3B Cell Membrane NOTE PACKET
advertisement

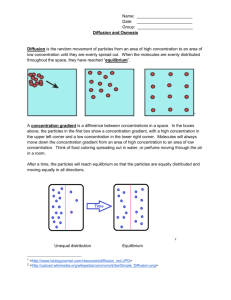
1 Name: ______________________ Date: _______________ Unit 3B Cell Membrane and Transport NOTES What is Cell Transport? • Transport- the movement of materials between an organism and its _______________ • Cellular Transport- movement of materials into and out of a cell • Materials move from the water based solution outside the cell (its environment) to the water based solution inside the cell (the cytoplasm/cytosol), or vice versa • Movement occurs across the __________ ______________________. Solutions • Solution- a type of mixture in which all components are evenly distributed • Made of a – Solvent- the substance that _________________________________________ (ex: water is an excellent solvent) – Solute- the substance that is ___________________ • Cells are surrounded by aqueous (_________________________) solutions and contain an aqueous solution called cytoplasm Cell Membranes • Found surrounding all cells • Made of a lipid bilayer • Protects and supports the cell • Regulates what comes in and out of the cell Additional Notes/Summary: 2 The Lipid Bilayer • Has 2 layers of ___________________ (“Bi” means two) • The layers are made up of molecules called __________________________ • Each phospholipid has a HYDROPHOBIC fatty acid tail region • and a HYDROPHILIC head region • HYDRO = means water Hydrophilic head region • PHOBIC = means afraid • PHILIC = means loving Hydrophobic tail region • Because the fatty acid tails are “afraid” of water (________________________), they turn towards each other so they won’t be exposed to the cytoplasm, or the outside of the cell (both of which contain water) The Fluid Mosaic Model • “Fluid” means moving • “Mosaic” means many different things put together – The Cell membrane contains different types of molecules that can move around through the phospholipids – Proteins in Membrane- allow for _________________ of molecules across the membrane (ABUNDANT) – Carbohydrates attached to proteins and act as ___________ for molecules to attach (NOT AS MANY) Additional Notes/Summary: 3 The Cell Membrane is Selectively Permeable (__________________________) • Some substances can pass through the membrane and some cannot. • The structure of the membrane and the proteins in it decide which molecules can enter and which can leave. How does a cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? – __________________________________________________________________ ______________(the correct amount of each material inside and outside each cell) 2 Main Types of Transport – passive -no energy needed from the cell – active -energy from cell needed 1. Passive Transport Diffusion- ___________________ move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration to maintain equilibrium – This is called movement “_____________ the concentration gradient” – A concentration gradient occurs where there are two _________________ concentrations of a particle on either side of the membrane – Particles move straight through the lipid bilayer and no energy is required. Ex: O2 and CO2 Additional Notes/Summary: 4 Dynamic Equilibrium Once diffusion has occurred and the cell has reached equilibrium, will the solutes stop moving entirely? • ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ • This is called dynamic equilibrium (dynamic means movement) What happens if a molecule/solute is too large and/or not dissolvable in lipids? Facilitated Diffusion -the molecule/solute will go through a __________________ specific for that molecule. -still goes from high to low concentration; so no energy needed. Additional Notes/Summary: 5 Water Can Use a Channel to get through the Cell Membrane • Why does water have difficulty dissolving through the cell membrane by regular diffusion? • __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ • Water needs the aquaporin protein channel to get through quickly! • This is an example of facilitated diffusion Osmosis • The simple or facilitated diffusion of __________________ molecules across a cell membrane. • From where there is more water (less solute) to where there is less water (more solute) • Depends upon the solvent/solute ratio Solutions can be classified by the amount of solutes they contain compared to other solutions: • HYPERTONIC: A solution with a _____________________ solute [concentration] – (Ex: a solution with 20% sugar and 80% water is hypertonic to a solution of 10% sugar and 90% water) • HYPOTONIC: a solution with a _________________ solute concentration – (Ex: a solution of 5% NaCl and 95% water is hypotonic to a solution of 20% NaCl and 80% water) • ISOTONIC: a solution with _______________ solute concentration with another solution – (Ex: outside of a cell has 10% NaCl and the cytoplasm inside the cell also has 10% NaCl) Additional Notes/Summary: 6 What happens to our cells if they are placed into a/an… HypErtonic Solution• Since the [solute] is higher and the [water] is lower outside the cell, the cell attempts to correct this by rushing water out (________________________________) • Result= cell ___________________________ • E for water exiting the cell HypOtonic Solution• Since the [solute] is lower and [water] is higher outside the cell, water rushes into the cell (osmotic pressure) • Result= _______________________________________________________ • O for the cell “opens the door” to let water in Isotonic Solution• Since the solution has a similar [solute] and [water] as the cytoplasm, water moves in/out at ____________________________ • Dynamic equilibrium • In addition to osmosis, solutes can also be moving at the same time by diffusion or facilitated diffusion Osmosis in Plant and Animal Cells What is different about the plant and animal cells during the process of osmosis? ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ Additional Notes/Summary: 7 Practice • • • • What is the solvent concentration of a solution with a 3% concentration of solute? ____ What is the solvent concentration of a solution with a 15% concentration of glucose? __ What is the solute concentration of a solution with 98% solvent? ________________ What is the solute concentration of a solution with 75% water? _________________ Fill in… Conditions Solute concentration in the environment is equal to that in the cell Solute concentration in the environment is greater than the cell Solute concentration in the environment is less than the cell Additional Notes/Summary: Water will… Environment is… (move in, out, or both?) (Hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic?) 8 Draw the following cells if placed in each type of environment: (draw a shrunken cell, a swelled cell, or a cell of the same size) 2. Active Transport • Cells move substances from ____________ concentrations to _________ concentrations • This is also called moving substances “______ their concentration gradient” • Energy is needed in the form of __________ Additional Notes/Summary: 9 A. Molecular Active Transport • Uses a _____________ in the cell membrane to carry the substance across • Allows for a cell to purposely ________________ a molecule in a particular location even when the forces of diffusion will want the molecule to move in the other direction Example: Sodium-Potassium Pump B. Bulk Transport (for large Molecules) 1. Some substances are too _______________ to pass through any of the pores, channels, and pumps in the cell membrane 2. Or _____________________________ need to be transported into/out of the cell 3. Vesicles are produced by the membrane: pouches that are extensions of the cell membrane that pinch off and surround the substance a. Endocytosis • _________________________ large particles (ingestion) • 2 Types: Pinocytosis- transports large amounts of ________________ solutes or liquids Phagocytosis- transport of _________________ molecules or whole cells (ex. white blood cells “eat” damaged cells) Cell membrane surrounds the particles and _________________________ to bring the materials into the cell using a ___________________. Additional Notes/Summary: 10 b. Exocytosis • Reverse of endocytosis • Materials to be ___________________ from the cell are taken into a vesicle • The vesicle _________________ with the cell membrane and ___________________ the materials from the cell (ex: releasing proteins) • This is how wastes are removed from many cells Additional Notes/Summary: