File
advertisement

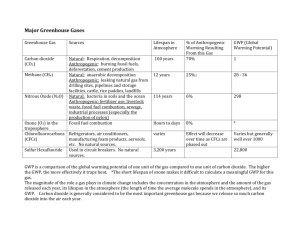
Environmental Science: AIR QUALITY AND CLIMATE UNIT NOTES PART 1 Name______________________Date_________Period______ The Atmosphere is a _____________ _____________ of _______________ that surrounds to earth. • • The reason there is life on Earth – we are protected from most of the _______ ___________________. Allows some light to reach the surface, supplying _______________ and allowing ___________________________________ (O and CO ) 2 • • • 2 78% N _________________, 21% O________________, 1%= water vapor, argon, carbon dioxide, neon, helium, and other gases The early atmosphere contained little _________________________. Bacteria appeared about 4 Billion Years Ago and evolved the ability to perform photosynthesis: _______________________________________________________________________ When organisms break down food molecules during cellular respiration, CO is released into the air. 2 C H O + O → CO + H O + Energy 6 12 6 2 2 The 5 Layers 2 TROPOSPHERE – – 75–80% of the earth’s air mass Closest to the _______________________ ____________________________ 0-11 km above sea level Chemical composition of air • Nitrogen ____% • Oxygen _____% • H 0, CO , trace amounts of others (Ar) – – Weather, climate and all life forms exist here As altitude increases, temperature decreases – – 2 2 STRATOSPHERE • 11-50 km (6-30 miles) above Earth's surface – Similar composition to the troposphere, with 2 exceptions • Much less water (1/1000) • O , ozone layer 3 1 As __________________ increases, _______________ increases Air motion is horizontal _______________________ __________ here • • • THE OZONE LAYER (_____) • Located in the __________________ • Absorbs most of the ______ light from the sun – UV light can cause ______________ damage to living organisms- can cause skin cancer, – faster ________, and cataracts, can kill one-celled organisms (___________________) that live in the surface of the ocean, and interfere with photosynthesis, resulting in lower crop yields • The ozone in the stratosphere acts as a _____________________ for Earth and its inhabitants. MESOPHERE 50-80 km (30-50 miles) ____________________________ atmosphere – Air thin, pressure low, Need _______________________ to live in this region. Air quite cold -90°C (-130°F) near the top of mesosphere THERMOSPHERE 80-500 km (50-310 miles) Very few atoms and molecules in this region. Intense UV – breaks O and N bonds _______________________________ ____________________ 2 2 ____________________ is here GREENHOUSE EFFECT • Greenhouse effect – the trapping of infrared radiation from the sun by gases in earth’s atmosphere which warms the planet • Raises earth’s temp to an average of __________ ⁰F. Without the greenhouse effect, the average temp would be __________⁰F. GLOBAL WARMING • Global warming – increase in Earth’s average surface temp. ______________ by an ________________ in ________________________ ______________. EVIDENCE OF GLOBAL WARMING Earth’s average temperature has risen ___° F in ___________ ______________ years. • Some argue natural fluctuation; however, corresponds w/ rising greenhouse gases According to the EPA, the global surface temperature has increased 0.9°F since 1880. The eight warmest years on record (since 1880) have all occurred since 2001, with the warmest years • • • being ___________ and ___________________. 2 GREENHOUSE GASES Methane (CH ) – ___________ times more ___________________effect than CO and increasing at 8 4 2 times the rate. • Methane production is faster than broken down • Main sources are wetlands, rice fields, ________________ _________________, _______________________, and __________________ • Remains in the air about 12 years • Nitrous oxides – _______________________ to breakdown (120 yrs) – Sources are _____________ _______________, fertilizers, deforestation • CFCs– slow breakdown; ______________ ___________________ X more infrared than CO (100 + years) 2 Sources are foams, ________________, __________________, solvents Water vapor – Warmed by CO ,the atmosphere is – • 2 thus able to absorb more water vapor. And that water vapor, in turn, causes further warming—it amplifies the effects of carbon dioxide. CFC’s • CFCs that are released in the troposphere can take 10-20 years to float into the stratosphere. One single chlorine atom can destroy ___________________molecules and remain in the stratosphere 65-385 years! THE OZONE HOLE • • Depletion of the ozone layer allows _______________ UV light to reach the Earth’s surface STOPPING THE OZONE EATERS 75-85% OF THE OZONE LOSS WAS FROM CFC’S AND OTHER OZONE DEPLETING CHEMICALS • The _______________________________________ – 1987 • The_______________________________________-1992 • Nations agreed to ____________________ their production of CFCs • US pledged to ban all substances that posed a danger to the ozone layer by 2000 • Developed countries agreed to set up a fund to help developing countries switch to CFC substitutes • CFCs remain active for more than 30 years, so it will take decades for the layer to recover. • THE NUMBER 1 SOURCE OF CFCs ARE ____________________________________________________! 