Pregnancy PowerPoint Student Packet Notes
advertisement

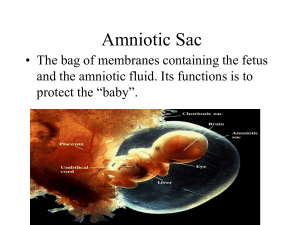
Name:______________ Block:______________ Pregnancy & Birth Terminology Student Packet 1. Signs of Pregnancy: a. Missed ______________ period b. Excessive tenderness in her breasts c. ______________ d. Change in appetite e. Morning sickness f. May have spotting or ____________, irregular menstrual flow 2. ______________ _______________: This is a quick simple test that test for the hormone ________________within the females urine. HCG is released by a women when the egg attaches to the lining of the Uterus. HCG is only released when a female is pregnant. (_________ = Early Pregnancy Test). 3. Blood Test: This test also detects HCG, but you must go to a doctor and have blood drawn. Most people get the blood test after they tested positive for the urine test. 4. Pregnancy is based on 40 weeks of development. 10 months in total. a. 1st month we DO NOT count due to the fact of not knowing b. Broken down into three sections called trimesters 5. Medical Specialist a. ___________________: Doctor who specializes in care of a pregnant women and the developing fetus. b. ___________________: Doctor who specilise in care of the female reproductive system. 6. Uterus: a. Is a muscular ______________ that ______________ and ______________ the ______________ ovum during pregnancy and ______________ during childbirth to help with ______________. 7. Fertilization: a. Is joining of an egg cell and a sperm cell Name:______________ Block:______________ b. ______________________ ______________________: i. Where fertilization takes place, connects an ovary and the uterus. The process begins when an egg is released from one of the woman’s ovaries and enters the fallopian tubes. The egg remains in the fallopian tube for two days, in order for fertilization to take place the sperm must also be in the fallopian tube. 8. Ovum: a. The _________ _________; if fertilization occurs, the ovum develops into an embryo. 9. Zygote: a. The cell produced when a sperm fertilizes an egg; contains _____________________ material that forms the baby. 10. ______________________________: a. A thin-walled hollow structure in early embryonic development that contains a cluster of cells called the inner cell mass from which the embryo arises. The outer layer of cells gives rise to the ___________________ and other supporting tissues needed for fetal development within the uterus while the inner cell mass cells gives rise to the tissues of the body. 11. Embryo: a. Is a developing baby through the __________ month of growth after conception: b. The rapidly dividing mass of cells inside the women’s uterus. 12. Fetus: a. Is a developing baby from the __________ ___________ after _____________ until birth. b. The name given to the embryo from the third month on. 13. Placenta (purpose): a. Supplies fetus with _____________ b. Supplies fetus with ______________ c. Passes out ___________ from the fetus Name:______________ Block:______________ 14. Umbilical Chord: a. Rope like structure that connects the _____________ to the placenta 15. What 3 vessels are contained in the cord? a. 1 large vein b. 2 ______________ 16. Amniotic Sac: a. ___________________ Control b. Protection from _______________ c. Barrier to __________________ 17. Types of insemination: a. Artificial Insemination: i. Procedure when sperm is ________________ into the female with a syringe b. In-vitro Fertilization: i. Procedure that involves _____________ a living egg from a female, inseminating the egg with a donor sperm and returning the _________________ egg back into the woman 18. Why is prenatal care important to the mother and the baby? List at least 3 reasons a. If baby doesn’t receive proper ______________ it may cause premature birth. b. A female should not drunk alcohol when pregnant. This can cause ___________ ____________ _______________, which is the presence of severe birth defects. c. Females should not __________________ or inhale smoke. This can cause smaller babies and unhealthy babies. 19. Why is diet and exercise important to the mother and baby? Name:______________ Block:______________ a. It increases the chances of a _________________ baby. b. Increases the chances of having a proper birth weight for the baby. c. Keeps the mother healthy during pregnancy. Also helps the mother lose the weight faster after pregnancy. d. Decrease chances of birth ________________ 20. Types of tests to check for abnormalities of the fetus a. _____________________: Test using sound waves to depict an image of the developing fetus. Usually performed at 10 weeks and on. b. Harmony: i. Harmony is more accurate than traditional Down syndrome _blood tests and much less likely to give a false-positive result. That means there will be much less chance your doctor would recommend follow-up testing, such as amniocentesis. ii. Harmony also tests for two other genetic conditions, trisomy 18 (Edward syndrome) and trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome). iii. In addition, with Harmony you have the option to evaluate X and Y sex chromosomes. c. Amniocentesis test: i. Checks for _______________________ abnormalities ii. Spina bifida, down syndrome, hemophilia, tay-sachs, sickle cell anemia d. Chronic villus sampling test (CVS test): i. Done during early pregnancy ii. A biopsy is taken of the villi in the _____________________. iii. Sickle cell anemia, hemophilia 21. Stages of pregnancy: a. First trimester (Months 1-3) (Initial development and rapid growth): i. At the end of the first month, the embryo has a _____________, a twolobed brain, and a spinal cord. ii. By the end of the second month, the embryo is recognizable as a human and is called a _____________. After two months, the embryo has started to form arms and legs as well as fingers, ears, and toes. Name:______________ Block:______________ The fetus can be visibly identifies as a male or female. By the end of the first trimester, the heart has four chambers. b. Second trimester (Months 4-6) (Fetus Continues to form): i. By the end of the