Air Review
advertisement

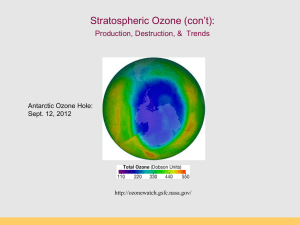
Air Review Weather, climate, and pollution Climate is the general pattern of weather over a period of at least a. 30 years b. 30 days c. 30 minutes d. 30 centuries Climate is the general pattern of weather over a period of at least a. 30 years Environmentalists are likely to a. ventilate their homes periodically b. use houseplants that filter the air c. maintain the vents for stoves, fireplaces, and heaters d. all of these answers Environmentalists are likely to a. ventilate their homes periodically b. use houseplants that filter the air c. maintain the vents for stoves, fireplaces, and heaters d. all of these answers Indoor air pollution could be sharply reduced by a. modifying building codes to prevent radon infiltration b. requiring exhaust hoods or vent pipes for stoves, refrigerators, or other appliances burning natural gas or other fossil fuels c. finding substitutes for potentially harmful chemicals d. all of these answers Indoor air pollution could be sharply reduced by a. modifying building codes to prevent radon infiltration b. requiring exhaust hoods or vent pipes for stoves, refrigerators, or other appliances burning natural gas or other fossil fuels c. finding substitutes for potentially harmful chemicals d. all of these answers Humans are protected from air pollution by a. sneezing and coughing b. mucus capturing small particles c. nasal hairs filtering out large particles d. all of these answers Humans are protected from air pollution by a. sneezing and coughing b. mucus capturing small particles c. nasal hairs filtering out large particles d. all of these answers In 1990, EPA rated indoor air pollution as the ____ out of 18 sources of cancer risk. a. first b. second c. third d. fourth In 1990, EPA rated indoor air pollution as the ____ out of 18 sources of cancer risk. a. first Acid deposition can a. release soluble aluminum ions b. deplete acid-buffering chemicals in the soil c. altering calcium and magnesium uptake from the soil d. all of these answers Acid deposition can a. release soluble aluminum ions b. deplete acid-buffering chemicals in the soil c. altering calcium and magnesium uptake from the soil d. all of these answers Acid deposition can affect living organisms by a. killing fish, aquatic plants, and microorganisms in lakes and streams b. damaging tree roots c. making trees more susceptible to diseases d. all of these answers Acid deposition can affect living organisms by a. killing fish, aquatic plants, and microorganisms in lakes and streams b. damaging tree roots c. making trees more susceptible to diseases d. all of these answers In general, acid deposition can have harmful effects when pH falls below the level of ___. a. 8.1 b. 5.1 c. 6.1 d. 7.1 In general, acid deposition can have harmful effects when pH falls below the level of ___. b. 5.1 Which of the following areas would be least likely to have a thermal inversion? a. an area near the coast b. an area in the central plains c. a valley surrounded by mountains d. the leeward side of a mountain range Which of the following areas would be least likely to have a thermal inversion? b. an area in the central plains Which of the following statements is true? a. thermal inversion occurs when a layer of cold air prevents warm air from rising b. thermal inversions exacerbate pollution problems c. thermal inversions last only a few minutes to a few hours d. normally, cool air near Earth’s surface expands and rises, carrying pollutants higher into the troposphere Which of the following statements is true? b. thermal inversions exacerbate pollution problems The frequency and severity of smog in an area depends least upon the a. local climate and topography b. fuels used in industry, heating, and transportation c. size of the ozone hole over the Arctic d. density of the population The frequency and severity of smog in an area depends least upon the c. size of the ozone hole over the Arctic Scientists classify indoor and outdoor air pollution as a. high-risk human health problems b. moderate-risk human health problems c. low-risk human health problems d. high-risk ecological problems Scientists classify indoor and outdoor air pollution as a. high-risk human health problems . In 1987, 36 nations meeting in Montreal, Canada developed the Montreal Protocol to reduce production of a. carbon dioxide b. nitrous oxide c. CFCs d. toxic wastes . In 1987, 36 nations meeting in Montreal, Canada developed the Montreal Protocol to reduce production of c. CFCs Human health problems closely associated with ozone depletion include all of the following except a. skin cancer b. eye cataracts c. increased incidence of heart disease d. suppression of the immune response Human health problems closely associated with ozone depletion include all of the following except disease c. increased incidence of heart Which of the following charges against the theory of ozone depletion is true? a. CFC molecules cannot reach the stratosphere because they are heavier than air b. The best models of ozone production and destruction estimate that global ozone levels should be 10% less than what we actually observe c. Sodium chloride from the evaporation of sea spray contributes more chlorine to the stratosphere than do CFCs. d. There is no scientific proof that ozone depletion is occurring. Which of the following charges against the theory of ozone depletion is true? b. The best models of ozone production and destruction estimate that global ozone levels should be 10% less than what we actually observe Which if the following is false? a. over 44 years passed from the first production of CFCs until the firs awareness that they could cause environmental damage b. CFCs are stable, odorless, nonflammable, nontoxic, and noncorrosive chemicals c. CFCs are found in bubbles in Styrofoam and insulation d. CFCs are important because they help screen out ultraviolet radiation from reaching Earth’s surface Which if the following is false? d. CFCs are important because they help screen out ultraviolet