ss and overview s3 2015
advertisement

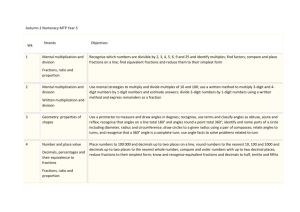
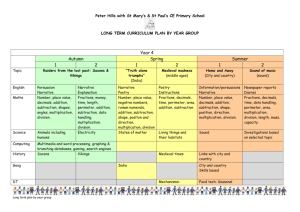
S3 Mathematics Scope & Sequence This scope and sequence is an example only, schools will need to make modifications as necessary dependent on school context and student needs. The same scope and sequence can be used in Year 5 and Year 6. Each term is organised into two parts – Early Term (the first half of term) and Later Term (the second half of term) to provide opportunities to develop deep knowledge and understanding. Number and Algebra Measurement and Geometry Early Term 1 Whole Numbers Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions and Decimals (relate to Length) Later Term 1 Whole Numbers (relate to Multiplication and Division) Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions and Decimals (relate to Addition and Subtraction) Early Term 2 Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions and Decimals (relate to Length) Later Term 2 Whole Numbers Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions and Decimals (relate to Addition and Subtraction) Patterns and Algebra Early Term 3 Whole Numbers (relate to Multiplication and Division) Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions and Decimals (relate to Length) Patterns and Algebra Area (relate to Fractions and Later Term 3 Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions and Decimals (relate to Multiplication and Division) (relate to Whole Numbers) Decimals) Early Term 4 Whole Numbers Multiplication and Division Fractions and Decimals (relate to Addition and Subtraction) Later Term 4 Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions and Decimals Patterns and Algebra 3D Space Angles Data (relate to Whole (relate to Multiplication and Division) 2D Space (relate to Data Time Position Length Volume and Capacity (relate 3D Space 2D Space (relate to to Multiplication and Division) 3D Space) Mass (relate to Fractions and 2D Space Angles Data Chance Length Time (relate to Whole Numbers) 2D Space (relate to Chance (relate to Angles) Fractions and Decimals) Position Data 3D Space Data Chance (relate to (relate to Fractions and Decimals) Area Patterns and Algebra (relate to Multiplication and Division) Decimals) Volume and Capacity (relate Angles Time Patterns and Algebra Mass (relate to Fractions and Decimals) Numbers) Area) to Fractions and Decimals) Note: The concept of percentages first appears in Part 2 of Fractions and Decimals in Stage Three. © Department of Education and Communities Length Statistics and Probability Fractions and Decimals) 2D Space Angles (relate to 2D Space) Stage 3 Mathematics Scope & Sequence of key ideas Number and Algebra Whole Numbers Read, write and order numbers of any size Measurement and Geometry Length Use the kilometre to measure lengths and distances State the place value of digits in numbers of any size Record numbers of any size using expanded notation Early Term 1 Addition and Subtraction Select and apply efficient mental, written and calculator strategies for addition and subtraction of numbers of any size Use estimation to check answers to calculations Select and use appropriate instruments and units to measure lengths Record lengths and distances using the abbreviations km, m, cm and mm 3D Space Name prisms and pyramids according to the shape of their ‘base’ Multiplication and Division Use and record a range of mental and written strategies to multiply by one- Describe and compare properties of prisms and and two-digit operators pyramids in terms of their faces, edges and vertices Solve word problems and record the strategy used Angles (relate to 3D Space) Use estimation to check answers to calculations Recognise the need for formal units to measure angles Fractions and Decimals (relate to Length) Compare and order unit fractions with denominators 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12 Measure, compare and estimate angles in and 100 degrees (up to 360°) Model and represent strategies to add and subtract fractions with the same denominator Express mixed numerals as improper fractions and vice versa Patterns and Algebra (relate to Fractions and Decimals) Identify, continue create and describe increasing and decreasing number patterns with fractions, decimals and whole numbers © Department of Education and Communities Statistics and Probability Data (relate to Whole Numbers) Collect categorical and numerical data by observation and by survey Construct data displays, including tables, column graphs, dot plots and line graphs, appropriate for the data type Stage 3 Mathematics Scope & Sequence of key ideas Number and Algebra Whole Numbers (relate to Multiplication and Division) Determine factors and multiples of whole numbers Measurement and Geometry Area (relate to Multiplication and Division) Recognise the need for square kilometres and hectares to measure area Identify and describe prime and composite numbers Record areas using the abbreviations km2 and ha Later Term 1 Addition and Subtraction Solve word problems and record the strategy used, including problems involving money Develop a strategy to find areas of rectangles (including squares) and record the strategy in words Create a simple budget Multiplication and Division Use and record a range of mental and written strategies to multiply by one- and two-digit operators Interpret remainders in division