(F) vocabulary term (B) (F) definition (part 1) State of water (B
advertisement

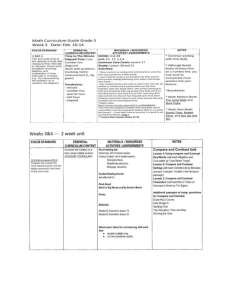
10 VOCABULARY TERM (B) evaporation condensation precipitation surface runoff erosion seepage infiltration percolation root-uptake transpiration surface storage standing-water ecosystems channel runoff flowing-water ecosystems subsurface flow 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 estuaries 19 (F) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 exhalation consumption excretion perspiration osmosis cellular respiration photosynthesis 22 23 subduction plate-tectonics eruption calcium carbonate and hydrate formation biomass storage ocean currents 24 open ocean 25 26 wave formation intertidal zone 27 3 cell model 28 29 wetlands coastal ocean 30 coral reefs 20 21 (F) DEFINITION (part 1) STATE of water (B) RESERVOIR/location (B) FORM of water (B) water vapor freshwater freshwater freshwater liquid water vaporizes to form atmospheric water atmospheric water binds together to form water droplets/clouds/fogs/mists atmospheric water binds together to form rain/snow/sleet/hail and falls due to gravity excess water from rain and melting snow flows over the land liquid gas gas liquid gas liquid or solid liquid land or ocean atmosphere atmosphere atmosphere land or ocean land water from rain and melting snow enters the soil liquid land under the earth's surface freshwater (ground water) water in the soil is absorbed by plants water flows through plants and evaporates from leaves water from rivers and streams forms ponds and lakes; a type of freshwater ecosystems liquid liquid gas liquid land biomass biomass atmosphere land freshwater water vapor freshwater water from rain and melting snow flows in rivers and streams; a type of freshwater ecosystems liquid land freshwater water flows under the earth's surface and forms aquifers liquid under the earth's surface land or ocean water is lost from the body as organisms breathe out water is gained by the body as organisms drink or eat foods with high water content water is lost from the body as organisms remove nitrogen wastes and feces water is lost from the body as organisms produce sweat to lower their body temperatures water enters and leaves the cell through the cell membrane due to diffusion water is produced by the mitochondria as carbohydrates are "burned" to produce ATP water is incorporated into carbohydrates by chloroplasts as light energy is used to form organic molecules type of wetlands formed when rivers meet the sea; contain constant mixture of fresh and salt water affected by tides water flows under the earth's crust as the oceanic plate is pulled under the continental plate water from under the earth's crust is released as steam through volcanoes water is incorporated into substances such as shells, minerals, and crystals liquid gas liquid liquid liquid gas liquid organic compounds liquid liquid organic compounds biomass atmosphere land biomass biomass land or ocean biomass atmosphere biomass biomass biomass liquid ocean freshwater (ground water) water vapor freshwater waste water water vapor freshwater freshwater organic compounds brackish water liquid ocean under the earth's crust saltwater gas liquid inorganic compounds under the earth's crust atmosphere ocean ocean floor freshwater inorganic compounds water is stored in the bodies of organisms that live in arid ecosystems flow of water caused by winds, unequal heating of earth’s surface and rotation of the earth; ocean flows in clockwise direction north of the equator and in counter-clockwise direction south of the equator, thus affecting weather and climate (affected by geographic features of the ocean floor) marine ecosystem that begins at the edge of the continental shelf; has low nutrient levels and low productivity water is moved by winds blowing over a vast stretch of ocean surface (not local winds) marine ecosystem that is between the high tide and low tide marks (at the shore); has zonation due to dominance of particular organisms in particular areas flow of air (winds) which is caused by unequal heating of earth’s surface and rotation of the earth; cold air near the poles and 30 sinks, then flows along the land, then rises at the equator and 60, thus affecting weather and climate by forming wet zones and dry zones (affected by geographic features such as mountains) fresh water ecosystem in which water covers the soil: bogs, marshes, and swamps marine ecosystem that is between the low tide mark and the edge of the continental shelf; has high nutrient levels and high productivity type of coastal ocean ecosystems found in warm tropical oceans; has low nutrient levels but high productivity due to symbiosis between corals and algae liquid liquid biomass ocean freshwater saltwater liquid ocean saltwater liquid liquid ocean ocean saltwater saltwater gas liquid or solid atmosphere land or ocean water vapor freshwater liquid liquid land ocean freshwater saltwater liquid ocean saltwater 31 benthic zone 32 33 glacier formation and ice calving upwelling 34 rain shadow 35 air currents 36 thermohaline circulation 37 microclimate 38 average residence time AGOGRSA 39 useable water SIFAB 40 high heat capacity of water marine ecosystem that covers the ocean floor, may be photic or aphotic depending on depth permanent snow accumulates and forms dense ice that moves and then breaks into chunks liquid ocean saltwater solid land ocean freshwater wind or geographic feature caused changes in ocean flow where cold nutrient rich water rises to the surface replacing warm nutrient depleted surface water geographic feature caused differences in rain pattern where mountains block the passage of rain producing weather systems causing dry areas on the “away from the wind” side flow of air (winds) which is caused by unequal heating of earth’s surface and rotation of the earth; cold air near the poles and 30 sinks, then flows along the land, then rises at the equator and 60, thus affecting weather and climate by forming east-prevailing winds and west-prevailing winds (affected by geographic features such as mountains) flow of water caused by winds, unequal heating of earth’s surface and rotation of the earth; cold water near the poles sinks, then flows along the ocean bottom, then rises at warmer regions, thus affecting weather and climate (affected by geographic features of the ocean floor) climate in an area that is different from the surrounding climate due to presence of ponds/lakes/rivers (example: oasis) average time a water molecule will spend in a specific reservoir Antarctica = 20,000 years Groundwater = 100 to 10,000 years Oceans = 3,200 years Glaciers = 20 to 100 years Rivers = 2 to 6 months Soil = 1 to 2 months Atmosphere = 9 days very little water on earth is freshwater and useable by people saltwater = 96.5 % ice (fresh water) = 1.8% freshwater = 1.7 % water in atmosphere = 0.001% water in biomass = 0.0001% water can absorb a large amount of heat without changing temperature; as a result, the oceans are warmer in winter and cooler in summer; thus moderating the weather and climate of nearby land liquid ocean saltwater gas liquid atmosphere land freshwater gas liquid or solid atmosphere land or ocean water vapor freshwater liquid ocean saltwater gas liquid atmosphere land gas liquid solid gas solid land under the earth's surface ocean atmosphere water vapor freshwater freshwater saltwater water vapor gas liquid solid ocean land atmosphere biomass freshwater saltwater water vapor liquid ocean saltwater