 2 broken which change the shape of the active site and therefore decrease the rate of reaction. substrate concentration – 3 points max; 1. at low substrate concentrations, an increase in substrate concentration causes an increase in rate of reaction (point a to b on graph -- See below); 2. Higher substrate concentration results in more chance of collision between substrate and enzyme / active site; 3. at a certain level of high substrate concentration, there is no change in rate as the substrate continues to increase in concentration, that is, the reaction rate reaches a plateau on the graph (point c on graph—See below); 4. At the levels of concentration of substrate where the reaction rate plateaus, all of the active sites on the enzymes are occupied/ saturated with substrate; (a) (i) 15.2 mg 3 hrs–1 (allow answers in the range of 15.0 to 15.4) (ii) 1.93 NAG units 3 hrs–1 (allow answers in the range of 1.92 to 1.95) 1 1 (b) You are asked to compare the correlation between men and women, and so you should make comparison about positive, negative or no relationships, and you should also compare strength of relationship (stronger, weaker), and you should compare steepness of the slope of the best fit line 1. Both men and women have a positive relationship; 2. Bothe men and women’s values are very scattered for both; 3. There is a more positive correlation/steeper gradient for men than for women; IB Questionbank Biology 3 4. The data is more scattered in women/greater range in hepatic activity / more scattered/ greater range in men in renal activity; 2 max Evaluate a hypotheses base on data = Clearly state if the data support the hypothesis or not? The explain/ discuss how data supports hypothesis or does not support hypothesis. 1. The hypothesis is supported because there is a positive correlation between both increased hepatic activity and renal damage/ people with more renal damage have more cytochrome activity ( hepatic activity is meant to be an indirect measurement of cadmium exposure/ toxicity). 2. The data shows a difference in the effect between men and women, for example: there is a greater hepatic (liver) effect in women than in men / there is a greater renal (kidney) effect in men than women; 3. While there is a positive relationship between renal damage and hepatic activity, this positive trend does not necessarily prove a direct causal relationship between hepatic and renal function with cadmium toxicity, and thus the hypothesis is not supported by this data 4. There are problems with the data, for example, there is a very wide range of data, which makes it very difficult to evaluate and it is possibly not statistically significant relationship (i.e. no R-Value/ correlation coefficient is reported) ; 5. From this data it is impossible to establish a causal relationship because there is no control group / other factors may be involved/ hepatic activity might not be a good measurement of cadmium toxicity;; IB Questionbank Biology 4