Chapter 21APES
advertisement

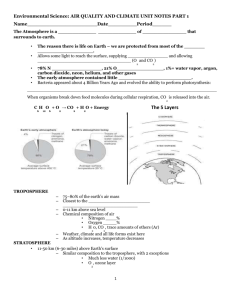
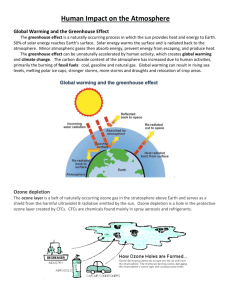
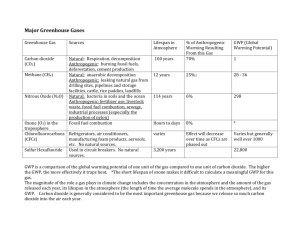
21 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. Which of the following best describes the earth's average surface temperature for the past 900,000 years? a. a steady warming trend b. fairly steady temperatures until recently c. many fluctuations of several degrees centigrade d. fairly steady with occasional cool spells e. fairly steady with a recent cooling trend 2. Over the last million years, glacial periods lasting about ____ years have alternated with interglacial periods lasting about ____. a. 10,000 . . . 100,000 b. 1,000 . . . 10,000 c. 10,000 . . . 10,000 d. 1,000 . . . 100,000 e. 10,000 . . . 1,000 3. The greenhouse effect is best described as a. consensus science. b. pioneer science. c. fantasy. d. a convention of florists. e. junk science. 4. The major greenhouse gases include all of the following except a. chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). b. carbon dioxide and water vapor. c. sulfur dioxide. d. ozone. e. nitrous oxide. 5. The two predominant greenhouse gases in the troposphere are a. carbon dioxide and ozone. b. carbon dioxide and water vapor. c. nitrogen and water vapor. d. nitrous oxide and sulfur dioxide. e. carbon dioxide and nitrogen. 6. Which of the following statements about the greenhouse effect is false? a. The amount of heat trapped in the troposphere depends on concentrations of greenhouse gases. b. The greenhouse effect is a new theory that explains the warming of the atmosphere. c. Heat trapped by greenhouse gases keeps the planet warm enough for life. d. The two predominant greenhouse gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide. e. It has been confirmed by numerous lab experiments and measurements of atmospheric temperatures at different altitudes. 7. All of the following greenhouse gases have increased in recent decades except a. carbon dioxide. b. methane. c. water vapor. d. nitrous oxide. ____ 8. ____ 9. ____ 10. ____ 11. ____ 12. ____ 13. ____ 14. ____ 15. ____ 16. e. CFCs. Increased greenhouse gases originate from a. burning fossil fuels. b. use of CFCs. c. deforestation. d. all of these answers e. none of these answers Estimated variations in the earth's mean surface temperature over the past 135 years correlate closely with a. ozone. b. water vapor. c. CFCs. d. carbon dioxide. Since 1861, mean global temperature has risen ____ degree(s) centigrade. a. 0.1-0.3 b. 0.6-0.7 c. 0.8-1.1 d. 1.0-1.5 e. 1.5-2.0 Initial conditions entered into a climate computer model might include all of the following except a. temperature b. air pressure. c. an equation describing the flow of solar radiation. d. concentrations of greenhouse gases. e. relative humidity. Boundary conditions entered into a climate computer model would include a. measurements of concentrations of greenhouse gases. b. measurements of atmospheric temperature. c. mathematical equations describing the flow of energy in the atmosphere. d. mathematical equations describing the flow of water in the oceans. e. measurements of atmospheric pressure. Correspondence between climate models and the real world depends upon a. chaos. b. the design and assumptions of the model. c. negative feedbacks. d. positive feedbacks. e. all of these answers The greatest uncertainty in current climate models comes from a. measurements of air pressure. b. measurements of wind speed and direction. c. patterns of variation in solar radiation. d. the effects of clouds and ecosphere on climate. e. measurements of air temperature. Major climate models project all of the following except a. a 1.0- to 3.5-degree centigrade rise in Earth's mean surface temperature by 2100. b. an Earth warmer than at any time in the last 10,000 years. c. the falling of global sea levels. d. more warming in the Northern Hemisphere than in the Southern Hemisphere. e. a 2.0- to 3.5-degree centigrade rise in Earth's mean surface temperature by 2050. All of the following have been reported and are possible signs of global warming except ____ 17. ____ 18. ____ 19. ____ 20. ____ 21. ____ 22. ____ 23. ____ 24. a. spread of some tropical diseases away from the equator. b. bleaching of coral reefs in tropical areas with warmer water. c. homestead farming in Antarctica. d. increased retreat of some glaciers on the tops of mountains in the Northern Cascades. e. northward migration of some warm-climate fish. We have the most certainty about a. variations in solar output. b. the role the oceans will play in global warming. c. patterns of glacial and interglacial periods in Earth's history. d. the role of