ANSWERS to C3 Vocab packet
advertisement

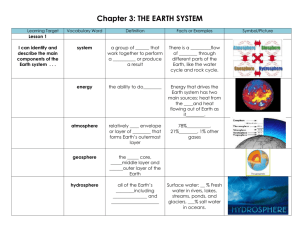
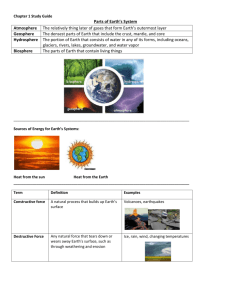
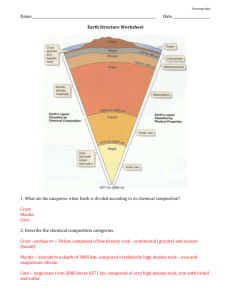
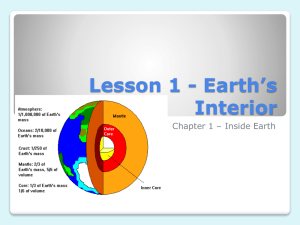
Chapter 3: THE EARTH SYSTEM Learning Target Vocabulary Word Definition Facts or Examples System A group of parts that work together to perform a function or produce a result There is a constant flow of matter through different parts of the Earth, like the water cycle and rock cycle. Energy The ability to do work. Energy that drives the Earth system has two main sources: heat from the sun and heat flowing out of Earth as it cools. Atmosphere Relatively thin envelope or layer of gases that forms Earth’s outermost layer. 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% other gases Geosphere The metal core, solid middle layer and rocky outer layer of the Earth. Hydrosphere All of the Earth’s water including ground water and surface water Lesson 1 I can identify and describe the main components of the Earth system . . . Surface water: 3% Fresh water in rivers, lakes, streams, ponds, and glaciers, 97% salt water in oceans. Symbol/Picture I can summarize the effects of constructive and destructive forces . . . Biosphere The parts of Earth that contain living organisms. Constructive forces Forces that shape the land’s surface by building up mountains and other land masses. Ex. Volcanoes spew lava that hardens into rock; Earthquakes can lift up mountains and rocks. Destructive forces Forces that destroy and wear away landmasses by weathering or erosion. Ex. Erosion – wearing down and carrying away of land by water, ice or wind. Lesson 2 I can explain how geologists learn about Earth’s inner structures . . . Rock samples Seismic waves Samples of rock brought up from drilled holes 12.3 km deep or from volcanoes blasting rock from 100 km deep. Waves produced by earthquakes, the speed & paths they take give clues about Earth’s interior This is direct evidence. This is indirect evidence. I can identify the characteristics of Earth’s crust, mantle, and core, & describe how temperature and pressure change inside Earth. . . Pressure A force pressing down on an area The deeper down inside Earth, the greater the pressure. (Temperature also increases) Crust Layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin Basalt Dark, fine-grained rock Oceanic crust is much like basalt Granite Light, coarse-grained rock Continental crust is much like granite Mantle A layer of hot, solid rock found under the crust. About 3,000 km thick, made up of layers. Lithosphere Crust and uppermost part of the mantle Strong, hard, rigid rock. Main elements are Oxygen & Silicon, varies from 5-40 km for most areas, up to 80 km for mountains, thinnest on ocean floor. Asthenosphere Below the lithosphere, hotter and more pressure Less rigid area of rock, can bend Mesosphere Below the asthenosphere, includes the lower mantle Hot and more rigid Outer Core Layer of molten (melted) metal surrounding the inner core, below the mantle. Liquid - 2,558 km thick Inner Core Dense ball of solid metal (iron & nickel) Radius of ball is 1,222 km thick. Radiation Transfer of energy that is carried in electromagnetic rays like light Ex. Outside of car gets hot from sun’s rays Lesson 3 I can explain how heat is transferred . . . Conduction Convection Heat transfer between materials that are touching each other Ex. When you touch the door handle of the car, the heat is felt by your hand. Heat transfer by the movement of a fluid (liquid or gas) Ex. When you open the car door, hot air rushes out to warm you. I can describe convection currents in Earth’s mantle . . . Convection currents The flow that transfers heat within a fluid. Heating and cooling a fluid changed the density and the force of gravity to cause a convection current to have motion. Heat from the core and mantle cause convection currents in the mantle. Warm rock rises (less density) & cool rock sinks (greater density) Learning Targets Chapter 3 Lesson 1 I can identify and describe the main components of the Earth system. . . The Earth system has four main spheres: the _________________________, the _________________, the ______________________m and the _____________________________. As a major source of energy for Earth processes, the _______ can be considered part of the Earth system as well. I can summarize the effects of constructive and destructive forces . . . Lands are constantly being created and ______________ by competing forces. _________________________ forces shape the land’s surface by building up ________________________ and other landmasses. _________________________ forces destroy and wear away landmasses through processes like ___________________ and ________________________. Lesson 2 I can explain how geologists learn about Earth’s inner structures . . . Geologists have used two main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior: direct evidence from _________________________________ and indirect evidence from _______________________________. I can identify the characteristics of Earth’s crust, mantle, and core, and describe how temperature and pressure change inside Earth . . . The deeper down inside Earth, the ________________ the pressure. The ______________________ inside Earth _______________ as depth increases. The three main layers of the Earth are the ______________________, _____________________ and ____________________. The ________________ is a layer of solid rock that includes dry ______________ and ocean ________________. The ________________ is about 3,000 km thick and is made of very _________, _____________ rock. The ________________ is mostly _______________ and nickel. It consists of a _________________ outer core and a _________________ inner core. Lesson 3 I can explain how heat is transferred . . . There are three types of heat transfer, _________________________, ___________________________ and __________________________. I can describe convection currents in Earth’s mantle . . . Heating and cooling of a fluid, changes the fluid’s _________________________ and the force of _________________ combine to set ______________________ ____________________ in motion Heat from the _____________ and the ________________ itself causes convection currents in the mantle.