radiation from reaching Earth’s surface Prevention approaches to global warming include all of the following except a. increase beef production to strengthen public health b. halt deforestation c. switch to sustainable agriculture d. slow population growth Prevention approaches to global warming include all of the following except a. increase beef production to strengthen public health The fossil fuel that released the least carbon dioxide per unit of energy is a. oil b. natural gas c. coal d. petroleum Scientists who claim the global climate system is so complex we will never have the level of certainty wanted by decision makers urge a. take no action now because global warming is all hype b. take action now based on the precautionary principle c. take no action until we get more data d. take action to reverse the climate changes we have caused thus far Scientists who claim the global climate system is so complex we will never have the level of certainty wanted by decision makers urge b. take action now based on the precautionary principle In a warmer world we would expect more a. droughts b. hurricanes c. prolonged heat waves d. all of these answers In a warmer world we would expect more a. droughts b. hurricanes c. prolonged heat waves d. all of these answers We are uncertain about how a. carbon dioxide will affect the rate of photosynthesis b. continued changes in polar ice will occur c. temperature fluctuations over the last 100 years d. all of these answers We are uncertain about how a. carbon dioxide will affect the rate of photosynthesis b. continued changes in polar ice will occur c. temperature fluctuations over the last 100 years d. all of these answers We have the most certainty about a. variations in solar output b. the role the oceans will play in global warming c. temperature fluctuations over the last 100 years d. the role of polar ice in global warming We have the most certainty about c. temperature fluctuations over the last 100 years Current global climate models suggest that climate change a. will never happen b. will be toward the warmer side over the next century c. will be toward the colder side over the next century d. will reach stabilization after two hundred years Current global climate models suggest that climate change b. will be toward the warmer side over the next century Correspondence between climate models and the real world depends upon a. the design and assumptions of the model b. the accuracy of the data c. factors that amplify or dampen changes in average global temperatures d. all of these answers Correspondence between climate models and the real world depends upon a. the design and assumptions of the model b. the accuracy of the data c. factors that amplify or dampen changes in average global temperatures d. all of these answers In 1995, the International Governmental Panel on Climate Change concluded that a. global climate change is a hoax b. the earth is likely to experience an Ice Age in the next century c. the slight rise in temperature observed over the last century was caused by changes in solar cycles d. the slight rise in temperature observed over the last century was probably influenced by human causes In 1995, the International Governmental Panel on Climate Change concluded that d. the slight rise in temperature observed over the last century was probably influenced by human causes Atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide a. was about 100 parts per million prior to the Industrial Revolution, according to ice core analysis b. has declined exponentially since the Industrial Revolution c. has increased exponentially since the Industrial Revolution d. is projected to decrease by half by 2050 Atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide c. has increased exponentially since the Industrial Revolution Increased greenhouse gases originate from a. burning fossil fuels b. deforestation c. use of CFCs d. all of these answers Increased greenhouse gases originate from a. burning fossil fuels b. deforestation c. use of CFCs d. all of these answers The most important greenhouse gas contribution by humans is a. chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) b. water vapor c. nitrous oxide d. carbon dioxide The most important greenhouse gas contribution by humans is d. carbon dioxide The primary greenhouse gas in the atmosphere is a. chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) b. water vapor c. nitrous oxide d. methane The primary greenhouse gas in the atmosphere is b. water vapor All of the following are greenhouse gases except a. carbon dioxide b. water vapor c. methane d. nitrogen All of the following are greenhouse gases except d. nitrogen The term greenhouse effect a. describes occupational diseases of florists b. describes the trapping of heat energy in the troposphere by certain gaseous molecules c. describes the trapping of heat energy in the stratosphere by nitrogen d. describes efforts being made by the White House to support environmental legislation The term greenhouse effect b. describes the trapping of heat energy in the troposphere by certain gaseous molecules Climate is influenced by a. the amount of incoming solar radiation b. Earth’s rotation c. tilt of the Earth’s axis and Earth’s revolutions d. all of these answers Climate is influenced by a. the amount of incoming solar radiation b. Earth’s rotation c. tilt of the Earth’s axis and Earth’s revolutions d. all of these answers The two most important factors in climate are a. temperature and insulation b. precipitation and pressure c. humidity, clouds, and wind d. temperature and precipitation The two most important factors in climate are d. temperature and precipitation Features of weather include all of the following except: a. temperature b. barometric pressure c. wind direction d. ozone concentration Stratospheric ozone helps to prevent a. sunburn b. skin cancer c. eye cancer and cataracts d. all of these answers Stratospheric ozone helps to prevent a. sunburn b. skin cancer c. eye cancer and cataracts d. all of these answers