polar ice in global warming. e. how changes in the earth's reflectivity will affect atmospheric temperature. We are uncertain about how a. carbon dioxide will affect the rate of photosynthesis. b. increased temperatures will affect insect populations. c. gas trapped in the permafrost will affect global warming. d. air pollution might affect climate. e. all of these answers Solar output varies in 11-year and 22-year cycles by about a. 0.001%. b. 0.01%. c. 0.1%. d. 1.0%. e. 2.0%. About 29% of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere by human activities a. remains in the atmosphere. b. is absorbed by the oceans. c. is absorbed by the growth of plants. d. is absorbed by the soil. e. none of these answers Pollutants might affect climate change by a. cooling effects of particles from volcanic eruptions. b. warming and cooling effects from sulfur dioxide emissions. c. cooling effects from particles in smoke from large-scale burning. d. all of these answers e. none of these answers As global warming progresses, methane a. might be absorbed as permafrost melts in the arctic tundra. b. might be absorbed from natural wetlands with rising carbon dioxide. c. may be released from oceanic mud as ocean waters warm. d. may be reduced by bacteria in tundra soils. e. all of these answers Which of the following possible consequences of global warming represents a negative feedback loop? Methane a. might be released as permafrost melts in the arctic tundra. b. might be released from natural wetlands with rising carbon dioxide. c. may be released from oceanic mud as ocean waters warm. d. may be rapidly oxidized by bacteria in tundra soils. e. all of these answers Projections from global climate models might be off by a factor of ____ 25. ____ 26. ____ 27. ____ 28. ____ 29. ____ 30. ____ 31. ____ 32. a. 10. b. 5. c. 2. d. 50%. e. 1. Evidence indicates that climate belts would shift toward the poles ____ miles for every 1°C increase. a. 10-30 b. 30-60 c. 60-90 d. 90-120 e. 120-150 Regarding food production, global climate models have projected a a. 10% to 50% loss in current cropland area. b. 10% to 50% gain in current cropland area. c. no change in the amount of land available to grow food. d. 10% to 70% gain in yields of food crops. e. 20% to 75% loss in current cropland area. In the event of global warming, food production might be negatively affected by all of the following except a. poorer soil in new crop-growing regions. b. increased insect populations. c. lack of irrigation water in some areas. d. decreased UV radiation resulting from increased ozone. e. changes in crop yields. The consequences of rapid climate change over decades might include a. premature deaths from lack of food. b. reduction in earth's biodiversity. c. social and economic chaos. d. increased death from heat and disease. e. all of these answers Tree species typically move ____ mile(s) per decade. a. 1 b. 5 c. 10 d. 20 e. 50 If climate belts move faster than trees migrate, there could be a. a large increase of forest area. b. mass extinctions of species that couldn't migrate. c. an increase in forest diversity. d. tropical forests in New England. e. all of these answers A warmer world is least likely to result in a. decreased food production. b. reductions in biodiversity. c. a rise in sea level. d. more moderate weather. e. spread of tropical diseases. A rise in sea level is least likely to a. flood areas where one-third of the world's human population lives. ____ 33. ____ 34. ____ 35. ____ 36. ____ 37. ____ 38. ____ 39. ____ 40. b. save the coral reefs. c. accelerate coastal erosion. d. contaminate coastal aquifers. e. disrupt coastal fisheries. In a warmer world, we would expect more a. droughts. b. hurricanes. c. prolonged heat waves. d. desert expansion. e. all of these answers Which of the following niches is likely to be most affected by global warming? a. generalist b. specialist c. keystone d. indicator e. spectator Which of the following statements about the potential effects of global warming on human health is false? a. Food and freshwater supplies are likely to be disrupted. b. People are likely to be displaced. c. Insect-borne diseases are likely to decrease in today's temperate zones. d. Sanitation systems in coastal cities may be flooded. e. There will likely be increased respiratory disease. In a warmer world, increasing numbers of environmental refugees would likely cause a. political instability. b. more good will among people. c. the quicker emergence of the fourth world order. d. quicker evolutionary adaptation among humans. e. a lower death rate. Scientists who claim the global climate system is so complex we will never have the level