problems Fractions and Decimals (relate to Addition and Subtraction) Determine, generate and record equivalent fractions Model and represent strategies to add and subtract fractions with the same denominator Add and subtract fractions, included mixed numerals, with the same or related denominators © Department of Education and Communities Time Convert between 12- and 24-hour time Determine and compare the duration of events 2D Space (relate to Area) Compare and describe side properties of the special quadrilaterals and special triangles Classify and draw regular and irregular twodimensional shapes from descriptions of their features Position Use grid-referenced maps to locate and describe positions Statistics and Probability Data Describe and interpret data presented in tables, column graphs, dot plots and line graphs Stage 3 Mathematics Scope & Sequence of key ideas Early Term 2 Number and Algebra Measurement and Geometry Addition and Subtraction Select and apply efficient mental, written and calculator strategies for addition and subtraction of numbers of any size Length Find perimeters of common two-dimensional shapes and record the strategy Use estimation to check answers to calculations Record lengths and distances using decimal notation to three decimal places Multiplication and Division Use and record a range of mental and written strategies to divide Volume and Capacity (relate to Multiplication and Division) numbers with three or more digits by a one-digit operator, Use cubic centimetres and cubic metres to measure including problems that result in a remainder and estimate volumes Use the formal algorithm for multiplication by one- and two-digit Select and use appropriate units to measure volume operators Fractions and Decimals (relate to Length) Apply the place value system to represent thousandths as decimals Compare, order and represent decimals with up to three decimal places Patterns and Algebra (relate to Multiplication and Division) Find missing numbers in number sentences involving multiplication or division on one or both sides of the equals sign Record volumes using the abbreviations cm3 and m3 3D Space Connect three-dimensional objects with their nets 2D Space (relate to 3D Space) Identify, name and draw right-angled, equilateral, isosceles and scalene triangles Explore angle properties of the special quadrilaterals and special triangles © Department of Education and Communities Statistics and Probability Stage 3 Mathematics Scope & Sequence of key ideas Later Term 2 Number and Algebra Measurement and Geometry Whole Numbers Read, write and order numbers of any size Mass (relate to Fractions and Decimals) Recognise the need for tonnes to measure mass State the place value of digits in numbers of any size Record masses using the abbreviations t, kg and g Record numbers of any size using expanded notation Select and use appropriate instruments and units to measure mass Addition and Subtraction Select and apply efficient mental, written and calculator strategies to solve word problems and record the strategy used Multiplication and Division Use and record a range of mental and written strategies to divide numbers with three or more digits by a one-digit operator, including problems that result in a remainder Distinguish between ‘gross mass’ and ‘net mass’ Solve problems involving mass 2D Space Use the terms ‘translate’, ‘reflect’ and ‘rotate’ to describe transformations of shapes Identify line and rotational symmetries Use the formal algorithm for multiplication by one- and twodigit operators Fractions and Decimals (relate to Addition and Subtraction) Model and represent strategies to add and subtract fractions with the same denominator Write fractions in their ‘simplest form’ Add and subtract fractions, included mixed numerals, with the same or related denominators © Department of Education and Communities Angles Record angle measurements using the symbol for degrees (°) Construct angles using a protractor (up to 360°) Describe angle size in degrees for each angle classification Statistics and Probability Data Construct data displays, including tables, column graphs, dot plots and line graphs, appropriate for the data type Describe and interpret data presented in tables, column graphs, dot plots and line graphs Chance List outcomes of chance experiments involving equally likely outcomes Represent probabilities using fractions Recognise that probabilities range from 0 to 1 Stage 3 Mathematics Scope & Sequence of key ideas Number and Algebra Whole Numbers (relate to Multiplication and Division) Determine factors and multiples of whole numbers Measurement and Geometry Length Convert between kilometres, metres, centimetres and millimetres Identify and describe prime and composite numbers Solve problems involving length and perimeter Model and describe square and triangular numbers Early Term 3 Addition and Subtraction Select and apply efficient mental, written and calculator strategies to solve word problems and record the strategy used Use estimation to check answers to calculations Multiplication and Division Solve word problems and record the strategy used Time (relate to Whole Numbers) Interpret and use timetables Draw and interpret timelines using a given scale 2D Space (relate to Angles) Make and compare enlargements of shapes/pictures Identify, use and describe combinations of translations, reflections and rotations