outline

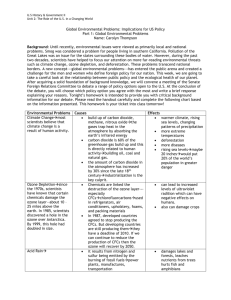
CLIMATE CHANGE
Global Warming” a long-term phenomenon
ATMOSPHERE warms, which in turn affects
OCEAN temps/currents, which in turn affects
WEATHER a short-term phenomenon
El Niño climate patterns (ENSOs) o Dry: desertification o Wet: flooding
Hurricane intensity, frequency
Affects on:
Vegetation (biomes)
Crops
Animal life
Humans (water, disease, habitable area)
Coastlines
“Greenhouse Effect”
Causes:
Water vapor
CO
2
N
2
O
Methane
CFCs
Burning fossil fuels
Deforestation
Fertilizer use
Livestock emissions
Sewage
Landfill decomp
Wetlands (rice paddies, swamps)
2005 Kyoto Protocol
OZONE DESTRUCTION
“holes” over poles, thinning
stratospheric ozone=GOOD
(protects)
tropospheric ozone=BAD (smog, asthma, unhealthy to breathe)
UV protection
Effects:
Skin cancer. Cataracts
Mutation rates
Plant destruction
Plankton decrease
Causes:
Aerosol propellants (prior to
1980’s)
CFCs (Freon) refrigerants
BFCs (Halon) fire extinguishants
1987 Montreal Protocol (43 nations)
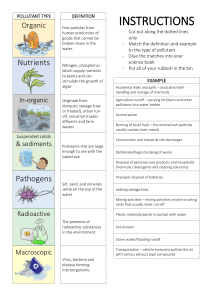
POLLUTION
Eutrophication
NITROGEN, PHOSPHORUS runoff into
Lakes, ponds, etc
Causes: excessive algal growth
When algae dies, it sinks to bottom and is
DECOMPOSED by bacteria, microbes
Lots of dead thing to decompose means the bacteria reproduce and increase greatly in number.
Many of these microbes are AEROBIC, and use up much of the oxygen in the pond, thus depriving the larger organisms, like
FISH. This often results in massive fish dieoff.
Sources:
Nitrogen: fertilizer runoff
Phosphorus: detergents, soaps
Both N and P are often found in sewage, animal waste. When this leaks into nearby bodies of water, problems ensue.
Another pollution problem:
BIOMAGNIFICATION of toxins (mercury,
PCBs, dioxin, lead, etc) in organisms in the food chain.