of certainty wanted by decision makers urge a. take no action now because global warming is all hype. b. take action now based on the precautionary principle. c. take no action until we get more data. d. continuing monitoring of the data. e. take no action until we see a greater effect. The boiled frog syndrome least exemplifies which of the following positions on global warming? a. no-problem b. waiting c. precautionary d. frogs have nothing to do with us or global climate change e. none of these answers The quickest, cheapest, and most effective way to reduce the buildup of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is to a. switch from fossil fuels to nuclear fuels. b. increase the efficiency of energy use. c. plant trees to trap more carbon dioxide. d. stop deforestation. e. slow population growth. The threat of global warming can be addressed by a. using energy more efficiently. ____ 41. ____ 42. ____ 43. ____ 44. ____ 45. ____ 46. ____ 47. b. halting deforestation. c. slowing population growth. d. shifting to renewable resources. e. all of these answers All of the following are prevention approaches to global warming except a. taxing gasoline and carbon dioxide emissions. b. shifting to perpetual and renewable energy sources. c. improving energy efficiency; transfer energy-efficiency and pollution prevention technologies to developing countries. d. dispersing methane from landfills to prevent explosions. e. slowing population growth. Prevention approaches to global warming include all of the following except a. increase beef production to strengthen public health. b. reduce deforestation. c. switch to sustainable agriculture. d. slow population growth. e. improve energy efficiency. It has been suggested that the threat of global warming can be addressed by all of the following "technofixes" except a. adding iron to the oceans. b. using foil-surfaced sun shields in space. c. injecting sulfate particulates into the stratosphere. d. covering the oceans with Styrofoam chips. e. releasing billions of helium-filled reflective balloons into the atmosphere. At the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro, ____ nations committed themselves to reducing greenhouse gas emissions to 1990 levels by the year 2000. a. 25 b. 50 c. 75 d. over 100 e. 150 The 1997 Kyoto treaty to reduce global warming would a. not require developing countries to make any cuts in their greenhouse gas emission unless they choose to do so. b. allow emissions trading. c. allow forested countries to get a break in their quotas. d. all of these answers Currently developing countries contribute ____ of global carbon dioxide emissions with a doubling time of ____ years. a. 40%. . . 14 b. 40%. . . 28 c. 50%. . . 50 d. 60%. . . 14 e. 50%. . . 16 Which of the following statements is false? a. The formation of the ozone layer enabled life on land to evolve. b. CFCs are odorless and stable. c. CFCs are nonflammable, nontoxic, and noncorrosive. d. Fluorine atoms are most responsible for the breakdown of ozone to molecular oxygen. ____ 48. ____ 49. ____ 50. ____ 51. ____ 52. ____ 53. ____ 54. ____ 55. e. CFCs are cheap to produce. The ozone layer is most effective in blocking a. UV-C, the highest-energy UV band. b. UV-B, the middle-energy UV band. c. UV-A, the lowest-energy UV band. d. CFCs. e. UV-A, the highest-energy UV band. Chlorofluorocarbons are a. nontoxic. b. corrosive. c. odorous. d. flammable. e. expensive. Chlorofluorocarbons are used in all of the following except a. air conditioners. b. aerosol spray cans. c. sterilants for hospital equipment. d. fire extinguishers. e. cleaners for computer chips. The story of the discovery of the effects of CFCs and the political response to that knowledge best illustrates which of the following components of complex systems? a. negative feedback loop b. positive feedback loop c. synergistic interaction d. lag time e. all of these answers Which of the following statements is false? a. Over 44 years passed from the first production of CFCs until the first awareness that they could cause environmental damage. b. CFCs are stable, odorless, nonflammable, nontoxic, and noncorrosive chemicals. c. CFCs are found in bubbles in Styrofoam and insulation. d. CFCs are important because they help screen out ultraviolet radiation from reaching Earth's surface. e. CFCs remain in the troposphere because they are insoluble in water and chemically unreactive. Which of the following statements is false? a. CFCs are relatively unreactive compounds. b. CFCs are heavy molecules that will sink in the atmosphere. c. Ultraviolet radiation will cause CFCs to break down and release chlorine. d. One chlorine molecule may