Interpret remainders in division problems Fractions and Decimals (related to Length) Represent, compare and order fractions with denominators 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12 and 100 Multiply fractions by whole numbers Find a simple fraction of a quantity Use mental, written and calculator strategies to add and subtract decimals with up to three decimal places Patterns and Algebra Continue, create, record and describe geometric and number patterns in words © Department of Education and Communities Angles Identify and name angle types formed by the intersection of straight lines, including ‘angles on a straight line’, ‘angles at a point’ and ‘vertically opposite angles’ Statistics and Probability Chance (relate to Fractions and Decimals) Compare observed frequencies in chance experiments with expected frequencies Represent probabilities using fractions, decimals and percentages Stage 3 Mathematics Scope & Sequence of key ideas Number and Algebra Statistics and Probability Addition and Subtraction Select and apply efficient mental, written and calculator strategies to solve word problems and record the strategy used Area (relate to Fractions and Decimals) Develop a strategy to find areas of triangles and record the strategy in words Data Interpret and create twoway tables Multiplication and Division Select and apply efficient mental, written and calculator strategies to solve word problems and record the strategy used Solve problems involving areas of rectangles (including squares) and triangles Interpret side-by-side column graphs Use estimation to check answers to calculations Later Term 3 Measurement and Geometry Fractions and Decimals (relate to Multiplication and Division) Use mental, written and calculator strategies to multiply decimals by one- and two-digit whole numbers Use mental, written and calculator strategies to divide decimals by one-digit whole numbers Multiply and divide decimals by 10, 100 and 1000 Patterns and Algebra (relate to Whole Numbers) Determine the rule for geometric and number patterns in words and use the rule to calculate values © Department of Education and Communities Position Follow a sequence of directions, including compass directions, to find a particular location on a map Describe routes using landmarks and directional language Stage 3 Mathematics Scope & Sequence of key ideas Number and Algebra Whole Numbers Recognise the location of negative numbers in relation to zero on a number line Multiplication and Division Recognise and use grouping symbols Measurement and Geometry Volume and Capacity (related to Fractions and Decimals) Connect volume and capacity and their units of measurement Record volumes and capacities using decimal notation to three decimal places Apply the order of operations in calculations Early Term 4 Convert between millilitres and litres Statistics and Probability Data Compare a range of data displays to determine the most appropriate display for particular sets of data Interpret and critically evaluate data presented in digital media and elsewhere Solve word problems and record the strategy used Fractions and Decimals (related to Addition and Subtraction) Solve word problems involving fractions and decimals, including money problems Make connections between equivalent percentages, fractions and decimals Develop a strategy to find volumes of rectangular prisms and record the strategy in words Time Convert between 12- and 24-hour time Determine and compare the duration of events Use mental, written and calculator strategies to calculate 10%, 25% and 50% of quantities, including as discounts © Department of Education and Communities 3D Space Construct prisms and pyramids using a variety of materials, and given drawings from different views Chance (related to Fractions and Decimals) Conduct chance experiments with both small and large numbers of trials Represent probabilities using fractions Recognise that probabilities range from 0 to 1 Stage 3 Mathematics Scope & Sequence of key ideas Later Term 4 Number and Algebra Measurement and Geometry Addition and Subtraction Select and apply efficient mental, written and calculator strategies to solve word problems and record the strategy used Mass (related to Fractions and Decimals) Record mass using decimal notation to three decimal places Multiplication and Division Select and apply efficient mental, written and calculator strategies to solve word problems and record the strategy used Convert between tonnes, kilograms and grams Recognise and use grouping symbols 2D Space Identify, describe, compare and draw diagonals of two-dimensional shapes Apply the order of operations in calculations Identify and name parts of circles Fractions and Decimals Compare, order and represent decimals with up to three decimal places Angles (related to 2D Space) Identify and name angle types formed by the intersection of straight lines, including ‘angles on a straight line’, ‘angles at a point’ and ‘vertically opposite angles’ Multiply fractions by whole numbers Find a simple fraction of a quantity Use mental, written and calculator strategies to add and subtract decimals with up to three decimal places Patterns and Algebra Locate and record the coordinates of points in all four quadrants of the Cartesian plane © Department of Education and Communities Use known angle results to find unknown angles in diagrams Statistics and Probability