fourth month, fingernails, toenails, eyebrows, and eyelashes have developed. ____________ begin to form, lips appear, and head hair may begin to grow. Movement of the _______________can be felt by the mother. The fetus can bend its arms and make a fist. During the fifth month, the heartbeat can be detected by a stethoscope. ii. By the end of the sixth month ____________ (keeps body from dehydrating and skin from getting wrinkled) appear on baby. c. Third trimester (Months 7-9) (Growth): i. By the seventh month ____________(fine hair grown to insulate the fetus) appears on the baby. ii. By the eighth months fetus growth slows down and moves into a ______________ - ____________ position. iii. By the ninth month the fetus is full term. Skin is smooth and waxy looking. The eyes are usually gray. Languo drops off. 22. Signs of Labor: a. The __________________: i. The mucous plug in the cervix, which acts as a seal during pregnancy, is passed as a blood stained or brownish discharge. ii. Contractions: Coordinated muscular contractions are generated in the upper part of the uterus, the fundus. This helps to gradually open, or dilate, the cervix. iii. Water breaks: 1. The ______________ ________ (membrane) around the baby ruptures, or breaks, allowing colorless amniotic fluid to pass out through the birth canal. 23. Stages of labor: a. _____________________ ______ _______________________: i. Longest stage of labor: Name:______________ Block:______________ ii. _________________ opening enlarges eight to ten centimeters, which is wide enough for the baby to move through. b. Delivery of the baby: i. Begins when cervix is completely ________________ ii. The baby moves farther down the birth canal, usually head first. The mother pushes, and the muscles in the ________________ contract to push the baby out. iii. Baby’s head will be visible, which is called crowning. iv. Ends with the delivery of the baby c. Delivery of the ____________: i. _________________ of the ___________________, which is the placenta that is expelled after delivery. If this does not occur naturally the physician removes it. 24. Crowning: a. The appearance of the baby’s _________________ during delivery. 25. Types of Birth: a. Natural birth: i. Delivery of a baby without using ______________ or surgery during birth. b. Induced labor: i. The __________________ of uterine contractions before they occur spontaneously. c. __________________ birth i. When baby delivered either foot first or buttocks first. 26. Types of Pregnancy: a. Inducing labor: i. __________________ given or water sac broken by plastic hook (amniohook) b. _______________ Section (C-Section): i. A form of childbirth in which a surgical incision is made through a mother's ________________ and uterus to deliver one or more babies. c. Epidural: i. A shot administered in the woman’s lower back to aid in ________________ relief. Name:______________ Block:______________ d. __________________________: i. An incision between the vagina and anus (perineum) help with crowning of the baby, to prevent muscles from tearing. e. Vacuum extraction: i. assist mother if she becomes too tired, cup on baby’s head with slight suction f. Forceps: i. guide baby’s head out of birth canal 27. Classes a. __________________: Breathing method used during the delivery process to redirect the focus from pain. 28. Birthing Options: a. Hospital: i. Safest and _________________ method of delivery to receive immediate medical treatment b. Home Birth: i. Comfort of delivery at own home, medical assistance is still needed c. Water Birth: d. Is for women with “____________________” pregnancies, drug free births and minimal intervention e. ___________________ ______________________: i. Are certified house nurses ii. The birth can take place at multiple different locations including a hospital, home or center f. Birth Center: i. Birth centers are for women who want a certain comfort zone and few people around 29. Birthing Positions: a. Occiput Posterior: (Most common) Head down, chest facing front of the mother. Name:______________ Block:______________ b. Occiput Anterior: Head down, baby’s back facing front of mother. c. Left Occiput Transverse: Head down, baby’s facing left hip. d. Right Occiput Transverse: Head down, baby’s facing right hip. 30. _________________ __________________: Is an assessment test on a scale of 1-10. Performed by a pediatrician. 7 or higher indicates baby in good condition. 4 to 6 babies may need assistance. Under 4 baby may need life saving techniques. 31. Types of disabilities a. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS): i. Caused by alcohol consumption during pregnancy. ii. May cause: 1. ___________________ ___________________ 2. Low birth weight 3. Small head 4. Abnormal facial features 5. Abnormalities in the heart 6. ____________________ _________________________ b. Down Syndrome: i. Environment and genetics ii. Extra _______st chromosome c. Cleft lip/palate: i. Environment and genetics ii. Two sides of upper lip do not grow together properly d. Club foot: i. Environment and genetics ii. One or both feet twisted (present at birth) e. Cystic fibrosis: i. Genetics ii. Thick mucus interferes with breathing, blocks lungs, and causes coughing. f. Diabetes: Name:______________ Block:______________ i. Environment and genetics ii. Extreme thirst and increased appetite. iii. Caused by obesity and is predicted that every 1 out of 3 children will be born with type two diabetes g. Hemophilia: i. Usually genetic ii. Blood does not clot properly h. Sickle cell Anemia: i. Genetics ii. Red blood cells are sickle-shaped instead of round-shaped. Severe Anemia i. Spina Bifida: i. Caused by environment and genetics ii. Spinal cord forms outside of spinal column iii. Problems range from loss of bowel and bladder control to paralysis and mental retardation j. Tay-Sachs: i. Genetics ii. Nervous system disorder iii. Baby will have poor psychomotor development, weakness and sluggishness. Eventually blindness, paralysis, mental retardation and seizures occur. Death usually takes place by five years of age