convert 100,000 molecules of ozone to molecular oxygen. e. all of these answers Between the first warnings about CFCs from the scientific community and a response to reduce CFCs from the political community there was a ____-year lag. a. one b. five c. ten d. fifteen e. twenty-five All of the following chemicals are ozone-eaters except ____ 56. ____ 57. ____ 58. ____ 59. ____ 60. ____ 61. ____ 62. ____ 63. a. methyl bromide. b. PCBs. c. halons. d. methyl chloroform. e. CFCs. CFCs take ____ years to reach the stratosphere. a. 1-2 b. 5-10 c. 10-20 d. 20-30 e. 30-50 CFCs are used for all of the following except a. coolants in refrigerators and air conditioners. b. propellants in aerosol spray cans. c. sterilants in hospitals. d. fuels in camp stoves. e. cleaners for electronic parts. CFCs are released into the atmosphere by all of the following except a. spray cans. b. discarded refrigerators. c. burning of artificial logs in fireplaces. d. leaking of air conditioners. e. cleaning computer chips. A single chlorine atom can convert as many as ____ ozone molecules to molecular oxygen molecules. a. 100 b. 1,000 c. 10,000 d. 100,000 e. 1,000,000 The single greatest contributor to CFC emissions in the United States is a. spray cans. b. discarded refrigerators. c. burning of artificial logs in fireplaces. d. leaking air conditioners. e. cleaning computer chips. Chemicals capable of destroying ozone include all of the following except a. chlorofluorocarbons. b. formaldehyde used as a preservative. c. halons in fire extinguishers and crop fumigants. d. carbon tetrachloride used as a solvent. e. methyl bromide used as a fumigant. In the 1980s, researchers discovered a ____ loss of ozone in the upper stratosphere over the Antarctic during the Antarctic springtime. a. 5-10% b. 20-25% c. 40-50% d. 70-80% e. 80-90% Which of the following statements is false? ____ 64. ____ 65. ____ 66. ____ 67. ____ 68. ____ 69. ____ 70. a. The ozone hole is larger in the Northern Hemisphere than in the Southern Hemisphere. b. Up to 50% of the ozone over Antarctica is destroyed each year. c. The large annual decrease in ozone over the South Pole is caused by spinning vortices with clouds of ice crystals with absorbed CFCs on their surfaces. d. 10-38% ozone loss has been reported in the Arctic springtime. e. none of these answers The lack of sodium in the lower stratosphere leads to the conclusion that a. sodium is primarily found in the form of salt in the oceans. b. chlorine from evaporation of sea spray does not play a large role in ozone depletion. c. Earth is moving away from the sun. d. humans will need to find other sources to maintain healthy nervous systems. e. none of these answers Increases in ultraviolet radiation will cause an increase in all but which one of the following? a. skin cancers b. yields of food crops c. eye cataracts d. suppression of the human immune system e. increased breakdown of materials such as paints and plastics Human health problems closely associated with ozone depletion include all of the following except a. skin cancer. b. eye cataracts. c. increased incidence of heart disease. d. suppression of the immune response. e. neurological damage. The fact that increased skin cancer rates may not show up for 15-40 years following ozone depletion illustrates the concept of a. positive feedback. b. negative feedback. c. lag time. d. suppression of the immune system. e. synergistic interaction. Damage to the ecological structure and function of lakes because of deeper penetration of UV light is cause by a. ozone depletion. b. acid deposition. c. global warming. d. a synergistic interaction among ozone depletion, acid deposition, and global warming. e. a and b only If all of the ozone-depleting substances were banned tomorrow, it would take about ____ years for Earth to recover to pre-1975 levels. a. 15-25 b. 50-100 c. 90-150 d. 125-200 e. 220-300 We can slow the rate of ozone hole creation by a. stopping production of ozone-depleting chemicals. b. recovering and reusing ozone-depleting chemicals. c. finding substitutes for CFCs. d. all of these answers e. none of these answers ____ 71. In 1987, 36 nations meeting in Montreal, Canada, developed the Montreal Protocol to reduce production of a. carbon dioxide. b. nitrous oxide. c. CFCs. d. toxic wastes. e. halons. ____ 72. To help protect the ozone layer, individuals should do all of the following except a. avoid purchasing products that contain CFCs. b. buy halon fire extinguishers. c. pressure legislators to ban all uses of CFCs, halons, and methyl bromide by 1995. d. buy new refrigerators that use vacuum insulation and helium as a coolant. e. encourage all countries to ban all ODCs.