3 CFC’s A ___________________________ gas AND an ____________________________________________ chemical. CANCER • Over ____ million new diagnosis each year. • • • About __________% of non-melanoma skin cancer is caused by ultra-violet exposure. Skin cancer accounts for nearly ________% of all cancers. It is the most common type of cancer in men over 50. GREENHOUSE GASES • _________ – most ______________________ greenhouse gas (GHG) Sources: burning _______________________, ______________________________ _________ cores have shown that CO increasing in atmosphere – ________% higher than pre-Industrial Rev. • • 2 Natural cycling of CO levels 2 Seasonal shift in CO production; high fall; low spring 2 SOURCES OF GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS 1. What is the highest source______________________________ LARGEST EMITTERS OF CARBON DIOXIDE List the 4 largest emitters 1.__________________________(______%) 2.__________________________(______%) 3.__________________________(______%) 4.__________________________(______%) MEASURING CARBON DIOXIDE IN THE ATMOSPHERE • There is a carbon dioxide detector in _________________________________ in Hawaii. • • Charles________________ took the first measurement in March of ______________, it was 0.0314%. These levels have rose steadily over the last 50 years. GLOBAL WARMING AND HURRICANES? _______________________ to link climate change and frequency of hurricanes and typhoons. Studies _____________________________ between ocean surface _____________________ and hurricane_____________________ and duration. 4 El Niño/ La Niña WEATHER PATTERNS There have been ______________________________ El Niño years than in prior history. GLOBAL WARMING EFFECTS ON POLES ____% of sheet ice is located in ______________________ and ____________________. Ice is ___________________ worldwide, but especially quickly at the poles. PREDICTED RESULTS OF GLOBAL WARMING • _______________________ patterns will ________________ - • more_____________________, typhoons, flooding and droughts. Agriculture – weather patterns will move farther north, shifting _________________________ _________ __________________ - polar regions ___________, icebergs melt, sea levels • ___________. Warming water also expands. ___________________ areas may _________________ • • Human health will be _______________________ • Heat index, more ground level ozone, more infectious diseases. • _______________________ that normally occur near the _____________________ will move northward. Diseases spread by mosquitoes and other insects due to warmer/wetter climates. • Plant and ________________________ species may ______________________ to maintain their preferred habitats • Not all __________________________ can adapt- some cannot ______________ their _______________ adequately • Certain birds/fishes may migrate • Not all can adapt- ___________________ will dry up, land-locked fish cannot seek colder rivers • Those that cannot adapt/migrate may experience regional _____________________________ GLOBAL COOLING • • • • Global cooling: natural Planetary albedo – low, thick clouds reflect sunlight, prevent warming __________________________ – dust reflect radiation Sulfate aerosols – from _____________________________, create haze, __________________ sunlight KYOTO PROTOCOL • The ___________________ ____________________is the _______________ 5 • international agreement (UN) to fight ____________________ warming. It set _________________________ for nations to __________________ greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. – 5% decrease against 1990 levels over the five-year period 2008-2012. It was signed by __________________ nations, including all European and all other • • developed industrial nations except the _____________ and ________________________. – Went into effect on February 16, 2005, and expires in 2012. Pres. Clinton supported Pres. Bush did not sign • CAP AND TRADE SYSTEM – – A limit on the amount of _____________________________ any specific factory or power plant can produce. Permits (or _________________) are required depending on how much carbon dioxide is emitted. • An organization can purchase additional credits from other organizations that do not need them. CARBON SINK • A carbon sink is anything that ____________________ more carbon that it releases, while a carbon source is anything that releases more carbon than is absorb. • Forests, ________________________, ______________________ and the atmosphere all store carbon and this carbon moves between them in a continuous cycle. OTHER IDEAS? The __________________________________is an idea developed to combat global warming by blocking some of the sunlight entering the Earth’s atmosphere. 6 WE CAN PREPARE FOR THE HARMFUL EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE • _____________________________ greenhouse gas emissions as much as possible • Move people from ______-___________ coastal areas • _____________________ coastal building • ____________________ hazardous material storage tanks away from the coast • Genetically _______________________ ___________________ more tolerant to ___________________ • • Stockpile ___-____ years of key foods • Waste ______________ water • Connect _________________ reserves with corridors The average amount of CO2 per capita produced in America is ____________ tons, which is 39, 600 pounds! THE MOST TERRIFYING VIDEO YOU WILL EVER SEE” Action vs. Inaction 1. Fill out the table below: Significant Action Global Climate Change is a fraud or is naturally occurring Global Climate Change is real and primarily humancaused 7 No Action