Earth Layers & Earthquakes Study Guide Draft
advertisement

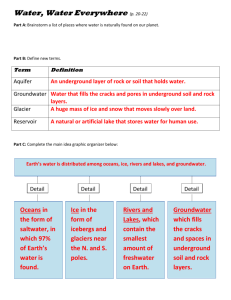
Water Cycle Test Study Guide I. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. When water changes from a gas to a liquid this is condensation. 2. When water changes from a liquid to a gas this is evaporation. 3. Solid or liquid water that falls to the ground is precipitation. 5. Water can exist in the following states of matter: gas, solid, and liquid. 6. Ocean water has a higher concentration of salt than fresh water. 7. What are three things you can do to help keep our rivers, streams, lakes, and beaches clean? write congress, help clean up beaches, and teach others about the dangers of polluting the oceans. 8. Where do most people get their drinking water? Underground aquifers. 9. How is acid rain formed? Exhaust from cars and burning coal to make electricity. 10. How does acid rain hurt the planet’s ponds and lakes? The acid kills the little fish and then the bigger fish have nothing to eat; eventually all the fish die. 11. How large is the Floridian Aquifer? It stretches between the South Carolina to all of Florida. 12. What is an artesian spring? Water that flows naturally out of the ground because of pressure. 13. What is the difference between a well and a spring? Springs are naturally formed locations where ground water comes to the surface and wells are man made structures designed to bring water to the surface from deep underground. 14. What type of rocks are in an aquifer? Rocks that have very large pores in them that allows them to hold large amounts of water. 15. Rain falls to the ground and collects in streams that flow into rivers, that eventually lead to the world’s oceans. 16. Rain, snow, sleet, and hail are all names for precipitation. 17. 97 % of the Earth’s water is in the oceans. 18. 69 % of the Earth’s fresh water is frozen. 19. 30 % of the Earth’s fresh water is underground. 20. Less than 0.65 % of the Earth’s fresh water is above ground and readily available for human consumption. 21. Porous means the rock has many holes and things can easily penetrate it and impermeable means the object does not have many holes in it and things cannot easily penetrate it. 22. Most rain falls on the Earth’s oceans and most of Earth is covered by water. 23. The salt in the Earth’s oceans comes from minerals dissolved from rocks as water moves toward the oceans. 24. If less fresh water flowed into the oceans in the future, the world’s oceans would become more salty. Conversely, if more fresh water flowed into the world’s oceans, they would become less salty. 25. Another term for groundwater is aquifer. 26. T F Many countries on Earth are experiencing a water shortage. 27. T F Water is a very valuable natural resource. 28. Why don’t more nations use ocean water for farming and human consumption? Cost. 29. The cap rock is a layer of rock immediately above an aquifer. 30. A layer of impermeable rock is located immediately below an aquifer. 31. What is saltwater intrusion? Saltwater from the ocean entering a fresh water aquifer. 32. How is saltwater intrusion affecting Effingham County? The aquifer where we get our fresh water is slowly losing water. Saltwater is beginning to enter the aquifer. If this process continues, it could negatively affect farming and drinking water for a very large area. 33. How do cities clean the water that comes out of your house? Cities use wastewater treatment plants to clean the water. 34. How does dumping toxic material in one state hurt people in another state? The material can sink underground and enter the underground aquifers. 35.How do we get water out of aquifers? We use pumps to pull the water up from the aquifer. 36. Rivers, streams, groundwater, and lakes are all examples of freshwater. 37. A man made structure that stores water above ground is a(n) reservoir. 38. Why is it unwise to drink from streams and rivers? Microscopic plants and animals live in the water and can cause humans serious illnesses and can lead to death. 39. A geyser is formed when heat from magma forces water to shoot out of the ground. II. Vocabulary (Review the following terms prior to the test) Cap Rock Porous Artesian Spring Transpiration Hail Sleet Rain Snow Water Vapor Surface Water Runoff Infiltration Sodium Chloride Groundwater - Water that is stored underground Eutrophication - Increase in nutrients in a lake or pond that can increase algae and kill off the fish. Evaporation - Process where liquid changes into gas Water cycle- Continuous movement of water on Earth, through the atmosphere and in the living things on Earth. Impermeable - Will not allow water to pass through Fresh Water – water that is not salty. Most lakes and rivers are made up of this. Precipitation - Any liquid or solid water that falls to Earth's surface Desalination - Process of removing salt from ocean water. Drainage basin - An area of land where water drains into a stream. Water Table - highest part in the ground that is completely filled with water Turnover - yearly rising and sinking of cold and warm water layers in a lake Iceberg - mass of floating ice Permeable - allowing the passage of water Artesian Well - pressurized water that flows upward to the surface. Condensation - process where gas changes into a liquid Divide - a ridge where water drains to one side or the other Salt - item in most water on Earth that makes 97% of our planet’s water undrinkable. Aquifer - underground lake