Study Guide Unit 9 - The Water Cycle

Name____________________
Test Date____________
Parent Signature____________________________
Study Guide Unit 9 - The Water Cycle
This unit addresses the movement of water through the crust, ocean, and atmosphere
#1 Students will recognize the significant role of water in earth processes.
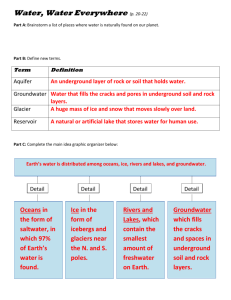
Explain that a large portion of the Earth’s surface is water, consisting of oceans, rivers, lakes, underground water, and ice.
Relate various atmospheric conditions to stages of the water cycle.
Describe the composition, location, and subsurface topography of the world’s oceans.
Explain the causes of waves, currents, and tides.
#2 Students will describe various sources of energy and with their uses and conservation.
Explain the role of the sun as the major source of energy and its relationship to wind and water energy.
Questions – students will be asked to answers these questions throughout the unit.
#1 How does the location of water on Earth's surface and the conditions of the atmosphere affect its path through stages of the water cycle?
#2 How does the amount of saltwater differ from the amount of freshwater on Earth?
#3 Does salt water and fresh water move through the same water cycle?
#4 Where does salt in the ocean come from?
#5 Why does water continually move through the water cycle?
SALT WATER vs. FRESH WATER
1. H
2
O is a compound that can exist as a __________________, _____________________, or ___________.
2. One water molecule has ___________________________ & ___________________________________
3. Fresh water is water that is ___________________ and has little or no taste, color, or odor.
4. Freshwater can be found in ___________________, many ______________,underground _____________, and in the form of ___________________.
5. All precipitation that falls to the surface of Earth is __________________________.
6. Salt water is water that contains ______________________________ and other ____________________.
7. Salt water is not for _________________________________________. Meaning humans cannot
__________________ saltwater or _______________saltwater.
8. The salt in the Earth’s oceans comes from ________________ dissolved from ________________ as water moves toward the oceans.
9. Most of the water on the Earth is _____________________ . Only a small amount is ________________
10. The majority of the ________________ ________________is covered with ________________ .
11. The water on Earth is not ________________ _________. Most of it is unsuitable _________________.
12. The ________________ ___________ of water on the Earth is ________________ cubic miles.
13. _____ of Earth’s water is in the oceans as salt water.
14. _____ of Earth’s water is fresh water.
15. _____ of Earth’s water is frozen in ice caps and glaciers.
16. _____ _____ (0.65%) of Earth’s water is fresh water in ___________________ , ___________________
,
____________________ , and ____________________ in the atmosphere.
WATER CYCLE
17. ________________ water) cycles through states of matter in the ________________ based on atmospheric ________________ .
18. The water cycle has three stages: ___________________ , ___________________ , _________________
19. The process in which water changes from ________________ _______________ is called evaporation.
20. ________________ _____is the evaporation of water from plants.
21. Condensation is the process in which ___________________________ in the atmosphere
____________________________ .
22. When water falls ________________ ______________ as ________________ or ________________ it is called precipitation.
23. The _____________________________ in and out of the atmosphere plays an important role in determining _____________________ patterns.
24. Water evaporation from the surface of the earth, ________________ and ________________ condenses into rain or snow, and ___________________________ to the surface.
25. Rain, snow, sleet, and hail are all for ___________________________ .
26. Rain falls to the ground and collects in ________________ that flow into ________________ , that eventually lead to the world’s __________________.
27. The water, which is a solvent, _________________________________collects in rivers and
__________________, __________________, &____________________________________, and much of it flows back into the __________________.
28. Most rain falls on the Earth’s ________________ because most of Earth is covered by _______________.
29. Most of the water that evaporates on Earth, evaporates from __________________. The ______________ and __________________are left behind in the ocean.
30. Salts have become concentrated in the _____________(compared with freshwater) because the sun's heat causes the _____________________________, leaving the _________________________________________
31. If less fresh water flowed into the oceans in the future, the world’s oceans would become ________ salty.
32. If more fresh water flowed into the world’s oceans, they would become ___________ salty.
GROUNDWATER
33. 2% of Earth’s __________________is frozen in ice caps and glaciers.
34. Less than 1% (0.65%) of Earth’s water is __________________in lakes and streams, groundwater, and water vapor in the atmosphere.
35. Most of the __________________on Earth is located in __________________ and __________________.
36. Groundwater is water that occurs as a ____________________________________that is dispersed through ____________________________________, __________________, __________________,
__________________, and __________________ in bodies of rock or sediment.
37. Porous means the rock has ___________________________ and things can easily __________________.
38. When something is __________________________ then water cannot easily penetrate it.
39. An aquifer is an _____________________ layer of ______________________or sediment that contains
__________________.
40. A layer of ________________________ rock is located immediately below an aquifer.
41. A layer of __________________ rock is located above an aquifer.
42 Aquifers have rocks that have very large __________________ in them. This allows them to hold large amounts of __________________.
43. How do we get water out of aquifers? _______________________________________________________
44. What is saltwater intrusion? ______________________________________________________________
45. A __________________is formed when heat from magma __________________________________and forces it to shoot out of the __________________.
46. Water in an ________________________________ flows naturally out of the ground because of pressure.
47. Springs are ____________________________________locations where ground water comes to the surface and wells are ____________________________________designed to bring water to the surface from deep __________________
WATER – THE IMPORTANT RESOURCE
48. Human have access to use ____________________________________of the water on Earth for
__________________ and ____________________________________.
49. This less than one percent is also used for _____________________, _____________________,
_____________________, __________________and __________________,
_______________________, and many other purposes.
50. Unless humans use freshwater __________________,rivers, lakes, and groundwater can become
__________________ or __________________, and unavailable or ___________________________.
51. Much of our municipal and industrial water comes ____________________________________.
52. Many countries on Earth are experiencing a ____________________________________.
53. Water is a valuable ______________________________.
54. Air pollution causes __________________. Rainwater picks up particles and gases when it falls through the air. If the air is__________________, the rainwater becomes __________________.
55. The acid rain can kill ________________ and __________________________ in lakes, rivers, and ponds.
56. Where do most people get their drinking water? __________________________.
57. The Floridian Aquifer stretches from __________________________ and __________________________
58. Why is the Floridian Aquifer important to ME? ______________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
59. Why is it unwise to drink from streams and rivers? ___________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
60. How do cities clean the water that comes out of your house? ________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
61. How does dumping toxic material in one state hurt people in another state? ________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
62. Why don’t more nations use ocean water for farming and human consumption? ____________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
VOCABULARY
The Water Cycle, deposition, gravity, composition, conservation, evaporation, condensation, precipitation transpiration, impermeable, permeable, aquifer, water table