ANSWER KEY Water water everywhere
advertisement
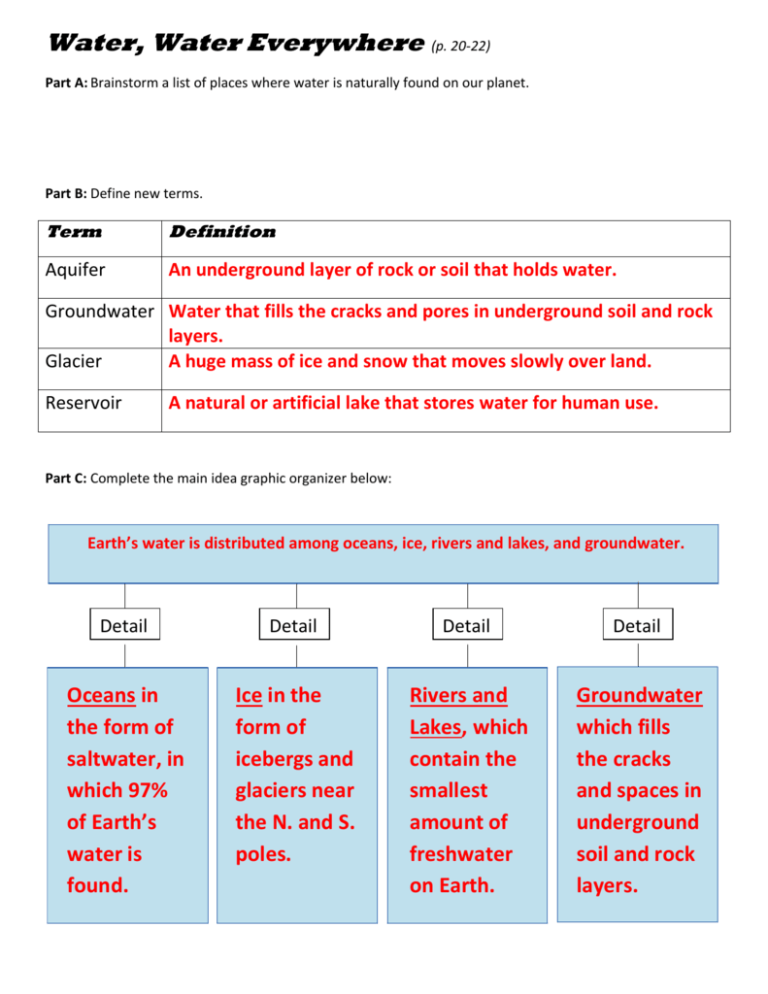
Water, Water Everywhere (p. 20-22) Part A: Brainstorm a list of places where water is naturally found on our planet. Part B: Define new terms. Term Definition Aquifer An underground layer of rock or soil that holds water. Groundwater Water that fills the cracks and pores in underground soil and rock layers. Glacier A huge mass of ice and snow that moves slowly over land. Reservoir A natural or artificial lake that stores water for human use. Part C: Complete the main idea graphic organizer below: Earth’s water is distributed among oceans, ice, rivers and lakes, and groundwater. Detail Detail Detail Detail Oceans in the form of saltwater, in which 97% of Earth’s water is found. Ice in the form of icebergs and glaciers near the N. and S. poles. Rivers and Lakes, which contain the smallest amount of freshwater on Earth. Groundwater which fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers. Part D: Use the graph on p. 20 in the textbook to answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Which source of fresh water is the largest? Ice 76% 2. Is this a source of freshwater commonly used by humans for drinking, watering the lawn, cleaning, etc.? Explain. No – frozen at N. and S. poles and not easily accessible! 3. Approximately what percentage of the Earth’s fresh water is ground water? 12% + 11% = 23% groundwater (both shallow and deep) 4. Where is most of Earth’s total water found? In the oceans 5. What percentage of the Earth’s fresh water is usable by humans (ground and surface waters)? Explain. 12% + 11% + 0.34% = 23.34% (groundwater + lakes and rivers) 6. What percentage of the Total Water on Earth is usable by humans (ground and surface waters)? Show your work and explain. Freshwater = 3% of total water on Earth *need to find 23.34% of this 3% 3 X 23.34% = 0.7% total water on Earth usable by humans.