Learning Intentions for Unit 2: Multicellular Systems

Learning Intentions for Unit 2:
Multicellular Systems
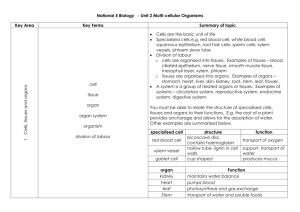
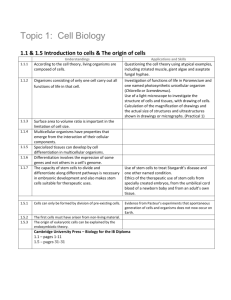
1.1 Cells, Tissues and Organs
1.
Explain how cells become specialised.
2.
Understand how the specialisation of cells contributes to the variety of tissue types in a multicellular organism.
3.
State how the possible variety of tissue types contributes to the formation of different organs & organ systems.
1.2
Stem Cells and Meristems
1.
State that stem cells are non-specialised animal cells that can develop into any of the specialised body cells of that animal.
2.
Understand that Stem cells have the capacity to divide to produce any type of plant cell and they contribute to growth.
3.
State that Stem Cells are involved in growth and repair.
4.
Demonstrate my understanding of the involvement of stem cells in growth and repair of tissues.
5.
Use of a variety of sources to investigate and discuss the ethical issues that arise from the scientific use of stem cells.
6.
Describe the role of meristems in plants.
2.3 Control and Communication
1.
List the main structures that make up the central nervous system (CNS)
2.
Identify structures of the brain and describe their function.
3.
Sate that the CNS is a communication system.
4.
Describe the role of the sensory neurone.
5.
Explain what a reflex action is and provide some examples
6.
Explain the importance of a reflex action
7.
Describe the role of the different neurones in a reflex arc
8.
Be able to describe what a hormone is and how it functions.
9.
To provide examples of different hormones, their function and where they are produced
10.
Explain what is meant by homeostasis and why it is important
11.
Describe how blood sugar levels are controlled in the body, by naming the hormones involved and explaining their functions.
12.
Understand the differences between Glucose, Glycogen and Glucagon
13.
Explain the causes and treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes
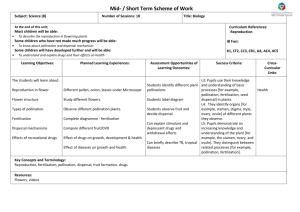
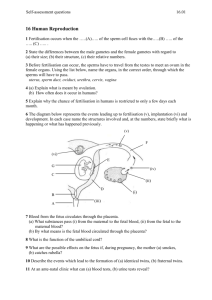
2.4 Reproduction
1. To be able to compare and contrast male and female sex cells.
2. To describe and apply the chromosome complement of human gametes
3. Label and state the functions of the different parts of both the male and female reproductive systems.
4. To be able to describe the process of fertilisation in animals
5. To be able to state what is meant by fertilisation.
6. To have an awareness of the different stages of the development of a human embryo -> a foetus.
7. To be able to state what the male and female gametes are and where they are produced in a plant.
8. To be able to describe the role of the different parts of the plant in fertilisation
9. To describe the processes of pollination (wind and insect pollination)
10. Describe fertilisation & fruit formation.
11.
Describe growth of pollen tube and gamete formation.
12.
Describe stages of fertilisation, seed and fruit formation.
2.5
Variation and Inheritance
1. To explain how sexual reproduction maintains variation within organisms.
2.
To be able to describe discrete and continuous variation using examples.
3.
To be able to explain what is meant by the term phenotype.
4.
Understand the term true-breeding and be able to apply this to solve problems.
5.
Be able to identify Dominant and Recessive phenotypes and apply these to solve problems.
6.
Explain what is meant by the terms ‘homozygous’ and ‘heterozygous’.
7.
Apply Punnett squares to predict patterns of inheritance.
8.
Understand the use of pedigree charts to investigate the inheritance of a characteristic
2.6
The Need for Transport
In Plants
7.
To be able to understand the need for transport systems in plants.
8.
To be able to describe the functions of the xylem and phloem in plant transport systems.
9.
To be able to describe the role and function of the stomata.
In Animals: Circulation
10.
To describe the structure and function of the arteries, capillaries and veins.
11.
To identify the different chambers of the heart and which vessels are attached to the different chambers.
12.
State the role of the coronary arteries
13.
Describe the structure and function of the arteries, veins and capillaries
14.
State the function of the red blood cells (RBCs) and explain how their structure complements their function, including the role of haemoglobin
In Animals: Gas exchange and nutrient absorption
1.
To be able to explain the process of the breathing system.
2.
Describe the process of gas exchange and where it takes place
3.
To describe how alveoli facilitate efficient gas exchange.
4.
Explain the role of cilia and mucus in protecting the lungs from infection
5.
To label different structures in the digestive system.
6.
To describe the process of peristalsis.
7.
To describe the structure of the villi and explain how their structure relates to their function.
2.7
Effects of human Lifestyle choices on human transport and exchange systems
1.
Explain how poor diet and a lack of exercise can affect transport and exchange systems causing diseases
2.
Explain how smoking tobacco and drinking alcohol can affect transport and exchange systems and how this can cause diseases